Exchange rates determine the value of one currency relative to another, influencing global trade, travel, and investment decisions. Fluctuations in exchange rates can impact the cost of imports and exports, affecting your purchasing power and business profitability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how exchange rates work and how they affect your financial choices.
Table of Comparison
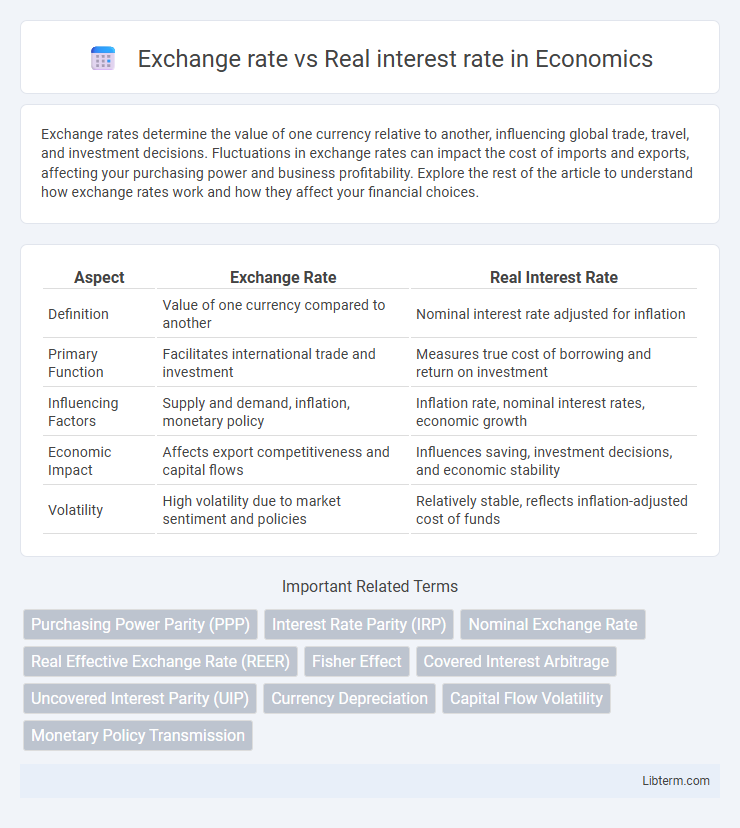
| Aspect | Exchange Rate | Real Interest Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Value of one currency compared to another | Nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation |
| Primary Function | Facilitates international trade and investment | Measures true cost of borrowing and return on investment |
| Influencing Factors | Supply and demand, inflation, monetary policy | Inflation rate, nominal interest rates, economic growth |
| Economic Impact | Affects export competitiveness and capital flows | Influences saving, investment decisions, and economic stability |
| Volatility | High volatility due to market sentiment and policies | Relatively stable, reflects inflation-adjusted cost of funds |
Introduction to Exchange Rate and Real Interest Rate
Exchange rate represents the value of one currency compared to another, influencing international trade and investment decisions. Real interest rate adjusts nominal interest rates by inflation, reflecting the true cost of borrowing and the real yield on investments. Understanding both metrics is essential for analyzing economic performance and making informed financial decisions in global markets.
Definition and Key Concepts
The exchange rate represents the value of one currency relative to another, influencing international trade and capital flows. The real interest rate adjusts the nominal interest rate by accounting for inflation, reflecting the true cost of borrowing and the real yield on investments. Understanding the relationship between exchange rates and real interest rates is crucial for assessing currency valuation and economic stability.
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates
Exchange rates are influenced by real interest rates, which reflect the inflation-adjusted return on investments in a country. Higher real interest rates attract foreign capital, increasing demand for the domestic currency and causing appreciation. Other factors such as inflation expectations, political stability, and central bank policies also play crucial roles in determining exchange rate movements.
Determinants of Real Interest Rates
Real interest rates are primarily determined by factors such as inflation expectations, central bank monetary policy, and economic growth prospects. Exchange rates influence real interest rates through their impact on import prices and inflation, affecting the purchasing power and investment returns of lenders and borrowers. Market demand for domestic versus foreign assets also plays a critical role in shaping real interest rates by altering capital flows and currency valuation.
Theoretical Relationship Between Exchange Rate and Real Interest Rate
The theoretical relationship between exchange rate and real interest rate is grounded in the interest rate parity and purchasing power parity theories, which suggest that higher real interest rates attract foreign capital, leading to currency appreciation. Real interest rates, adjusted for inflation, directly influence investment returns, making currencies with higher real interest rates more attractive to investors and impacting exchange rate movements. Consequently, changes in real interest rates signal shifts in expected returns, driving exchange rate fluctuations through international capital flows.
Impact of Real Interest Rate Changes on Exchange Rates
Changes in real interest rates directly influence exchange rates by affecting capital flows and investment attractiveness; higher real interest rates tend to attract foreign capital, leading to currency appreciation. Conversely, lower real interest rates decrease the return on investments denominated in that currency, causing depreciation. Empirical data confirms that real interest rate differentials are a primary driver of short- to medium-term exchange rate fluctuations.
Case Studies: Historical Interactions
Historical interactions between exchange rates and real interest rates illustrate how currency valuation shifts respond to changes in domestic and foreign inflation-adjusted returns. Case studies from the 1990s Japanese yen and the post-2008 US dollar reveal that higher real interest rates tend to attract foreign capital, leading to currency appreciation. Conversely, episodes like the 1997 Asian financial crisis demonstrate how real interest rate hikes can exacerbate currency depreciations amidst capital flight and market uncertainty.
Implications for International Trade and Investment
Exchange rates directly influence the competitiveness of a country's exports and imports by affecting relative prices, while real interest rates impact foreign investment flows by determining the return on capital after inflation adjustments. A higher real interest rate tends to attract foreign capital, strengthening the domestic currency and potentially making exports more expensive, which can reduce trade balances. Conversely, lower real interest rates may weaken the currency, enhancing export competitiveness but potentially discouraging investment inflows, highlighting a critical balance for policymakers in managing international trade and investment dynamics.
Policy Considerations and Central Bank Roles
Central banks influence exchange rates through monetary policy adjustments that affect real interest rates, thereby impacting capital flows and currency value stability. Policy considerations emphasize maintaining a balance between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth while ensuring exchange rate competitiveness to avoid excessive volatility. Effective management of real interest rates helps central banks anchor expectations, stabilize exchange rates, and foster investor confidence in the domestic currency.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Future Trends
Exchange rate movements are closely influenced by real interest rate differentials across countries, as higher real interest rates attract foreign capital, leading to currency appreciation. Future trends indicate increasing volatility driven by geopolitical risks, central bank policies, and inflation dynamics, which will continue to shape the interplay between exchange rates and real interest rates. Investors and policymakers must monitor these factors to navigate currency fluctuations and optimize investment strategies effectively.
Exchange rate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com