Interest rate policy plays a crucial role in controlling inflation, stabilizing the economy, and influencing borrowing costs for consumers and businesses. Central banks adjust interest rates to either stimulate growth during downturns or cool down overheated markets, directly impacting your loan rates and investment returns. Explore the detailed mechanisms behind interest rate policies and how they affect your financial decisions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
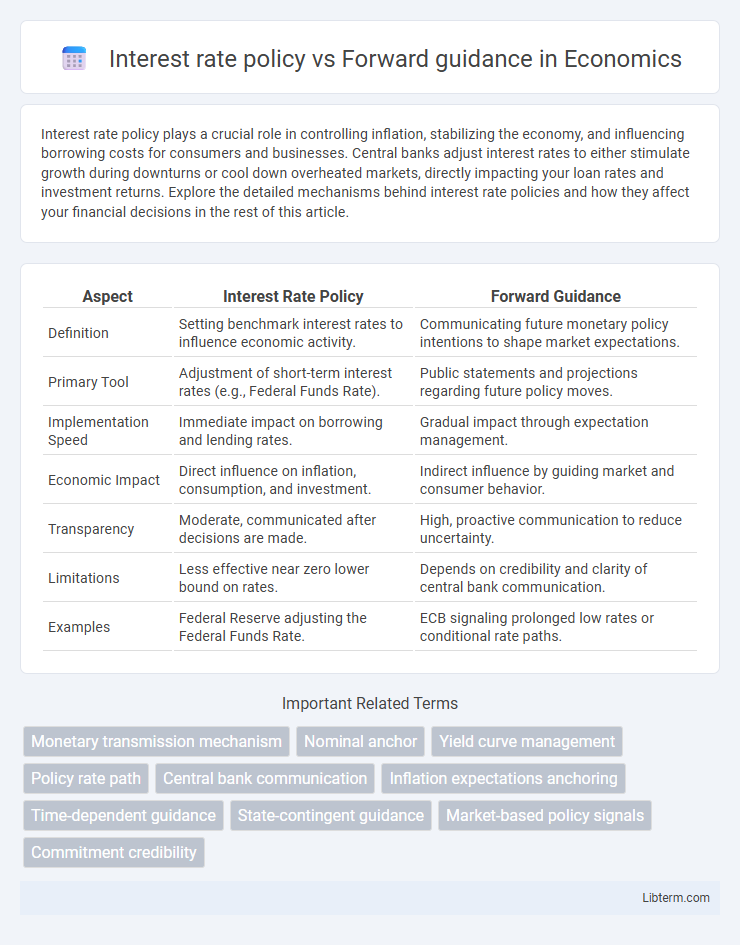
| Aspect | Interest Rate Policy | Forward Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Setting benchmark interest rates to influence economic activity. | Communicating future monetary policy intentions to shape market expectations. |
| Primary Tool | Adjustment of short-term interest rates (e.g., Federal Funds Rate). | Public statements and projections regarding future policy moves. |
| Implementation Speed | Immediate impact on borrowing and lending rates. | Gradual impact through expectation management. |
| Economic Impact | Direct influence on inflation, consumption, and investment. | Indirect influence by guiding market and consumer behavior. |
| Transparency | Moderate, communicated after decisions are made. | High, proactive communication to reduce uncertainty. |
| Limitations | Less effective near zero lower bound on rates. | Depends on credibility and clarity of central bank communication. |
| Examples | Federal Reserve adjusting the Federal Funds Rate. | ECB signaling prolonged low rates or conditional rate paths. |
Introduction to Interest Rate Policy and Forward Guidance
Interest rate policy involves central banks adjusting benchmark rates to influence economic activity, control inflation, and stabilize currency value. Forward guidance provides explicit communication about the future path of interest rates, aiming to shape market expectations and enhance policy transparency. Both tools are integral to monetary policy strategies, with interest rate adjustments delivering immediate effects and forward guidance targeting anticipatory market behaviors.
Defining Interest Rate Policy
Interest rate policy involves central banks setting benchmark rates to influence economic activity, inflation, and employment levels. This policy directly impacts borrowing costs and investment decisions by adjusting short-term interest rates to either stimulate or restrain economic growth. Forward guidance complements interest rate policy by providing explicit communication about future monetary policy intentions, aiming to shape market expectations and stabilize financial conditions.
Understanding Forward Guidance
Forward guidance is a critical tool used by central banks to communicate the likely path of future interest rates, shaping market expectations and influencing long-term borrowing costs. By providing clear signals about future monetary policy actions, forward guidance enhances transparency and reduces uncertainty, supporting better decision-making for investors and businesses. Unlike traditional interest rate policy, which adjusts rates directly, forward guidance leverages communication strategies to guide economic behavior and stabilize financial markets.
Key Differences Between Interest Rate Policy and Forward Guidance
Interest rate policy involves direct adjustments to the central bank's benchmark rates to influence economic activity, targeting inflation and employment levels. Forward guidance communicates the central bank's anticipated future policy path to shape market expectations and economic decisions without immediate rate changes. The key difference lies in immediate market impact; interest rate policy alters financial conditions directly, while forward guidance relies on signaling to guide future economic behavior.
Effectiveness in Achieving Monetary Policy Goals
Interest rate policy directly influences borrowing costs and consumer spending, making it a potent tool for controlling inflation and stimulating economic growth. Forward guidance shapes market expectations by communicating future monetary policy intentions, enhancing policy effectiveness through improved transparency and predictability. Combining interest rate adjustments with clear forward guidance strengthens monetary policy outcomes by aligning market behavior with central bank goals.
Impact on Financial Markets and Economic Expectations
Interest rate policy directly influences financial markets through adjustments in central bank rates, affecting borrowing costs, asset prices, and investment decisions. Forward guidance shapes economic expectations by communicating future policy intentions, reducing uncertainty and guiding market behavior without immediate rate changes. Together, these tools stabilize markets by managing inflation expectations and reinforcing confidence in economic outlooks.
Communication Strategies in Forward Guidance
Forward guidance employs clear, transparent communication strategies to influence market expectations about future interest rate paths, enhancing policy effectiveness beyond traditional interest rate adjustments. Central banks use forward guidance to provide explicit information on future monetary policy intentions, thereby reducing uncertainty and stabilizing financial markets. This strategy relies heavily on consistent messaging and credible commitments to shape economic behavior proactively.
Case Studies: Central Banks’ Use of Both Tools
Central banks like the Federal Reserve and the Bank of England use interest rate policy and forward guidance together to influence market expectations and economic behavior effectively. The Federal Reserve's use of explicit forward guidance during the 2008 financial crisis helped anchor inflation expectations while maintaining low interest rates supported economic recovery. Similarly, the European Central Bank combined negative interest rates with clear communication strategies to stabilize financial markets and boost lending across the Eurozone.
Challenges and Limitations of Interest Rate Policy vs Forward Guidance
Interest rate policy faces challenges such as delayed effects on the economy and limited impact when rates approach the zero lower bound, reducing central banks' ability to stimulate growth. Forward guidance struggles with credibility and communication difficulties, as markets may doubt future policy commitments or misinterpret ambiguous signals. Both tools have limitations in managing expectations and require complementary measures to effectively influence inflation and economic stability.
Future Trends in Central Bank Policy Tools
Interest rate policy remains the primary instrument for central banks to influence economic activity by adjusting borrowing costs, but forward guidance increasingly shapes market expectations through clear communication about future policy directions. Future trends indicate a growing reliance on forward guidance as central banks seek to enhance transparency and manage long-term inflation and growth expectations amidst economic uncertainty. This shift reflects a complementary approach where interest rate adjustments are supported by detailed forward guidance to stabilize markets and improve monetary policy effectiveness.
Interest rate policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com