Intra-industry trade involves the exchange of similar products belonging to the same industry, such as cars for cars or electronics for electronics, between countries. This type of trade enhances economic efficiency by allowing firms to specialize in niche markets, increasing product variety and fostering innovation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how intra-industry trade influences global markets and benefits your business strategy.
Table of Comparison
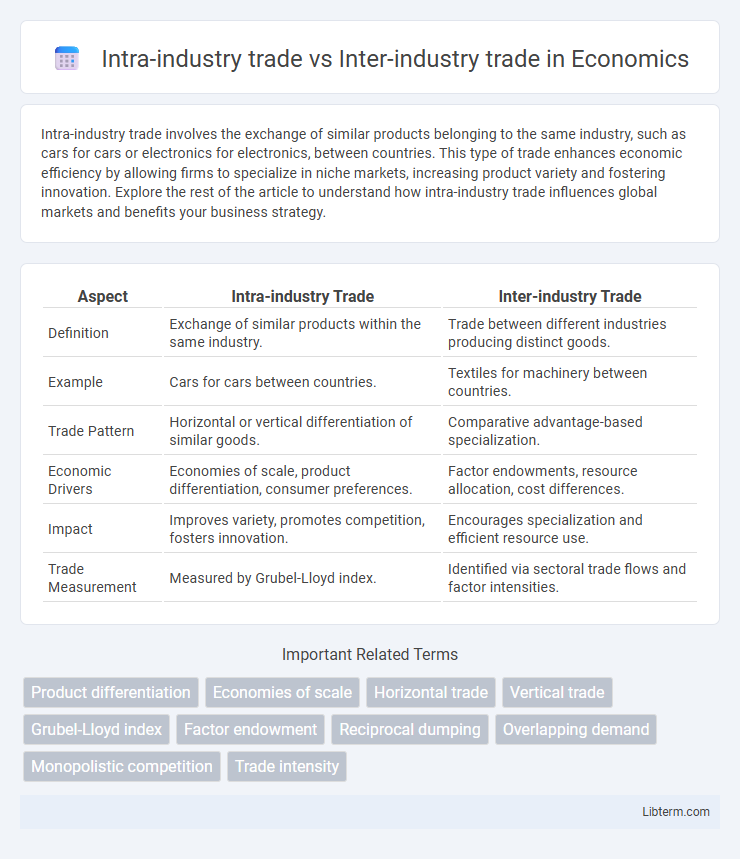
| Aspect | Intra-industry Trade | Inter-industry Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange of similar products within the same industry. | Trade between different industries producing distinct goods. |
| Example | Cars for cars between countries. | Textiles for machinery between countries. |
| Trade Pattern | Horizontal or vertical differentiation of similar goods. | Comparative advantage-based specialization. |
| Economic Drivers | Economies of scale, product differentiation, consumer preferences. | Factor endowments, resource allocation, cost differences. |
| Impact | Improves variety, promotes competition, fosters innovation. | Encourages specialization and efficient resource use. |
| Trade Measurement | Measured by Grubel-Lloyd index. | Identified via sectoral trade flows and factor intensities. |
Introduction to Intra-Industry and Inter-Industry Trade
Intra-industry trade involves the exchange of similar products within the same industry between countries, emphasizing economies of scale and product differentiation. Inter-industry trade, by contrast, occurs when countries export and import entirely different goods based on comparative advantage, such as machinery for agricultural products. Understanding these trade patterns is essential for analyzing global market dynamics and the benefits of specialization and diversification in international trade.
Defining Intra-Industry Trade
Intra-industry trade refers to the exchange of similar products belonging to the same industry between countries, such as the import and export of different car models or electronics. This type of trade highlights product differentiation and economies of scale within industries, allowing countries to specialize in specific varieties or qualities of goods. Unlike inter-industry trade, which involves trading distinctly different products between sectors, intra-industry trade reflects more complex patterns driven by consumer preferences and production efficiencies.
Defining Inter-Industry Trade
Inter-industry trade involves the exchange of goods and services between different industries, such as machinery for textiles, reflecting differences in factor endowments and comparative advantage. It typically occurs between countries with distinct economic structures, where one specializes in manufacturing while the other focuses on agriculture or raw materials. This form of trade contrasts with intra-industry trade, which entails the exchange of similar products within the same industry.
Key Differences Between Intra-Industry and Inter-Industry Trade
Intra-industry trade involves the exchange of similar products within the same industry, typically between countries with comparable economic structures and consumer preferences, driven by product differentiation and economies of scale. Inter-industry trade occurs between countries specializing in different industries based on comparative advantage, where one country exports goods from one sector while importing from another sector. The key differences lie in the type of goods exchanged, the economic structure of trading partners, and the underlying reasons for trade, with intra-industry trade emphasizing specialization within an industry and inter-industry trade reflecting sectoral specialization across industries.
Factors Influencing Intra-Industry Trade
Intra-industry trade is significantly influenced by factors such as product differentiation, economies of scale, and consumer preferences for variety, which encourage the exchange of similar but differentiated goods within the same industry. Technological advancements and reduced transportation costs further enhance the feasibility and volume of intra-industry trade. In contrast, inter-industry trade is primarily driven by comparative advantage and differences in factor endowments between countries, leading to the exchange of distinctly different products from separate industries.
Determinants of Inter-Industry Trade
Determinants of inter-industry trade primarily include differences in factor endowments, technology, and production costs between countries, driving the exchange of distinct goods from separate industries. Variations in resource availability, such as capital and labor intensity, result in nations specializing in industries where they hold comparative advantages, fostering trade of differentiated products. Trade policies, market structures, and tariff barriers further influence the scale and patterns of inter-industry trade by affecting the cost and accessibility of foreign goods.
Economic Benefits of Intra-Industry Trade
Intra-industry trade enhances economic efficiency by allowing countries to specialize in different varieties of similar products, leading to increased economies of scale and product differentiation. It reduces adjustment costs associated with changing industries, thereby promoting stable employment and smoother economic transitions compared to inter-industry trade. This type of trade also fosters innovation and competitive markets, generating greater consumer choice and higher overall welfare.
Advantages of Inter-Industry Trade
Inter-industry trade allows countries to capitalize on their comparative advantage by specializing in industries where they have efficiency, leading to increased overall productivity and economic growth. This type of trade fosters diversification of the economy by enabling access to goods and services not produced domestically, enhancing consumer choice and competitive markets. Furthermore, inter-industry trade often leads to improved resource allocation worldwide and strengthens global economic integration by linking distinct industries across nations.
Examples of Intra-Industry and Inter-Industry Trade
Intra-industry trade occurs when countries simultaneously import and export similar types of goods, such as Germany trading cars with France, where both nations exchange different car models or brands. Inter-industry trade involves the exchange of completely different products, exemplified by the United States exporting agricultural products like corn to China while importing electronics like smartphones in return. These trade patterns highlight the complexity of global commerce, with intra-industry trade often seen in sectors with differentiated products and inter-industry trade linked to comparative advantage in distinct industries.
Policy Implications and Future Trends
Intra-industry trade, characterized by the exchange of similar products within the same industry, necessitates policies that emphasize innovation, product differentiation, and reducing trade barriers to enhance specialization and competitiveness. In contrast, inter-industry trade, involving trade between distinct sectors, requires policies that support resource reallocation, sectoral adjustment, and labor mobility to manage structural changes in the economy. Future trends indicate a rise in intra-industry trade due to technological advancements and globalization, urging policymakers to focus on intellectual property rights, digital trade frameworks, and supply chain integration.
Intra-industry trade Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com