Spot price represents the current market value at which a commodity or asset can be bought or sold for immediate delivery, reflecting real-time supply and demand. It is essential for investors and traders to understand spot prices to make informed decisions in volatile markets. Explore the rest of the article to discover how spot prices impact your trading strategy and financial planning.
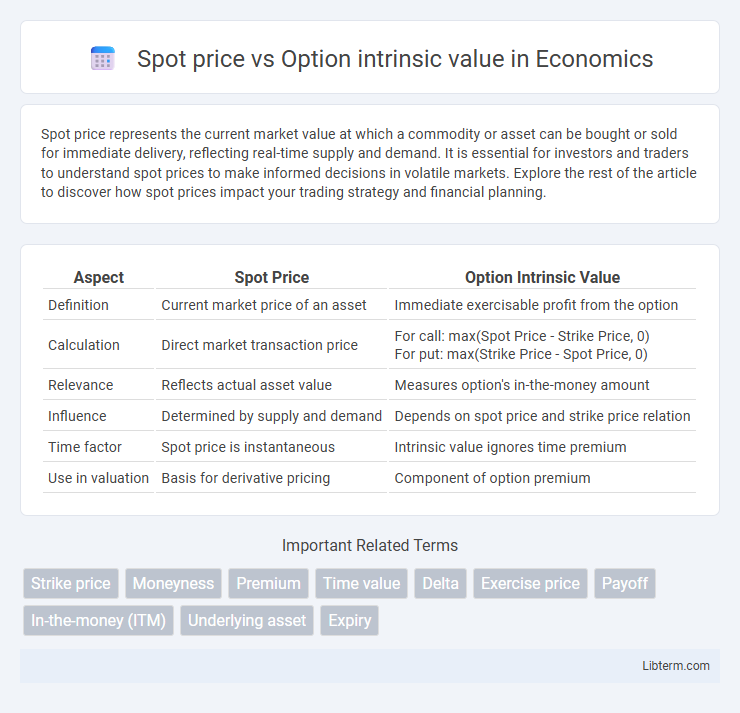
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Spot Price | Option Intrinsic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Current market price of an asset | Immediate exercisable profit from the option |
| Calculation | Direct market transaction price |
For call: max(Spot Price - Strike Price, 0) For put: max(Strike Price - Spot Price, 0) |
| Relevance | Reflects actual asset value | Measures option's in-the-money amount |
| Influence | Determined by supply and demand | Depends on spot price and strike price relation |
| Time factor | Spot price is instantaneous | Intrinsic value ignores time premium |
| Use in valuation | Basis for derivative pricing | Component of option premium |
Introduction to Spot Price and Option Intrinsic Value
Spot price represents the current market value at which an asset can be bought or sold for immediate delivery, reflecting real-time supply and demand dynamics. Option intrinsic value is the difference between the underlying asset's spot price and the option's strike price, indicating the immediate exercise profit potential of a call or put option. Understanding the interplay between spot price and option intrinsic value is crucial for evaluating option profitability and trading strategies.
Understanding Spot Price in Financial Markets
Spot price represents the current market value at which an asset can be bought or sold for immediate delivery, reflecting real-time supply and demand dynamics. It serves as a crucial reference point for determining the intrinsic value of options, which is calculated as the difference between the option's strike price and the spot price. Understanding spot price fluctuations is essential for traders to accurately assess option profitability and make informed investment decisions in financial markets.
Defining Option Intrinsic Value
Option intrinsic value is the immediate profit potential of an option if exercised at the current spot price of the underlying asset. It is calculated as the difference between the spot price and the option's strike price for a call option, or vice versa for a put option, ensuring a non-negative result. This value represents the in-the-money portion of the option, excluding any time value or volatility premium.
Key Differences Between Spot Price and Intrinsic Value
Spot price represents the current market price of an underlying asset, such as a stock or commodity, while intrinsic value refers to the real, tangible value of an option based on the difference between the spot price and the option's strike price. The key difference lies in the fact that spot price is a direct measure of asset value at a specific moment, whereas intrinsic value measures the profitability of exercising the option if it were done immediately. Spot price fluctuates constantly with market conditions, but intrinsic value only increases if the option is in-the-money, reflecting immediate exercise advantage.
How Spot Price Affects Option Pricing
The spot price directly impacts option intrinsic value by determining whether an option is in-the-money, at-the-money, or out-of-the-money, influencing its immediate exercisable worth. When the spot price exceeds the strike price for a call option, or falls below the strike price for a put option, the intrinsic value increases, thereby raising the option's premium. Option pricing models, such as the Black-Scholes model, incorporate the spot price as a critical input, reflecting its essential role in the valuation of both call and put options.
Calculating the Intrinsic Value of Options
The intrinsic value of an option is calculated by comparing the spot price of the underlying asset to the option's strike price. For a call option, intrinsic value equals the spot price minus the strike price when the spot price is higher; for a put option, it equals the strike price minus the spot price when the spot price is lower. If these differences are negative or zero, the intrinsic value is zero, reflecting the minimum value derived from exercising the option immediately.
Factors Influencing Spot Price Fluctuations
Spot price fluctuations are primarily influenced by supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, and macroeconomic indicators such as inflation and interest rates. Market sentiment, weather conditions, and inventory levels also play critical roles in driving short-term price volatility for commodities and securities. These factors directly affect the intrinsic value of options by altering the underlying asset's current market price relative to the strike price.
Impact of Volatility on Option Intrinsic Value
Volatility impacts an option's intrinsic value by influencing the likelihood that the spot price will move beyond the strike price, thus affecting potential profitability. High volatility increases the chances of significant price swings, which can enhance the intrinsic value of call and put options by creating opportunities for in-the-money positions. Traders often assess implied volatility alongside spot price movements to gauge option attractiveness and intrinsic value changes.
Practical Applications in Trading Strategies
Spot price directly influences the intrinsic value of options by determining whether an option is in-the-money, at-the-money, or out-of-the-money, guiding traders in making immediate exercise decisions. In trading strategies, the intrinsic value helps assess potential profitability while the spot price aids in forecasting short-term market movements to optimize entry and exit points. Understanding the relationship between spot price and intrinsic value enables traders to structure hedging, speculative, and arbitrage strategies effectively, minimizing risk and maximizing returns.
Conclusion: Maximizing Profits Using Spot Price and Intrinsic Value
Maximizing profits involves understanding the relationship between the spot price and the option's intrinsic value, which represents the immediate exercise gain. Profitable option strategies leverage intrinsic value by executing options when the spot price significantly exceeds the strike price, ensuring immediate value capture. Monitoring both metrics enables investors to time option exercises and trades effectively, enhancing overall portfolio returns.
Spot price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com