Quantitative easing is a monetary policy used by central banks to stimulate the economy by increasing money supply and lowering interest rates through large-scale asset purchases. This approach helps boost lending and investment when traditional policy tools have limited impact. Explore the rest of the article to understand how quantitative easing can affect your financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
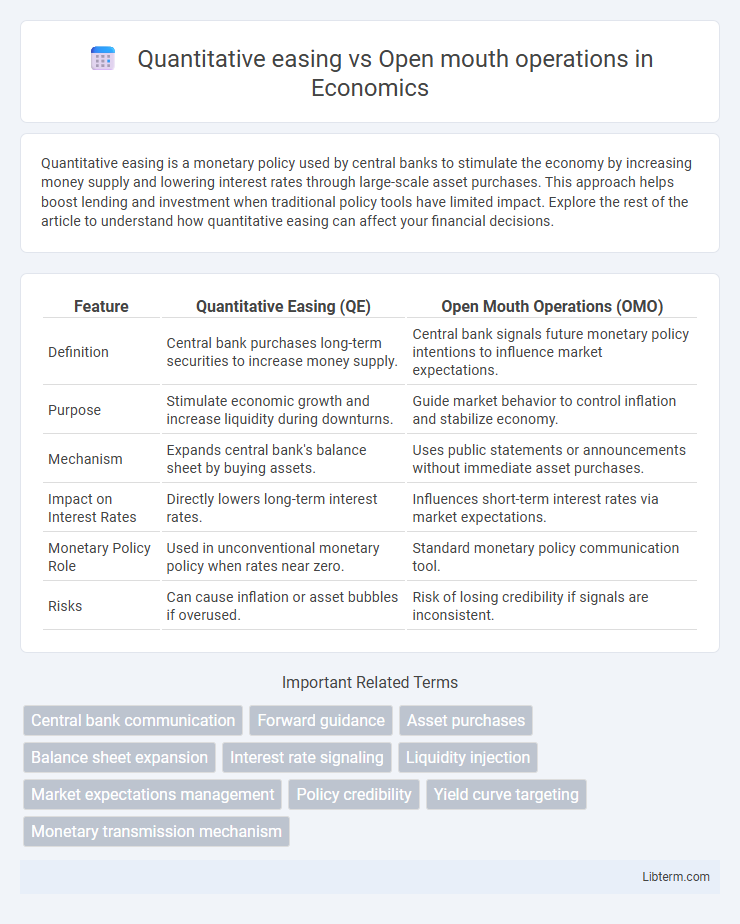
| Feature | Quantitative Easing (QE) | Open Mouth Operations (OMO) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Central bank purchases long-term securities to increase money supply. | Central bank signals future monetary policy intentions to influence market expectations. |
| Purpose | Stimulate economic growth and increase liquidity during downturns. | Guide market behavior to control inflation and stabilize economy. |
| Mechanism | Expands central bank's balance sheet by buying assets. | Uses public statements or announcements without immediate asset purchases. |
| Impact on Interest Rates | Directly lowers long-term interest rates. | Influences short-term interest rates via market expectations. |
| Monetary Policy Role | Used in unconventional monetary policy when rates near zero. | Standard monetary policy communication tool. |
| Risks | Can cause inflation or asset bubbles if overused. | Risk of losing credibility if signals are inconsistent. |
Introduction to Quantitative Easing and Open Mouth Operations
Quantitative easing (QE) involves large-scale asset purchases by central banks to inject liquidity and stimulate economic activity during periods of low interest rates. Open mouth operations refer to deliberate public communication strategies by central banks to influence market expectations and interest rates without immediate asset transactions. Both tools aim to manage monetary policy but differ in direct market intervention versus expectation management.
Defining Quantitative Easing
Quantitative easing (QE) is a monetary policy tool used by central banks to increase money supply by purchasing long-term securities, aiming to lower interest rates and stimulate economic activity during periods of low inflation or recession. Open mouth operations (OMO) differ as they primarily involve verbal communications or forward guidance to influence market expectations without immediate asset purchases. QE directly injects liquidity into the financial system, while OMO relies on signaling effects to shape investor behavior.
Understanding Open Mouth Operations
Open Mouth Operations are a form of central bank communication where policymakers signal future monetary policy intentions without immediate market intervention, influencing expectations and financial markets proactively. Unlike Quantitative Easing, which involves direct asset purchases to inject liquidity into the economy, Open Mouth Operations rely on credible verbal guidance to affect interest rates and inflation expectations. Effective Open Mouth Operations can shape market behavior quickly and costlessly by managing investor anticipation and confidence in the central bank's policy direction.
Key Objectives and Mechanisms
Quantitative easing (QE) primarily aims to stimulate economic growth by increasing money supply through large-scale asset purchases, lowering long-term interest rates and encouraging investment. Open mouth operations (OMO) focus on influencing expectations and signaling future monetary policy direction without immediate market transactions, thus shaping market behavior via communication. Both tools seek to manage liquidity and control inflation but operate through distinct mechanisms--QE through direct bond purchases and OMO through strategic central bank announcements.
Historical Context and Notable Examples
Quantitative easing (QE) emerged prominently after the 2008 global financial crisis as a large-scale asset purchase program to inject liquidity into the economy, with the Federal Reserve buying over $1.7 trillion in mortgage-backed securities and Treasury bonds between 2008 and 2014. Open mouth operations, a term coined by former Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke, involve verbal interventions to influence market expectations and credit conditions without direct asset purchases, exemplified by Bernanke's 2002 statement warning of the Fed's readiness to provide liquidity during a potential market crisis. The Bank of Japan's QE measures in the early 2000s and the Fed's forward guidance during the COVID-19 pandemic provide notable examples of these strategies deployed under differing economic conditions.
Comparative Effectiveness on Financial Markets
Quantitative easing (QE) involves large-scale asset purchases by central banks, directly increasing liquidity and lowering long-term interest rates, which typically leads to more pronounced impacts on financial markets, including higher asset prices and improved market confidence. Open mouth operations rely on central bank communication to influence market expectations and short-term interest rates without immediate changes in the balance sheet, often yielding subtler and more transient effects. Empirical studies indicate that QE tends to produce stronger and more sustained responses in bond yields and equity markets compared to open mouth operations, especially during periods of economic distress or near-zero interest rates.
Impact on Inflation and Economic Growth
Quantitative easing (QE) increases money supply by purchasing long-term securities, directly stimulating economic growth but potentially raising inflation if overused. Open mouth operations influence market expectations by signaling future monetary policy changes without immediate asset purchases, helping to stabilize inflation and moderate economic growth. Both tools affect inflation and growth, with QE having a more direct and sizable impact, while open mouth operations rely on communication to shape market behavior.
Communication Strategies in Monetary Policy
Quantitative easing involves central banks purchasing long-term securities to inject liquidity directly into the economy, while open mouth operations use verbal communication to influence market expectations without immediate asset purchases. Effective communication strategies in monetary policy are crucial for managing investor confidence and guiding economic forecasts, with open mouth operations often serving as a cost-effective tool to signal future policy intentions. Central banks optimize transparency and forward guidance to enhance the credibility and impact of both quantitative easing and open mouth operations in stabilizing financial markets.
Risks and Limitations of Each Approach
Quantitative easing (QE) carries risks such as asset bubbles, inflationary pressures, and diminished central bank balance sheet flexibility, potentially leading to market distortions and wealth inequality. Open mouth operations rely heavily on market expectations and communication credibility, with limitations including uncertainty in achieving desired outcomes and vulnerability to misinterpretation or loss of central bank trust. Both approaches face constraints in effectiveness during prolonged low-interest environments and may contribute to financial instability if mismanaged.
Quantitative Easing vs Open Mouth Operations: Future Prospects
Quantitative easing (QE) involves large-scale asset purchases by central banks to inject liquidity and stimulate economic growth, whereas open mouth operations rely on verbal guidance to influence market expectations and interest rates. Future prospects suggest QE may face limitations due to rising inflation concerns and balance sheet constraints, while open mouth operations could gain importance as a cost-effective, flexible tool for managing market sentiment in uncertain economic environments. The evolving economic landscape demands a balanced approach combining tangible asset purchases with strategic communication to optimize monetary policy effectiveness.
Quantitative easing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com