A flexible budget constraint adapts to changes in activity levels, allowing businesses to adjust expenses and revenues based on actual performance rather than fixed estimates. This dynamic approach improves cost control and financial planning by providing more accurate comparisons between budgeted and actual figures. Explore the rest of the article to understand how implementing a flexible budget constraint can enhance your financial management strategies.
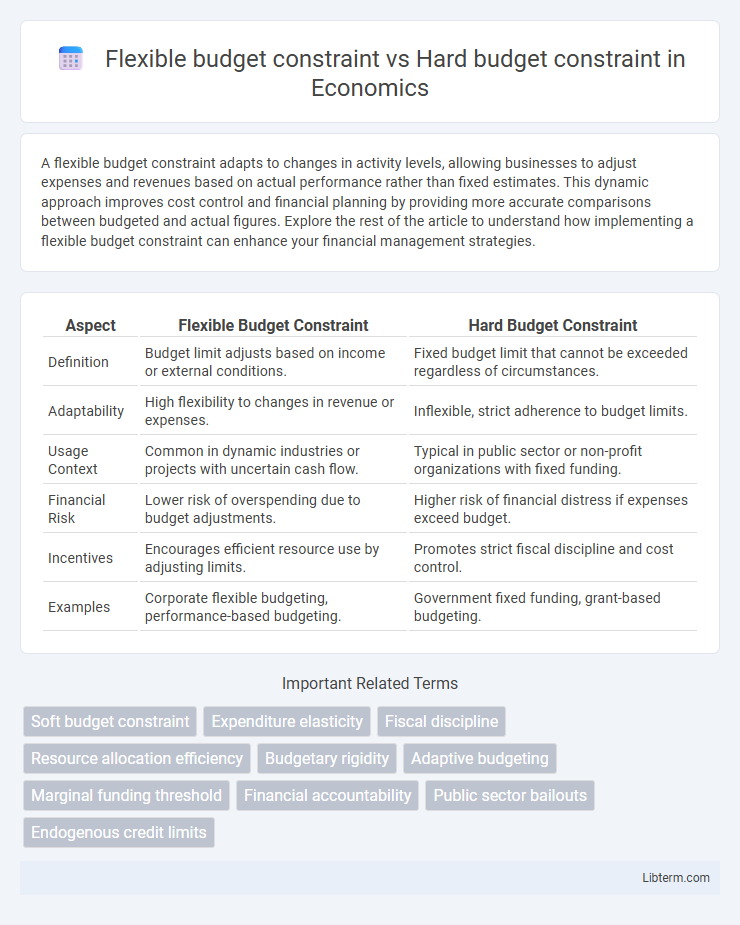
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Flexible Budget Constraint | Hard Budget Constraint |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Budget limit adjusts based on income or external conditions. | Fixed budget limit that cannot be exceeded regardless of circumstances. |
| Adaptability | High flexibility to changes in revenue or expenses. | Inflexible, strict adherence to budget limits. |
| Usage Context | Common in dynamic industries or projects with uncertain cash flow. | Typical in public sector or non-profit organizations with fixed funding. |
| Financial Risk | Lower risk of overspending due to budget adjustments. | Higher risk of financial distress if expenses exceed budget. |
| Incentives | Encourages efficient resource use by adjusting limits. | Promotes strict fiscal discipline and cost control. |
| Examples | Corporate flexible budgeting, performance-based budgeting. | Government fixed funding, grant-based budgeting. |
Introduction to Budget Constraints
Budget constraints represent limits on spending based on available resources, defining the feasible allocation of goods or services. A flexible budget constraint adjusts according to changes in income or prices, allowing more adaptability for consumers or firms under varying economic conditions. In contrast, a hard budget constraint reflects a fixed spending limit, often imposed by strict financial rules or external borrowing caps, restricting flexibility.
Defining Flexible Budget Constraints
Flexible budget constraints adjust expenditure limits based on actual activity levels or output, allowing organizations to respond dynamically to changing financial conditions. Unlike hard budget constraints, which impose fixed spending caps regardless of performance, flexible budgets align resources with real-time operational needs and revenue fluctuations. This adaptability enhances financial control, improves resource allocation efficiency, and supports better decision-making in variable economic environments.
Understanding Hard Budget Constraints
Hard budget constraints limit an organization's spending strictly to its available financial resources, preventing deficit financing and forcing precise allocation of funds. Unlike flexible budget constraints that adjust expenditures based on revenue fluctuations, hard budget constraints enforce financial discipline and accountability, ensuring no overspending beyond allocated budgets. This constraint is crucial in public sector budgeting and organizations dependent on fixed funding sources, promoting sustainability and efficient resource management.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Hard Budget Constraints
Flexible budget constraints adjust according to actual levels of activity, allowing spending limits to vary with changes in production or sales volume, while hard budget constraints impose fixed spending limits regardless of performance fluctuations. Flexible budgets enhance adaptability and provide more accurate performance evaluation by aligning expenditures with real-time operational conditions. Hard budgets promote strict cost control and fiscal discipline by preventing overspending but may limit responsiveness to unforeseen changes in business dynamics.
Advantages of Flexible Budget Constraints
Flexible budget constraints allow businesses to adjust spending based on real-time revenue fluctuations, enhancing financial agility in dynamic market conditions. This adaptability supports better resource allocation and operational efficiency by aligning expenses with actual performance. Organizations benefit from improved financial control and risk management, enabling strategic decision-making during economic variability.
Drawbacks of Flexible Budget Constraints
Flexible budget constraints often lead to inefficiencies because they allow for variable spending that can encourage overspending and reduce cost control. Organizations may struggle to allocate resources effectively as the budget adjusts to changing conditions, resulting in less financial discipline. This lack of firm limits can create uncertainty, impairing long-term financial planning and accountability.
Benefits of Hard Budget Constraints
Hard budget constraints enforce strict spending limits, promoting disciplined financial management and reducing the risk of overspending. Organizations under hard constraints are incentivized to optimize resource allocation and improve operational efficiency to meet targets within fixed budgets. This approach enhances accountability and encourages cost control, leading to sustainable financial stability.
Limitations of Hard Budget Constraints
Hard budget constraints limit an organization's ability to adapt to unforeseen expenses, often resulting in operational inefficiencies due to lack of financial flexibility. These constraints can stifle innovation and responsiveness, as strict spending caps prevent reallocating resources to emergent priorities. In contrast, flexible budget constraints adjust expenditures based on actual performance and needs, promoting better resource management and financial resilience.
Impact on Organizational Financial Management
Flexible budget constraints allow organizations to adjust expenses based on actual revenue fluctuations, improving responsiveness and resource allocation efficiency in financial management. Hard budget constraints impose fixed spending limits regardless of revenue variations, promoting strict cost control but potentially limiting adaptability and innovation. Organizations using flexible budgets tend to better manage cash flow uncertainties, while those with hard budgets emphasize accountability and predictable financial planning.
Choosing the Right Budget Constraint Approach
Choosing the right budget constraint approach depends on the predictability of revenues and expenses within a project or organization. Flexible budget constraints adapt to changes in activity levels, allowing for dynamic resource allocation and improved variance analysis, particularly useful in volatile industries. Hard budget constraints impose strict financial limits, fostering discipline and cost control, which is critical for entities with fixed funding or regulatory requirements.
Flexible budget constraint Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com