Normal profit represents the minimum earnings a business needs to cover all its opportunity costs, ensuring it remains viable without generating economic profit. It reflects the break-even point where total revenue equals total costs, including both explicit and implicit expenses. Explore the rest of the article to understand how normal profit influences business decisions and economic sustainability.
Table of Comparison
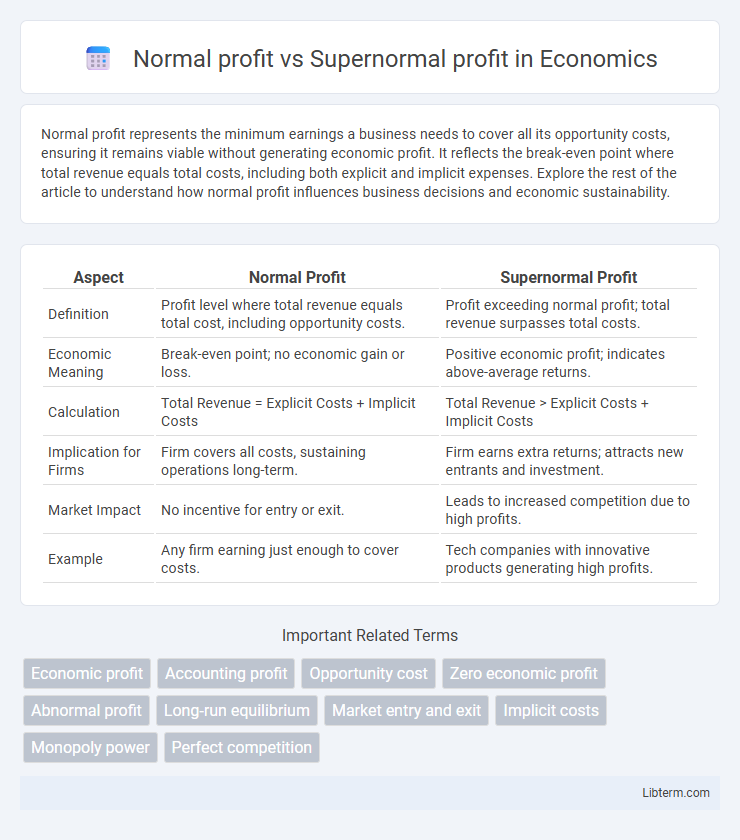
| Aspect | Normal Profit | Supernormal Profit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profit level where total revenue equals total cost, including opportunity costs. | Profit exceeding normal profit; total revenue surpasses total costs. |
| Economic Meaning | Break-even point; no economic gain or loss. | Positive economic profit; indicates above-average returns. |
| Calculation | Total Revenue = Explicit Costs + Implicit Costs | Total Revenue > Explicit Costs + Implicit Costs |
| Implication for Firms | Firm covers all costs, sustaining operations long-term. | Firm earns extra returns; attracts new entrants and investment. |
| Market Impact | No incentive for entry or exit. | Leads to increased competition due to high profits. |
| Example | Any firm earning just enough to cover costs. | Tech companies with innovative products generating high profits. |
Understanding Profit: Definition and Types
Normal profit represents the minimum earnings necessary to keep a firm operating in the long run, covering all explicit and implicit costs, including opportunity costs. Supernormal profit, also known as economic profit, occurs when total revenue exceeds both explicit and implicit costs, leading to returns greater than the normal profit level. Understanding the distinction between these profit types is crucial for evaluating business performance and making informed economic decisions.
What is Normal Profit?
Normal profit is the minimum level of profit required for a firm to remain competitive in the market, covering all explicit and implicit costs including opportunity costs. It represents the breakeven point where total revenue equals total costs, ensuring no incentive for firms to exit or enter the industry. Normal profit is essential for sustainable business operations and reflects the opportunity cost of capital and entrepreneurial efforts.
Key Features of Normal Profit
Normal profit occurs when total revenue equals total costs, including both explicit and implicit costs, indicating a break-even point. It represents the minimum level of profit needed for a firm to remain competitive and continue operations in the long run. Unlike supernormal profit, normal profit does not provide excess earnings above opportunity costs but ensures sustainability.
What is Supernormal Profit?
Supernormal profit, also known as economic profit, occurs when a firm's total revenue exceeds both its explicit and implicit costs, including the opportunity costs of all resources employed. It signifies earnings above the normal profit level, which covers only the opportunity costs necessary to keep resources in their current use. Supernormal profit indicates a competitive advantage or market power, often driving new entrants or innovation in the industry.
Key Features of Supernormal Profit
Supernormal profit, also known as economic profit, exceeds the normal profit level and indicates a firm's ability to generate more revenue than the total costs, including opportunity costs. Key features of supernormal profit include its reflection of a competitive advantage, signaling market dominance or innovation that allows a firm to earn above-average returns. This profit surplus typically attracts new entrants, influencing market dynamics until profits normalize.
Major Differences between Normal and Supernormal Profit
Normal profit represents the minimum earnings required for a firm to remain operational, covering all explicit and implicit costs, while supernormal profit exceeds these total costs, indicating higher-than-average returns. Normal profit occurs when total revenue equals total costs, including opportunity costs, whereas supernormal profit results from total revenue surpassing total costs. The key difference lies in normal profit acting as a breakeven point, whereas supernormal profit indicates economic profit beyond sustaining business continuity.
Causes of Supernormal Profit
Supernormal profit arises when a firm's total revenue exceeds both its explicit and implicit costs, including normal profit, typically caused by unique advantages such as technological innovation, brand loyalty, or market power stemming from limited competition. Firms achieving supernormal profit often benefit from economies of scale, access to exclusive resources, or favorable regulatory environments that create barriers to entry for competitors. These factors enable sustained profitability beyond the normal profit level, signaling above-average returns in the market.
Implications of Earning Supernormal Profit
Earning supernormal profit indicates that a firm's total revenue exceeds total costs, including opportunity costs, signaling strong market dominance and competitive advantage. This level of profit attracts new entrants, potentially increasing market competition and driving innovation and efficiency improvements. Persistent supernormal profits may lead to regulatory scrutiny and antitrust actions aimed at maintaining market fairness and consumer protection.
Examples of Normal Profit and Supernormal Profit
Normal profit occurs when a business's total revenue exactly covers both explicit costs, like wages and rent, and implicit costs, such as opportunity costs, exemplified by a local bakery earning just enough to cover ingredients, labor, and the owner's foregone salary. Supernormal profit arises when total revenue exceeds all costs, demonstrated by a tech startup generating significantly higher income due to innovative software products outperforming competitors, leading to extraordinary financial gains. Firms achieving supernormal profits often reinvest to maintain competitive advantage, while businesses at normal profit sustain operations without excess financial surplus.
Conclusion: Why Profit Type Matters in Business
Understanding normal profit versus supernormal profit is crucial for business sustainability and growth strategies. Normal profit represents the minimum earnings required to keep resources in their current use, indicating a break-even point where opportunity costs are covered. Supernormal profit signals market advantage and financial surplus beyond all costs, guiding investment decisions and competitive positioning in dynamic industries.
Normal profit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com