Monetary policy shapes the economy by controlling money supply and interest rates, influencing inflation, employment, and economic growth. Central banks implement these strategies to stabilize prices and encourage sustainable development. Discover how monetary policy impacts your financial future by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
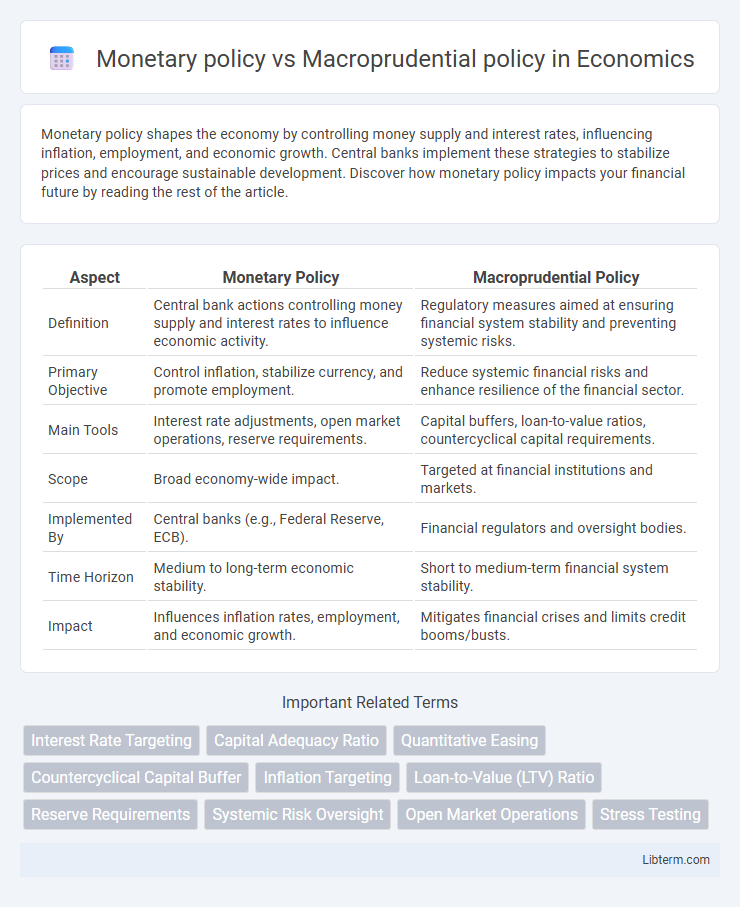
| Aspect | Monetary Policy | Macroprudential Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank actions controlling money supply and interest rates to influence economic activity. | Regulatory measures aimed at ensuring financial system stability and preventing systemic risks. |
| Primary Objective | Control inflation, stabilize currency, and promote employment. | Reduce systemic financial risks and enhance resilience of the financial sector. |
| Main Tools | Interest rate adjustments, open market operations, reserve requirements. | Capital buffers, loan-to-value ratios, countercyclical capital requirements. |
| Scope | Broad economy-wide impact. | Targeted at financial institutions and markets. |
| Implemented By | Central banks (e.g., Federal Reserve, ECB). | Financial regulators and oversight bodies. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long-term economic stability. | Short to medium-term financial system stability. |
| Impact | Influences inflation rates, employment, and economic growth. | Mitigates financial crises and limits credit booms/busts. |
Introduction to Monetary and Macroprudential Policies
Monetary policy involves managing interest rates and money supply to achieve macroeconomic stability, primarily targeting inflation control and economic growth. Macroprudential policy focuses on safeguarding the financial system by addressing systemic risks and preventing financial crises through regulatory measures and capital requirements. Both policies play crucial roles, with monetary policy influencing overall economic conditions and macroprudential policy ensuring financial sector resilience.
Defining Monetary Policy: Goals and Tools
Monetary policy primarily aims to control inflation, stabilize currency, and achieve full employment through tools like interest rate adjustments, open market operations, and reserve requirements. Central banks use these instruments to influence money supply and credit conditions in the economy. Defining monetary policy involves understanding its goal to balance economic growth with price stability and its mechanism to steer macroeconomic variables.
Understanding Macroprudential Policy: Scope and Instrumentation
Macroprudential policy targets the stability of the financial system by mitigating systemic risks such as credit booms, asset bubbles, and interconnectedness among financial institutions. Its scope includes monitoring banks, markets, and infrastructure to prevent widespread disruptions, employing instruments like countercyclical capital buffers, loan-to-value (LTV) limits, and stress testing frameworks. Unlike monetary policy, which primarily manages inflation and economic growth through interest rates and money supply, macroprudential policy focuses on safeguarding financial resilience and minimizing the likelihood of financial crises.
Key Differences Between Monetary and Macroprudential Policies
Monetary policy primarily targets inflation control and economic growth by adjusting interest rates and controlling money supply, while macroprudential policy focuses on financial system stability by mitigating systemic risks such as excessive credit growth and asset bubbles. Monetary policy decisions affect aggregate demand and inflation, whereas macroprudential policy implements tools like countercyclical capital buffers and loan-to-value ratios to reduce vulnerabilities in the banking sector. The key difference lies in their objectives: monetary policy manages the overall economy, and macroprudential policy safeguards the resilience of the financial system against shocks.
Interactions and Overlaps: How the Policies Influence Each Other
Monetary policy, which primarily targets inflation and economic growth through interest rates and money supply adjustments, influences macroprudential policy by affecting credit conditions and financial stability risks. Macroprudential policies, designed to mitigate systemic financial risks via tools like countercyclical capital buffers and loan-to-value limits, can impact the transmission and effectiveness of monetary policy by altering banks' risk-taking behavior and lending standards. The interaction between these policies creates overlaps where central banks must coordinate to balance objectives, ensuring that efforts to stabilize prices do not unintentionally amplify financial vulnerabilities, and vice versa.
Policy Frameworks: Implementation Strategies
Monetary policy frameworks primarily rely on adjusting interest rates and controlling money supply through central banks to influence inflation and economic growth, while macroprudential policy frameworks focus on regulatory measures aimed at ensuring financial system stability by addressing systemic risks and vulnerabilities. Implementation strategies for monetary policy often involve inflation targeting and open market operations, whereas macroprudential policies employ tools such as countercyclical capital buffers, loan-to-value ratios, and stress testing to mitigate risks in banking and credit markets. Coordination between these frameworks enhances overall economic resilience by balancing growth objectives with the prevention of financial crises.
Effectiveness in Achieving Financial Stability
Monetary policy primarily targets inflation control and economic growth through interest rate adjustments, indirectly influencing financial stability by affecting credit conditions and asset prices. Macroprudential policy directly addresses systemic risks by implementing regulations such as capital buffers and loan-to-value limits, enhancing the resilience of the financial system against shocks. Combining these policies improves overall financial stability by balancing broad economic objectives with targeted risk mitigation, as evidenced by the effectiveness of integrated frameworks in post-2008 crisis regulatory reforms.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Policy
Monetary policy faces challenges such as time lags between implementation and economic impact, limited effectiveness during liquidity traps, and potential conflicts between inflation targeting and economic growth objectives. Macroprudential policy struggles with identifying systemic risks accurately, the difficulty of coordinating multiple regulatory bodies, and the risk of regulatory arbitrage where financial institutions exploit loopholes. Both policies have limitations in predicting and preventing financial crises due to the complex, interconnected nature of global financial systems.
Case Studies: Global Approaches and Outcomes
Monetary policy primarily targets inflation control and economic growth through interest rate adjustments, exemplified by the Federal Reserve's response during the 2008 financial crisis to stabilize markets. Macroprudential policy focuses on financial system stability by addressing systemic risks, as seen in the Bank of England's implementation of countercyclical capital buffers post-2010 to strengthen bank resilience. Countries like South Korea successfully combined both approaches by tightening loan-to-value ratios while maintaining accommodative monetary policy during the COVID-19 pandemic, preventing asset bubbles without hindering economic recovery.
Future Trends in Monetary and Macroprudential Regulation
Future trends in monetary and macroprudential regulation emphasize enhanced integration of data analytics and real-time monitoring to improve responsiveness to financial instability and economic fluctuations. Central banks and regulatory authorities increasingly adopt advanced AI-driven tools for predictive analysis, enabling more precise calibration of interest rates and capital requirements. Collaboration between monetary and macroprudential policy frameworks aims to balance economic growth with systemic risk reduction, fostering resilient financial systems in an era of rapid technological change.
Monetary policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com