Seasonal unemployment occurs when workers lose jobs during off-peak seasons due to fluctuations in industry demand such as agriculture, tourism, or retail. This type of unemployment is predictable and temporary, often influenced by weather conditions or holiday schedules. Discover how seasonal unemployment impacts your job prospects and methods to navigate its challenges in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
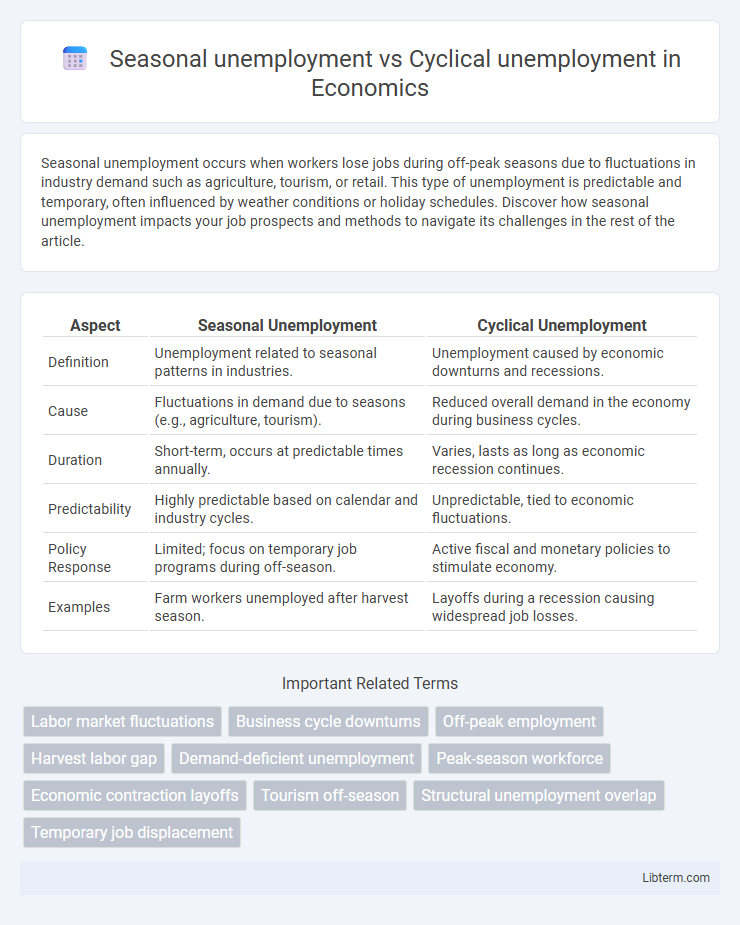
| Aspect | Seasonal Unemployment | Cyclical Unemployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unemployment related to seasonal patterns in industries. | Unemployment caused by economic downturns and recessions. |
| Cause | Fluctuations in demand due to seasons (e.g., agriculture, tourism). | Reduced overall demand in the economy during business cycles. |
| Duration | Short-term, occurs at predictable times annually. | Varies, lasts as long as economic recession continues. |
| Predictability | Highly predictable based on calendar and industry cycles. | Unpredictable, tied to economic fluctuations. |
| Policy Response | Limited; focus on temporary job programs during off-season. | Active fiscal and monetary policies to stimulate economy. |
| Examples | Farm workers unemployed after harvest season. | Layoffs during a recession causing widespread job losses. |
Understanding Seasonal Unemployment
Seasonal unemployment occurs when workers lose jobs due to predictable changes in demand tied to specific seasons, such as agriculture, tourism, or holiday retail. This type of unemployment typically repeats annually and is linked to industries whose operations depend on factors like weather or festive periods. Understanding seasonal unemployment helps policymakers design targeted support measures during off-peak seasons to stabilize the labor market.
Defining Cyclical Unemployment
Cyclical unemployment occurs due to fluctuations in the business cycle, typically rising during economic recessions and falling during periods of expansion. It reflects a lack of demand for goods and services, causing firms to reduce their workforce temporarily. Seasonal unemployment, in contrast, results from regular, predictable changes in labor demand related to seasons or specific calendar periods.
Key Differences Between Seasonal and Cyclical Unemployment
Seasonal unemployment occurs due to regular fluctuations in demand and labor needs during specific times of the year, commonly affecting industries like agriculture, retail, and tourism. Cyclical unemployment arises from economic downturns and recessions when overall demand for goods and services declines, leading to widespread job losses across various sectors. The key difference lies in seasonality being predictable and temporary, while cyclical unemployment depends on the broader economic cycle and can persist until economic recovery.
Causes of Seasonal Unemployment
Seasonal unemployment occurs due to fluctuations in labor demand linked to specific times of the year, such as agriculture, tourism, and holiday-related retail jobs. This type of unemployment is caused by variations in weather, agricultural cycles, and predictable consumer demand surges during particular seasons. Unlike cyclical unemployment, which results from economic recessions and downturns, seasonal unemployment is a recurring and predictable pattern tied directly to calendar-driven industries.
Causes of Cyclical Unemployment
Cyclical unemployment arises primarily due to fluctuations in the business cycle, where economic downturns reduce aggregate demand, leading to job losses across various industries. This type of unemployment intensifies during recessions when consumer spending, investment, and production decline sharply. In contrast, seasonal unemployment results from predictable, recurring patterns in labor demand related to specific times of the year or seasonal industries.
Industries Most Affected by Seasonal Unemployment
Industries most affected by seasonal unemployment include agriculture, tourism, and retail, where demand fluctuates significantly with seasons and holidays. Agricultural workers face job losses during off-harvest periods, while tourism jobs decline in the low travel seasons, and retail experiences peaks mainly during holiday shopping times. These seasonal patterns contrast with cyclical unemployment, which results from broader economic downturns affecting various sectors year-round.
Economic Impacts of Cyclical Unemployment
Cyclical unemployment rises during economic downturns when demand for goods and services decreases, leading to business layoffs and reduced income levels. This form of unemployment exacerbates economic recessions by lowering consumer spending and increasing government welfare expenses, thereby slowing overall economic growth. In contrast, seasonal unemployment occurs predictably based on industry cycles, such as agriculture or tourism, and does not typically have the same broad negative impact on economic stability.
Strategies to Reduce Seasonal Unemployment
Seasonal unemployment occurs due to predictable fluctuations in demand linked to specific times of the year, such as agriculture or tourism seasons, while cyclical unemployment results from overall economic downturns affecting labor demand across industries. Strategies to reduce seasonal unemployment include diversifying local economies to create year-round job opportunities, implementing workforce training programs to equip workers with skills for off-season employment, and promoting development of industries less sensitive to seasonal changes. Additionally, governments can support temporary public works projects during low seasons and encourage businesses to adopt flexible staffing models to maintain employment continuity.
Policy Responses to Cyclical Unemployment
Policy responses to cyclical unemployment prioritize stimulating aggregate demand through monetary and fiscal measures such as interest rate cuts, increased government spending, and tax reductions to boost consumption and investment. Unemployment benefits and job training programs are also enhanced during economic downturns to support affected workers and facilitate workforce re-entry. These interventions differ from seasonal unemployment strategies, which typically involve temporary, occupation-specific adjustments rather than broad economic stimuli.
Comparing Solutions for Seasonal vs Cyclical Unemployment
Seasonal unemployment solutions focus on enhancing workforce flexibility through temporary job placements, job retraining programs tailored to off-season skills, and promoting diversification of local economies to reduce dependence on seasonal industries. Cyclical unemployment requires macroeconomic policies such as fiscal stimulus measures, monetary easing, and public sector job creation to counter downturn-driven job losses. Targeted interventions like unemployment benefits extensions address cyclical unemployment, whereas seasonal unemployment benefits correlate with predictable industry cycles and regional labor demands.
Seasonal unemployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com