Per capita income measures the average income earned per person in a specific area, offering insight into the economic well-being of its residents. It helps gauge living standards and allows comparisons across regions or countries. Discover how understanding your area's per capita income can influence financial decisions by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
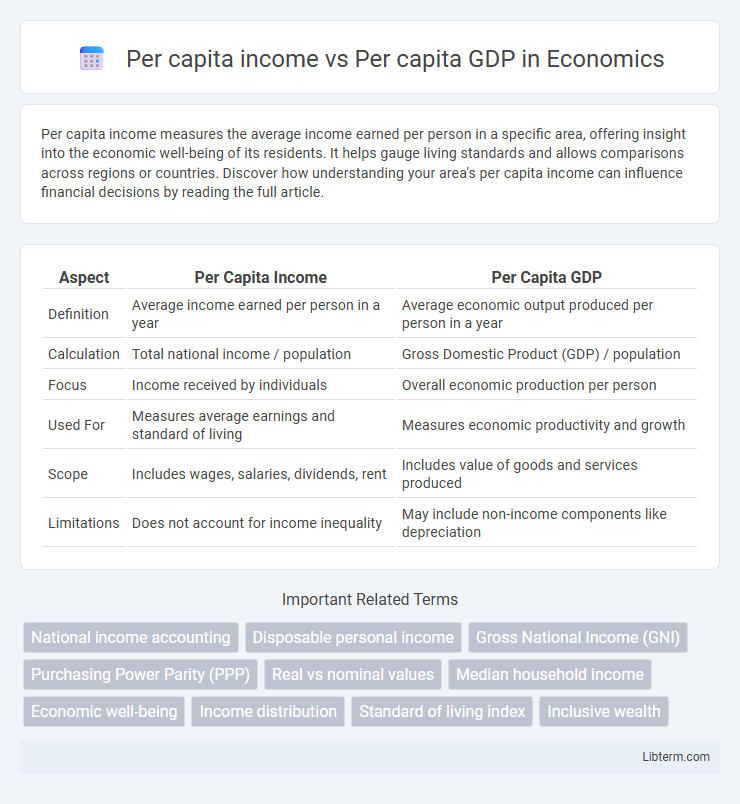
| Aspect | Per Capita Income | Per Capita GDP |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Average income earned per person in a year | Average economic output produced per person in a year |
| Calculation | Total national income / population | Gross Domestic Product (GDP) / population |
| Focus | Income received by individuals | Overall economic production per person |
| Used For | Measures average earnings and standard of living | Measures economic productivity and growth |
| Scope | Includes wages, salaries, dividends, rent | Includes value of goods and services produced |
| Limitations | Does not account for income inequality | May include non-income components like depreciation |
Introduction to Per Capita Income and Per Capita GDP
Per capita income measures the average income earned per person in a specific area, reflecting individual economic well-being and income distribution within the population. Per capita GDP calculates the total gross domestic product divided by the population, indicating the average economic output and overall economic performance of a country. Both metrics provide valuable insights for comparing economic standards and living conditions across regions.
Defining Per Capita Income
Per capita income refers to the average income earned by each individual in a specific area, calculated by dividing the total personal income of the population by the number of people. It measures the average earnings of residents, reflecting household income levels and economic well-being. Unlike per capita GDP, which assesses overall economic output per person, per capita income provides a direct indicator of individual financial resources and living standards.
Understanding Per Capita GDP
Per capita GDP measures the average economic output per person by dividing a country's gross domestic product by its population, providing a broad indicator of economic performance and living standards. Unlike per capita income, which reflects the average earnings of individuals, per capita GDP captures the total market value of all final goods and services produced, offering insights into overall economic productivity. Understanding per capita GDP helps assess economic growth and compare productivity levels across countries or regions.
Key Differences between Per Capita Income and Per Capita GDP
Per capita income measures the average income earned by individuals in a specific area, reflecting the distribution of earnings among the population, while per capita GDP calculates the average economic output per person, emphasizing overall economic productivity. Per capita income accounts for net income from abroad and personal earnings, whereas per capita GDP is strictly based on the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders. These distinctions highlight that per capita income provides insight into individual economic well-being, whereas per capita GDP offers a broader perspective on national economic performance.
Calculation Methods Explained
Per capita income is calculated by dividing the total personal income of a country's residents by its population, reflecting average individual earnings. Per capita GDP is obtained by dividing the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by the total population, representing the average economic output per person. Unlike per capita GDP, which measures overall economic productivity, per capita income accounts for income distribution and taxation effects within the population.
Significance in Economic Analysis
Per capita income measures the average income earned per person in a specific area, reflecting individual earning capacity and living standards. Per capita GDP represents the total economic output divided by the population, offering insights into overall economic productivity and growth. Comparing these metrics helps economists assess wealth distribution, economic well-being, and policy effectiveness within a country.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Metric
Per capita income measures the average income earned per person in a specific area, offering insight into individual earning power and living standards but may exclude non-monetary benefits and informal economies. Per capita GDP calculates the total economic output divided by population, reflecting overall economic productivity but often overlooks income distribution and welfare disparities. Both metrics provide valuable economic perspectives, yet combining them yields a more comprehensive understanding of economic well-being and societal wealth.
Impacts on Policy and Decision Making
Per capita income and per capita GDP both serve as critical indicators for assessing economic performance but differ in focus; per capita GDP measures average economic output, while per capita income reflects average earnings of individuals, including wages and transfer payments. Policymakers prioritize per capita income to design social welfare programs and tax policies targeting income distribution and poverty alleviation. Conversely, per capita GDP guides decisions on economic growth strategies, investment in infrastructure, and sector development to enhance overall productivity and living standards.
Global Comparisons and Rankings
Per capita income measures the average individual earnings in a country, while per capita GDP reflects the total economic output divided by the population, capturing overall national productivity. High per capita GDP rankings in countries like Luxembourg and Switzerland indicate robust economic activity, whereas per capita income highlights disparities in wealth distribution and living standards. Global comparisons reveal that nations with similar per capita GDP can have varying per capita incomes due to taxation, social welfare policies, and income inequality factors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Indicator
Per capita income measures the average income earned per person, reflecting individual economic well-being, while per capita GDP represents the total economic output divided by the population, indicating overall economic productivity. Selecting the right indicator depends on the context: per capita income is more suitable for assessing living standards and purchasing power, whereas per capita GDP better captures economic growth and development. Understanding the distinct focus of each metric ensures accurate analysis and policy-making tailored to specific socio-economic goals.
Per capita income Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com