Portfolio weight defines the proportion of each asset within your investment portfolio, directly influencing risk and return. Properly balancing these weights helps optimize diversification and achieve financial goals. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively manage your portfolio weight for maximum benefit.
Table of Comparison
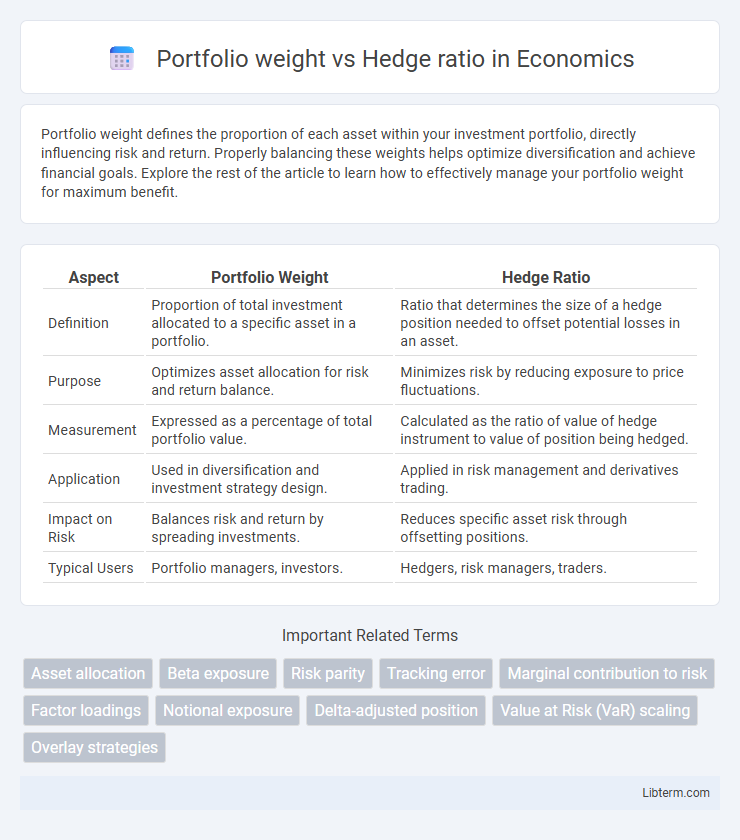
| Aspect | Portfolio Weight | Hedge Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proportion of total investment allocated to a specific asset in a portfolio. | Ratio that determines the size of a hedge position needed to offset potential losses in an asset. |
| Purpose | Optimizes asset allocation for risk and return balance. | Minimizes risk by reducing exposure to price fluctuations. |
| Measurement | Expressed as a percentage of total portfolio value. | Calculated as the ratio of value of hedge instrument to value of position being hedged. |
| Application | Used in diversification and investment strategy design. | Applied in risk management and derivatives trading. |
| Impact on Risk | Balances risk and return by spreading investments. | Reduces specific asset risk through offsetting positions. |
| Typical Users | Portfolio managers, investors. | Hedgers, risk managers, traders. |
Understanding Portfolio Weight: Definition and Importance
Portfolio weight represents the proportion of an individual asset's value relative to the total value of the investment portfolio, crucial for determining the overall risk and return profile. Accurate calculation of portfolio weights enables investors to allocate assets efficiently, balancing exposure and diversification. Understanding portfolio weight is essential for optimizing investment strategies and effectively managing portfolio risk.
What is a Hedge Ratio? Key Concepts Explained
A hedge ratio measures the extent to which a portfolio's risk is mitigated through hedging instruments, usually expressed as the ratio of the value of the position being hedged to the value of the hedging instrument. It plays a crucial role in portfolio management by quantifying the proportion of exposure offset to minimize potential losses from price movements. Optimizing the hedge ratio helps align the portfolio weight with risk management objectives, balancing return potential against downside risk.
Portfolio Weight vs Hedge Ratio: Core Differences
Portfolio weight represents the proportion of a specific asset within an investment portfolio, reflecting its relative importance in the overall asset allocation. Hedge ratio quantifies the extent to which a position is hedged, indicating the ratio of the value of the hedge to the value of the exposure. The core difference lies in portfolio weight focusing on allocation and diversification, while hedge ratio centers on risk mitigation and exposure management.
Calculating Portfolio Weights: Methods and Examples
Calculating portfolio weights involves determining the proportion of each asset's value relative to the total portfolio value, commonly expressed as weight = asset value / total portfolio value. Methods such as market value weighting, equal weighting, and fundamental weighting provide various frameworks depending on investment goals and risk preferences. For example, a portfolio with $50,000 in stocks and $50,000 in bonds has equal weights of 50% each, while a portfolio of $70,000 in stocks and $30,000 in bonds has weights of 70% and 30%, respectively.
Determining the Hedge Ratio: Step-by-Step Guide
Determining the hedge ratio begins with calculating the portfolio's value and estimating the sensitivity of its returns to the hedging instrument, often measured as the portfolio beta or duration for fixed income. Next, identify the size and price of the hedging instrument, such as futures contracts or options, to align the hedge proportionally with the portfolio exposure. The hedge ratio is then derived by dividing the portfolio's risk exposure by the value of one hedging instrument, ensuring precise risk mitigation tailored to market fluctuations.
Role of Portfolio Weight in Risk Management
Portfolio weight plays a crucial role in risk management by determining the proportion of total investment allocated to each asset, directly influencing overall portfolio risk and return characteristics. Adjusting portfolio weights allows investors to diversify and optimize exposure to various asset classes, reducing unsystematic risk and enhancing risk-adjusted returns. Effective allocation strategies balance portfolio weights to achieve desired hedge ratios, mitigating potential losses from market volatility and improving financial stability.
How Hedge Ratio Influences Portfolio Protection
The hedge ratio determines the proportion of an asset's exposure that is offset by a hedging instrument, directly impacting portfolio protection by minimizing potential losses during market downturns. A precise hedge ratio ensures that the protective position closely matches the portfolio's risk, reducing volatility without sacrificing returns. Adjusting the hedge ratio in relation to portfolio weight optimizes risk management, balancing cost-efficiency with effective downside coverage.
Applications of Portfolio Weight in Asset Allocation
Portfolio weight is a critical metric in asset allocation, representing the proportion of investment allocated to each asset within a portfolio to optimize risk and return. It directly influences diversification strategies by balancing exposure across asset classes, sectors, and geographies, thereby reducing portfolio volatility. Effective portfolio weight adjustments facilitate dynamic rebalancing to respond to market changes, ensuring alignment with investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Optimal Hedge Ratio Strategies for Investors
Optimal hedge ratio strategies for investors balance portfolio weight to minimize risk and maximize returns by aligning asset exposure with market volatility. Calculating the hedge ratio involves determining the proportion of a position to hedge, often using regression analysis or variance minimization techniques for precision. Effective portfolio weighting combined with an optimized hedge ratio enhances risk management and improves overall portfolio efficiency.
Common Mistakes in Managing Portfolio Weight and Hedge Ratio
Common mistakes in managing portfolio weight and hedge ratio include misestimating asset correlation, which leads to ineffective risk mitigation and suboptimal diversification. Over-reliance on historical data without accounting for market regime shifts often results in poorly calibrated hedge ratios that fail during periods of high volatility. Ignoring transaction costs and liquidity constraints can further distort actual portfolio exposure, reducing the effectiveness of both portfolio weighting and hedging strategies.
Portfolio weight Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com