Piece rate wage systems pay employees based on the number of units they produce, incentivizing higher productivity and efficiency in manufacturing and assembly line jobs. This payment method aligns workers' earnings directly with their output, encouraging speed and accuracy to maximize income. Discover how piece rate wages can impact your work performance and earnings throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
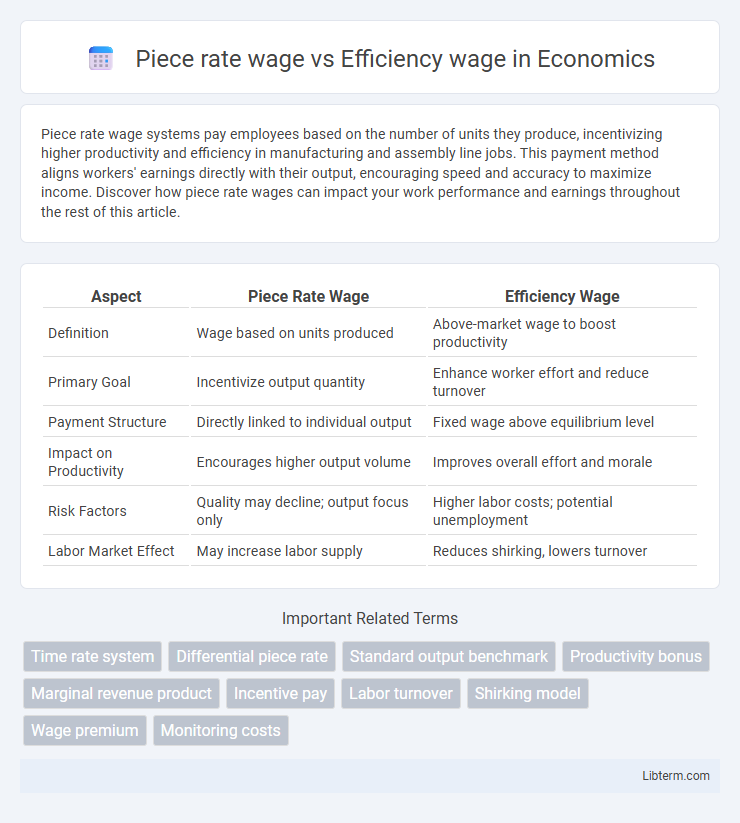
| Aspect | Piece Rate Wage | Efficiency Wage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Wage based on units produced | Above-market wage to boost productivity |
| Primary Goal | Incentivize output quantity | Enhance worker effort and reduce turnover |
| Payment Structure | Directly linked to individual output | Fixed wage above equilibrium level |
| Impact on Productivity | Encourages higher output volume | Improves overall effort and morale |
| Risk Factors | Quality may decline; output focus only | Higher labor costs; potential unemployment |
| Labor Market Effect | May increase labor supply | Reduces shirking, lowers turnover |
Introduction to Piece Rate Wage and Efficiency Wage
Piece rate wage compensates workers based on the quantity of output produced, incentivizing higher productivity through direct performance rewards. Efficiency wage theory proposes paying employees above-market wages to increase motivation, reduce turnover, and enhance overall efficiency. Both wage systems aim to optimize labor productivity but differ fundamentally in payment structure and motivational strategy.
Key Differences Between Piece Rate and Efficiency Wage
Piece rate wage compensates workers based on the quantity of units produced, directly linking pay to individual output and encouraging higher productivity per unit. Efficiency wage offers a fixed salary above the market rate to incentivize better overall performance, reduce turnover, and boost employee motivation and effort. Unlike piece rate systems that reward tangible output, efficiency wages focus on increasing worker loyalty and minimizing shirking through higher guaranteed pay.
Advantages of Piece Rate Wage System
Piece rate wage systems incentivize employees by directly linking pay to output, leading to higher productivity and motivation. This system reduces labor costs for employers since wages correspond strictly to the quantity produced, minimizing idle time and inefficiency. Workers experience greater earning potential through increased effort, fostering a performance-driven work environment.
Drawbacks of Piece Rate Wage System
The Piece Rate Wage system often leads to inconsistent income for workers, creating financial instability and decreased job satisfaction. It can encourage excessive work pace, resulting in fatigue and higher risk of errors or injuries, which compromises overall productivity and safety. This system may also foster unhealthy competition among employees, undermining teamwork and collaboration essential for organizational success.
Benefits of Efficiency Wage Approach
The Efficiency Wage approach enhances worker productivity by incentivizing higher effort and reducing shirking through above-market pay, leading to improved overall firm performance. It also lowers employee turnover rates, saving recruitment and training costs while fostering greater loyalty and motivation. By promoting better health and morale, efficiency wages can create a more stable and committed workforce compared to the variability typically seen with piece rate wage systems.
Limitations of Efficiency Wage Models
Efficiency wage models, which propose paying workers above market wages to boost productivity and reduce turnover, face limitations such as increased labor costs that may lead to reduced employment opportunities or wage inflation. These models often assume perfect information and homogeneous worker productivity, ignoring the complexity of diverse skill levels and external labor market conditions. Moreover, efficiency wages can create wage rigidity, making it difficult for firms to adjust wages in response to economic downturns or shifts in demand.
Impact on Employee Motivation and Performance
Piece rate wage systems directly link employee compensation to productivity, incentivizing higher output and efficiency but potentially leading to rushed work and quality issues. Efficiency wage models pay above-market rates to attract better talent, reduce turnover, and promote loyalty, resulting in sustained motivation and improved overall performance. Both approaches influence employees differently; piece rates boost short-term productivity, while efficiency wages support long-term commitment and consistent work quality.
Suitability for Different Industries
Piece rate wage systems suit industries with easily measurable output and repetitive tasks, such as manufacturing and agriculture, where productivity is directly linked to individual performance. Efficiency wages are more effective in sectors like technology, healthcare, and service industries, where employee motivation, retention, and skill development are critical to maintaining high-quality output. The choice depends on balancing output measurability and the importance of workforce stability and engagement in a given industry.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Case studies reveal that piece rate wage systems, such as those implemented in manufacturing plants in China, significantly boost worker productivity by directly linking pay to output quantity. In contrast, efficiency wage models, exemplified by firms like Toyota in Japan, enhance employee loyalty and reduce turnover by offering above-market salaries, which incentivizes higher effort and quality. Both wage strategies demonstrate distinct advantages depending on industry requirements and organizational goals.
Choosing the Right Wage System for Your Organization
Selecting the appropriate wage system significantly impacts employee motivation and organizational productivity. Piece rate wages directly link pay to output, encouraging higher individual performance but may risk quality control issues. Efficiency wages offer above-market pay to boost morale and reduce turnover, fostering long-term commitment and consistent work quality.
Piece rate wage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com