Regulatory harmonization streamlines compliance processes by aligning standards across different jurisdictions, reducing complexity and costs for businesses operating internationally. This approach enhances market access and fosters innovation by creating a more predictable regulatory environment. Discover how regulatory harmonization can impact Your global operations and benefit your strategic planning in the full article.
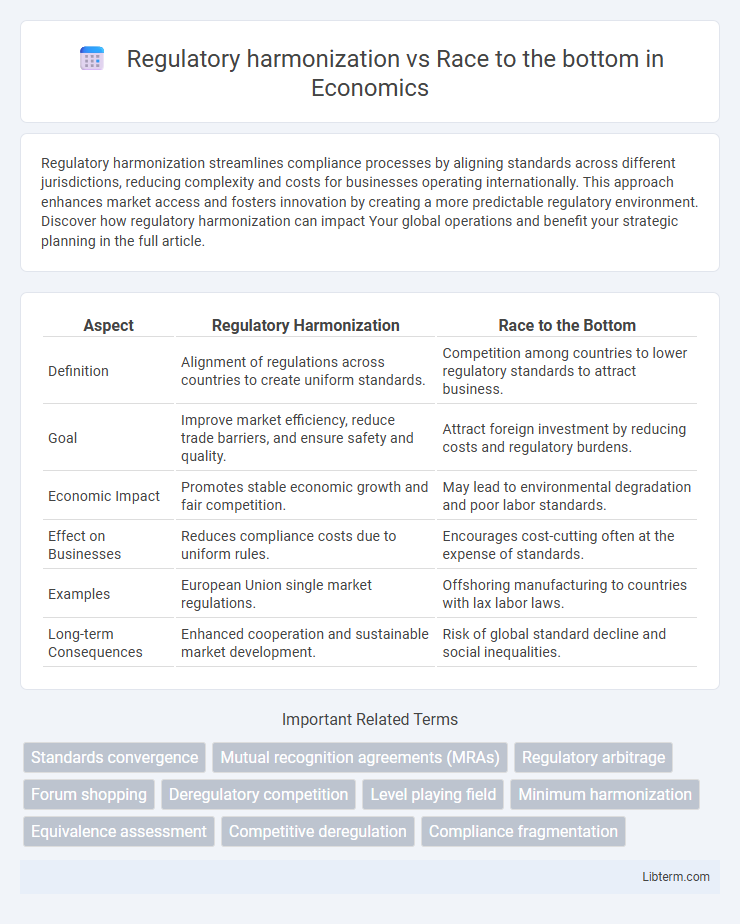
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Regulatory Harmonization | Race to the Bottom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Alignment of regulations across countries to create uniform standards. | Competition among countries to lower regulatory standards to attract business. |
| Goal | Improve market efficiency, reduce trade barriers, and ensure safety and quality. | Attract foreign investment by reducing costs and regulatory burdens. |
| Economic Impact | Promotes stable economic growth and fair competition. | May lead to environmental degradation and poor labor standards. |
| Effect on Businesses | Reduces compliance costs due to uniform rules. | Encourages cost-cutting often at the expense of standards. |
| Examples | European Union single market regulations. | Offshoring manufacturing to countries with lax labor laws. |
| Long-term Consequences | Enhanced cooperation and sustainable market development. | Risk of global standard decline and social inequalities. |
Defining Regulatory Harmonization
Regulatory harmonization involves aligning policies, standards, and regulations across jurisdictions to facilitate trade, ensure product safety, and promote economic integration without compromising quality. This process reduces compliance costs for businesses by creating consistent legal frameworks while maintaining robust protections for consumers and the environment. Contrarily, the race to the bottom describes competitive deregulation where countries lower standards to attract investment, potentially undermining public welfare and regulatory effectiveness.
Understanding the “Race to the Bottom”
The "Race to the Bottom" describes a competitive scenario where countries or jurisdictions lower regulatory standards, especially in labor, environmental, and corporate governance, to attract business investments at the expense of public welfare. This dynamic undermines regulatory harmonization efforts, which aim to establish consistent and high-quality standards across borders to prevent exploitation and maintain fair competition. Understanding this phenomenon is crucial for policymakers to design frameworks that balance economic growth with social and environmental protections, mitigating the risks of downward regulatory spirals.
Key Drivers of Regulatory Convergence
Regulatory harmonization is driven by key factors such as globalization, economic integration, and the need for reducing trade barriers, promoting standardized compliance frameworks across jurisdictions. In contrast, the race to the bottom arises when countries compete by lowering regulatory standards to attract investment, leading to potential regulatory erosion. Key drivers of regulatory convergence include international agreements, multinational corporations' demand for consistent regulations, and technological advancements facilitating cross-border cooperation.
Risks and Consequences of Deregulatory Competition
Regulatory harmonization aims to establish consistent standards across jurisdictions, reducing the risk of a race to the bottom where countries compete by lowering regulations to attract businesses. Deregulatory competition often leads to weakened environmental protections, compromised labor rights, and increased financial instability. Persistent under-regulation may result in market failures, eroded public trust, and long-term socioeconomic damage.
Impact on Environmental Standards
Regulatory harmonization promotes consistent environmental standards across countries, reducing pollution and encouraging sustainable practices by establishing unified regulations and enforcement. In contrast, the race to the bottom undermines environmental protection as governments lower standards to attract investment, leading to increased pollution and resource depletion. Harmonized regulations facilitate global cooperation on climate goals, while competitive deregulation compromises ecological integrity and long-term sustainability.
Global Trade and Cross-Border Regulations
Regulatory harmonization facilitates smoother global trade by aligning standards and reducing compliance costs for cross-border transactions, enhancing economic integration among participating countries. In contrast, the race to the bottom occurs when nations competitively lower regulatory standards to attract foreign investment, potentially undermining consumer protection, labor rights, and environmental sustainability. Effective cross-border regulations balance the benefits of harmonization with safeguards against regulatory dilution, promoting fair competition and sustainable global trade practices.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Regulatory harmonization enhances market efficiency by aligning standards across countries, as seen in the European Union's success with unified product safety regulations that boost trade and consumer trust. Conversely, the race to the bottom often results in weakened labor or environmental standards to attract business, exemplified by textile manufacturing shifts to developing countries with lax regulations, which have faced criticism for exploiting workers and degrading the environment. Case studies reveal that balanced regulatory frameworks combining international cooperation and enforcement mechanisms are crucial to prevent negative outcomes while promoting sustainable economic growth.
Policy Approaches for Balanced Regulation
Regulatory harmonization aims to create consistent standards across jurisdictions to facilitate trade and ensure consumer protection without compromising safety or quality. Race to the bottom occurs when jurisdictions lower regulatory standards to attract business, risking environmental, labor, or safety protections. Balanced regulation requires policies that incentivize collaboration on minimum standards while maintaining flexibility for local innovation and enforcement.
Stakeholder Perspectives and Interests
Regulatory harmonization aims to align standards across jurisdictions, ensuring consistent compliance and reducing costs for multinational corporations while protecting consumer safety and environmental quality. Stakeholders such as governments and industry groups advocate for harmonization to create a level playing field and facilitate trade, whereas labor unions and environmental organizations often express concerns about weakened regulations. In contrast, the race to the bottom involves jurisdictions lowering standards to attract business investment, benefiting industries seeking lower costs but risking negative impacts on workers and the environment, generating significant opposition from advocacy groups focused on social and ecological justice.
Future Outlook: Achieving Sustainable Regulatory Alignment
Future outlook for regulatory harmonization emphasizes achieving sustainable alignment through collaborative frameworks that balance economic growth with social and environmental protections. Advancements in digital technologies and data sharing enable more transparent and adaptive regulatory systems, minimizing the risk of a race to the bottom where countries might weaken standards to attract investment. Sustainable regulatory alignment promotes global trade efficiency while safeguarding public interests by integrating best practices and consistent enforcement mechanisms across jurisdictions.
Regulatory harmonization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com