A budget deficit occurs when a government's expenditures exceed its revenues during a fiscal period, leading to increased borrowing and national debt. Managing a budget deficit requires careful policy decisions to balance economic growth with fiscal responsibility. Explore the rest of the article to understand how budget deficits impact your economy and what strategies can be employed to address them.
Table of Comparison
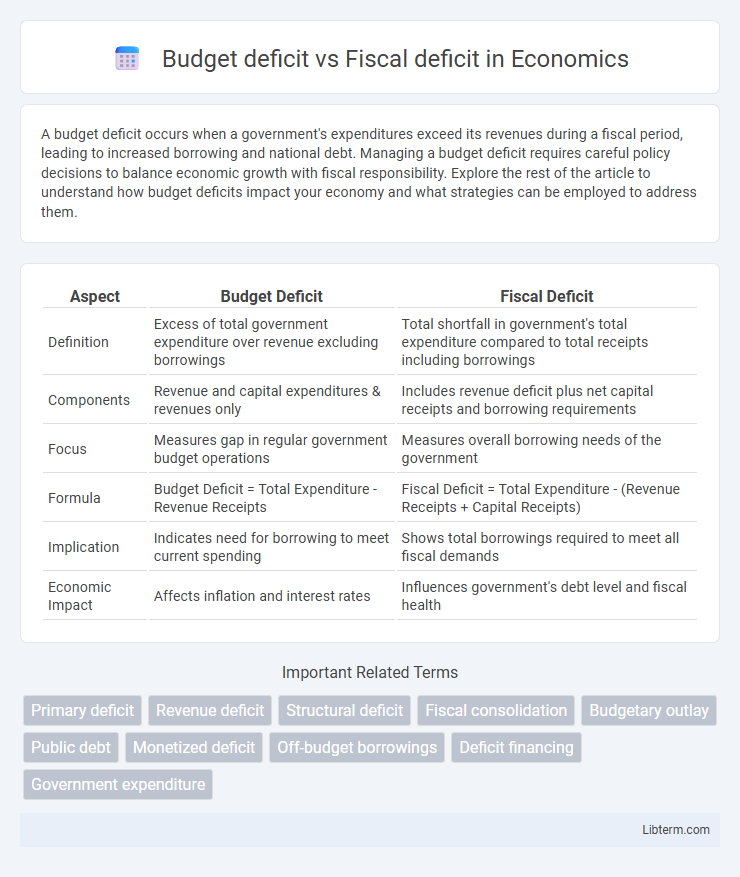
| Aspect | Budget Deficit | Fiscal Deficit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excess of total government expenditure over revenue excluding borrowings | Total shortfall in government's total expenditure compared to total receipts including borrowings |
| Components | Revenue and capital expenditures & revenues only | Includes revenue deficit plus net capital receipts and borrowing requirements |
| Focus | Measures gap in regular government budget operations | Measures overall borrowing needs of the government |
| Formula | Budget Deficit = Total Expenditure - Revenue Receipts | Fiscal Deficit = Total Expenditure - (Revenue Receipts + Capital Receipts) |
| Implication | Indicates need for borrowing to meet current spending | Shows total borrowings required to meet all fiscal demands |
| Economic Impact | Affects inflation and interest rates | Influences government's debt level and fiscal health |
Understanding Budget Deficit: Definition and Key Concepts
Budget deficit occurs when government expenditures exceed its revenues within a fiscal year, indicating the need for borrowing to cover the shortfall. It reflects the difference between total spending and total income, excluding debt repayments, highlighting the immediate impact on fiscal policy and economic stability. Understanding this concept is crucial for evaluating a government's financial health and its approach to managing public resources.
What is Fiscal Deficit? An Overview
Fiscal deficit occurs when a government's total expenditure exceeds its total revenue, excluding borrowings, during a specific period. It indicates the amount of borrowing a government needs to meet its expenses and is a crucial indicator of the country's financial health. Measuring fiscal deficit helps assess the sustainability of fiscal policies and the impact on economic growth and inflation.
Budget Deficit vs Fiscal Deficit: Core Differences
Budget deficit refers to the shortfall when a government's total expenditures exceed its total revenues, excluding borrowings, within a fiscal year. Fiscal deficit represents the total amount of borrowing required by the government to cover the excess of its total expenditure, including capital and interest payments, over its total receipts, excluding borrowings. The core difference lies in that budget deficit measures the gap between revenue and expenditure, while fiscal deficit reflects the actual borrowing needed to finance the budget deficit.
Key Components of Budget Deficit
The budget deficit primarily reflects the shortfall when government expenditures exceed revenues during a fiscal year, excluding borrowings, which is a crucial component distinguishing it from the broader fiscal deficit. Key components of the budget deficit include revenue deficit, which measures the gap between revenue receipts and revenue expenditure, and capital account balance, addressing the financing of capital expenditure through borrowings or asset sales. Understanding these elements helps in analyzing government fiscal health, where a higher revenue deficit often indicates inadequate current revenues to meet expenses, impacting the overall budget stance.
Main Elements of Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit represents the total shortfall between a government's total expenditure and its total revenue, excluding borrowings, while budget deficit specifically refers to the gap between total revenue and total expenditure in the budget. The main elements of fiscal deficit include revenue deficit, which occurs when revenue expenditure exceeds revenue receipts, and capital expenditure that is financed through borrowing, contributing to the overall deficit. Understanding these components is essential for assessing the government's borrowing needs and fiscal health.
Causes Behind Budget and Fiscal Deficits
Budget deficit occurs when government expenditures exceed revenues excluding borrowings, primarily driven by increased public spending on infrastructure, subsidies, and defense, or reduced tax collections due to economic downturns. Fiscal deficit measures the total borrowing requirements of the government, reflecting not only the budget deficit but also interest payments on past debts, which escalate with rising debt levels and inefficient fiscal management. Both deficits are influenced by structural factors like tax policy inefficiencies, low revenue mobilization, and cyclical factors such as recession-induced declines in tax revenue and increased welfare spending.
Economic Impacts: Budget Deficit vs Fiscal Deficit
A budget deficit occurs when government expenditures exceed revenue within a specific budget period, potentially leading to increased borrowing that can raise interest rates and crowd out private investment. Fiscal deficit includes the overall shortfall in the government's total expenditure over total receipts, excluding borrowings, reflecting the broader economic health and influencing inflation and currency stability. Both deficits impact economic growth, with persistent fiscal deficits potentially causing higher debt levels and inflationary pressures, while budget deficits directly affect short-term fiscal policy effectiveness.
How Governments Finance Deficits
Governments finance budget deficits primarily through borrowing by issuing bonds and treasury bills, which increases public debt. Fiscal deficits encompass borrowing needs beyond current revenue, including off-budget expenditures funded by both internal and external sources. Central banks may also monetize deficits by purchasing government securities, impacting inflation and monetary policy stability.
Policy Measures to Manage Deficits
Policy measures to manage budget deficits and fiscal deficits often include implementing expenditure control, enhancing revenue generation through tax reforms, and improving public financial management practices. Governments frequently adopt austerity measures, such as reducing subsidies and cutting non-essential spending, while promoting economic growth to increase tax base and reduce reliance on borrowing. Structural reforms focusing on transparency, fiscal responsibility laws, and debt management strategies also play critical roles in maintaining sustainable deficit levels.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Deficit Indicator
Selecting the appropriate deficit indicator depends on the specific economic analysis or policy goal: a budget deficit reflects the shortfall between government revenues and expenditures within a fiscal year, while a fiscal deficit provides a broader measure by including off-budget borrowings and other financial obligations. Policymakers should prioritize the fiscal deficit for a comprehensive understanding of government borrowing needs and debt sustainability, whereas the budget deficit serves well for yearly fiscal discipline assessment. Accurate deficit measurement ensures better fiscal management, debt control, and economic planning.
Budget deficit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com