Net profit represents the actual earnings remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs have been deducted from total revenue, reflecting a company's financial health and profitability. Understanding net profit helps you assess the efficiency of business operations and make informed decisions for growth. Discover more insights into maximizing your net profit in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
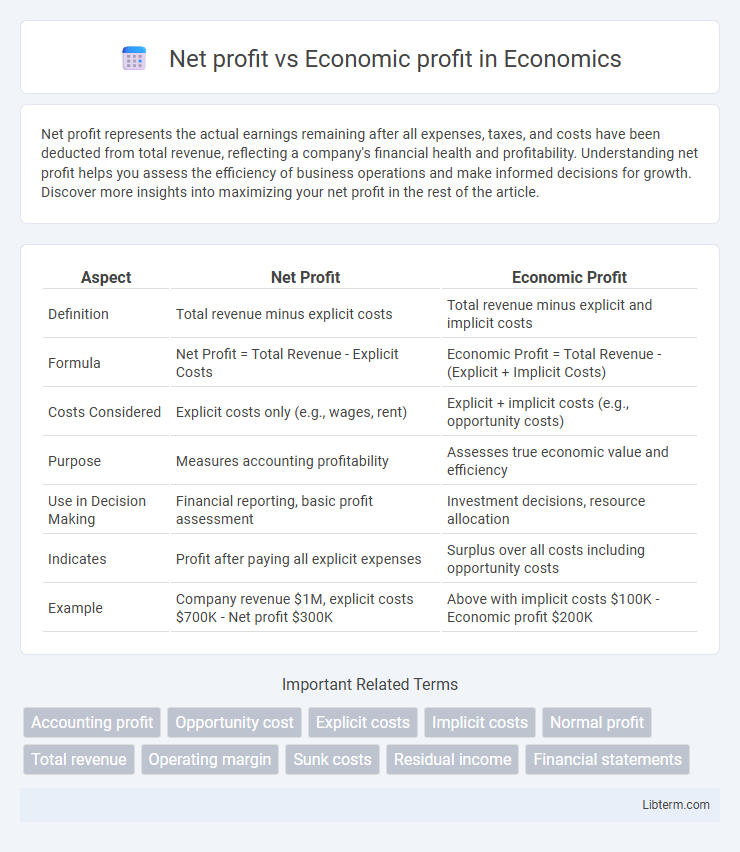
| Aspect | Net Profit | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total revenue minus explicit costs | Total revenue minus explicit and implicit costs |
| Formula | Net Profit = Total Revenue - Explicit Costs | Economic Profit = Total Revenue - (Explicit + Implicit Costs) |
| Costs Considered | Explicit costs only (e.g., wages, rent) | Explicit + implicit costs (e.g., opportunity costs) |
| Purpose | Measures accounting profitability | Assesses true economic value and efficiency |
| Use in Decision Making | Financial reporting, basic profit assessment | Investment decisions, resource allocation |
| Indicates | Profit after paying all explicit expenses | Surplus over all costs including opportunity costs |
| Example | Company revenue $1M, explicit costs $700K - Net profit $300K | Above with implicit costs $100K - Economic profit $200K |
Introduction to Net Profit and Economic Profit
Net profit represents the residual earnings of a business after deducting all explicit costs, including operating expenses, taxes, and interest from total revenue. Economic profit goes beyond net profit by accounting for both explicit costs and implicit costs, such as opportunity costs of capital and resources. Understanding the distinction between net profit and economic profit is essential for evaluating true business performance and informed decision-making.
Defining Net Profit
Net profit represents the total revenue remaining after deducting all explicit costs, including operating expenses, taxes, interest, and depreciation, reflecting the company's financial performance on the income statement. It serves as a crucial indicator for shareholders and managers to assess profitability and efficiency in generating earnings from core operations. Unlike economic profit, which factors in both explicit and implicit costs such as opportunity costs, net profit focuses solely on tangible, recorded expenses and revenues.
What is Economic Profit?
Economic profit measures a company's financial performance by subtracting both explicit costs and implicit costs, including opportunity costs, from total revenue, providing a deeper insight into true profitability. Unlike net profit, which only accounts for explicit expenses, economic profit captures the cost of foregone alternatives, helping businesses evaluate whether resources are being used efficiently. This metric is crucial for long-term decision-making and investment strategies as it reflects the real value created beyond accounting profits.
Key Differences Between Net Profit and Economic Profit
Net profit represents the total revenue minus explicit costs, reflecting a company's financial performance on its income statement. Economic profit accounts for both explicit and implicit costs, including opportunity costs, providing a more comprehensive measure of true profitability. The key difference lies in economic profit's inclusion of opportunity costs, which often results in a lower value compared to net profit, highlighting whether resources could be better utilized elsewhere.
Calculation Methods for Net Profit
Net profit is calculated by subtracting total expenses, including operating costs, taxes, interest, and depreciation, from total revenue, providing a clear measure of a company's profitability over a specific period. This accounting-based method focuses on explicit costs recorded on financial statements, excluding opportunity costs considered in economic profit calculations. Understanding net profit calculation is essential for assessing operational efficiency and financial health within standard accounting frameworks.
Calculating Economic Profit: Step-by-Step
Calculating economic profit involves subtracting both explicit and implicit costs from total revenue, where explicit costs are direct monetary payments and implicit costs represent opportunity costs of resources. Begin by determining net profit, which is total revenue minus explicit costs, then deduct the implicit costs such as forgone income or alternative investments. The resulting figure accurately reflects economic profit, providing a comprehensive measure of profitability beyond accounting net profit.
Importance of Net Profit in Financial Analysis
Net profit represents a company's total earnings after deducting all expenses, providing a clear indicator of operational efficiency and profitability. It is crucial in financial analysis as it directly reflects the company's ability to generate income, informing stakeholders about sustainable business performance. Unlike economic profit, which includes opportunity costs, net profit offers a straightforward measure for assessing financial health and guiding investment decisions.
Significance of Economic Profit in Decision-Making
Economic profit provides a more comprehensive measure of a firm's financial performance by accounting for both explicit costs and opportunity costs, unlike net profit which only considers accounting expenses. This metric is crucial for decision-making as it reveals whether a company is generating sufficient returns beyond the minimum required to justify the use of its resources. Firms utilize economic profit to assess true profitability, guide investment choices, and enhance long-term value creation.
Net Profit vs. Economic Profit: Practical Examples
Net profit represents the total revenue minus explicit costs, reflecting a company's profitability on its income statement. Economic profit accounts for both explicit and implicit costs, including opportunity costs, offering a more comprehensive measure of true profitability. For example, a business earning $100,000 in net profit with $30,000 opportunity costs has an economic profit of $70,000, highlighting the importance of considering forgone alternatives in financial decision-making.
Summary: Choosing the Right Profit Metric
Net profit reflects a company's total revenue minus explicit costs, providing a clear view of accounting profitability, while economic profit incorporates both explicit and implicit costs, offering a more comprehensive measure of true financial performance by considering opportunity costs. Selecting the right profit metric depends on business goals: net profit suits short-term financial reporting, whereas economic profit aids strategic decision-making and long-term value creation. Understanding these distinctions ensures more accurate assessments of a company's health and guides optimal resource allocation.
Net profit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com