Production subsidies lower costs for manufacturers, encouraging increased output and competitiveness in the market. These financial supports can enhance your business's ability to scale and innovate by reducing initial production expenses. Explore the rest of the article to understand how production subsidies can impact your industry and opportunities.
Table of Comparison
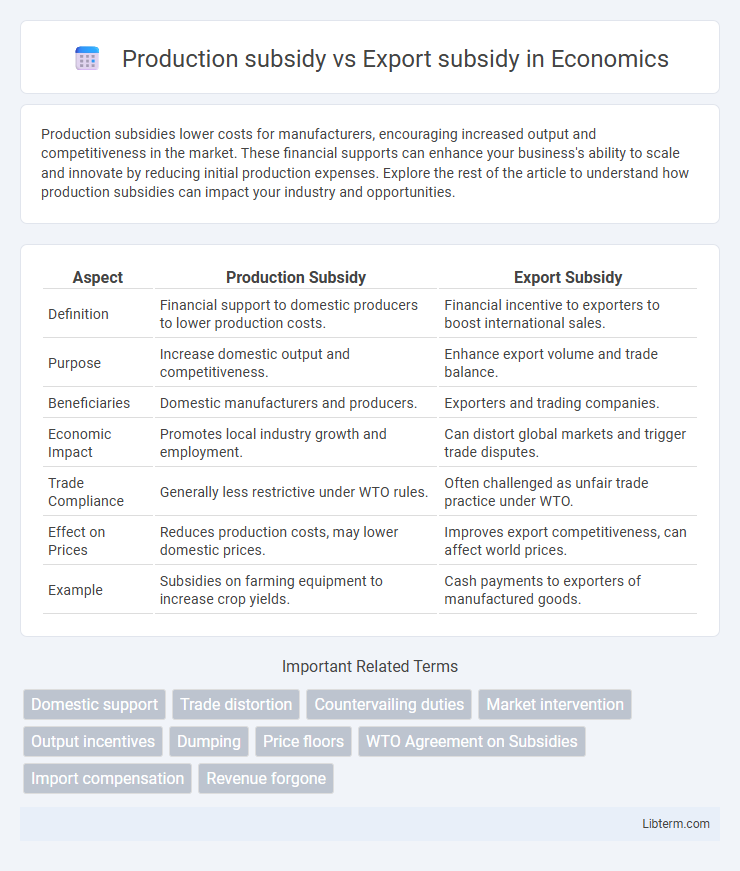
| Aspect | Production Subsidy | Export Subsidy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial support to domestic producers to lower production costs. | Financial incentive to exporters to boost international sales. |
| Purpose | Increase domestic output and competitiveness. | Enhance export volume and trade balance. |
| Beneficiaries | Domestic manufacturers and producers. | Exporters and trading companies. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes local industry growth and employment. | Can distort global markets and trigger trade disputes. |
| Trade Compliance | Generally less restrictive under WTO rules. | Often challenged as unfair trade practice under WTO. |
| Effect on Prices | Reduces production costs, may lower domestic prices. | Improves export competitiveness, can affect world prices. |
| Example | Subsidies on farming equipment to increase crop yields. | Cash payments to exporters of manufactured goods. |
Introduction to Production Subsidy and Export Subsidy
Production subsidies are financial incentives provided by governments to domestic producers to lower their production costs, increase output, and enhance competitiveness within the home market. Export subsidies specifically target goods destined for foreign markets, aiming to boost export volumes by reducing export costs and improving international price competitiveness. Both types of subsidies significantly influence trade dynamics, domestic industry growth, and global market positioning.
Defining Production Subsidy
A production subsidy is a financial aid provided by the government to domestic producers to lower their production costs and encourage higher output of goods and services. Unlike export subsidies, which specifically support goods destined for foreign markets, production subsidies aim to strengthen the overall competitiveness of local industries within both domestic and international markets. This form of subsidy can include grants, tax breaks, or direct payments that reduce the expense of raw materials, labor, or capital investment.
Understanding Export Subsidy
Export subsidies are government financial supports aimed specifically at boosting a country's international trade by lowering the export price of goods, making them more competitive in global markets. Unlike production subsidies that reduce costs for domestic manufacturers regardless of the product's final destination, export subsidies target goods bound for foreign markets, encouraging increased export volume and market share. Understanding export subsidies requires analyzing their impact on trade balances, global price competition, and compliance with World Trade Organization (WTO) regulations.
Key Differences Between Production and Export Subsidies
Production subsidies directly lower the cost of manufacturing goods, boosting domestic output and supporting local industries, while export subsidies provide financial incentives to sellers for shipping goods abroad, aiming to increase a country's export volume and competitiveness in international markets. Production subsidies often target raw materials, labor costs, or technology investments, whereas export subsidies typically take the form of tax rebates or direct cash payments tied to the export quantity or value. The primary difference lies in their economic impact: production subsidies encourage overall supply growth within the domestic economy, whereas export subsidies specifically promote international trade expansion.
Economic Impacts of Production Subsidies
Production subsidies enhance domestic output by lowering production costs, leading to increased supply and potential market distortions. These subsidies can cause overproduction, inefficient resource allocation, and fiscal burdens on governments while protecting local industries from international competition. The economic impact often includes reduced prices for consumers but may provoke trade tensions and retaliation from trading partners.
Economic Effects of Export Subsidies
Export subsidies increase the competitiveness of domestic goods in international markets by lowering export prices, which can lead to trade distortions and retaliatory tariffs from trade partners. These subsidies often result in an inefficient allocation of resources, as producers prioritize subsidized exports over potentially more valuable domestic markets. While production subsidies support domestic manufacturing broadly, export subsidies specifically target foreign sales, creating tensions in global trade and potentially harming long-term economic growth due to market distortions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Production Subsidies
Production subsidies encourage domestic manufacturing by lowering production costs, boosting local employment, and enhancing industry competitiveness. However, they can distort market prices, lead to inefficient resource allocation, and create trade tensions if perceived as unfair advantages. These subsidies may also burden taxpayers and discourage innovation by supporting less efficient producers.
Pros and Cons of Export Subsidies
Export subsidies boost competitiveness in international markets by lowering export prices, which can increase market share and support domestic industries. However, they risk trade disputes and retaliations under World Trade Organization rules, potentially escalating costs and harming global trade relations. While promoting short-term export growth, export subsidies may distort market efficiency and create dependence, leading to long-term economic inefficiencies.
Global Trade Implications of Subsidies
Production subsidies lower domestic production costs, potentially leading to overproduction and distorted market prices, which can harm international competitors by flooding global markets with cheaper goods. Export subsidies specifically boost the competitiveness of domestic products in foreign markets, often triggering trade disputes and retaliatory tariffs as they are seen as unfair trade practices under World Trade Organization (WTO) rules. Both forms of subsidies disrupt global trade balance, reducing efficiency and potentially sparking protectionist measures that hinder free trade and economic growth worldwide.
Policy Recommendations and Conclusion
Production subsidies lower domestic manufacturing costs, encouraging local industry growth but potentially causing market distortions and inefficiencies. Export subsidies promote international competitiveness by reducing export prices, yet may provoke trade disputes and retaliatory tariffs under World Trade Organization rules. Policymakers should balance subsidies' benefits with compliance to trade regulations, prioritizing transparent, targeted support that fosters innovation and competitiveness without triggering protectionist backlash.
Production subsidy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com