Discount rate policy influences the economy by determining the interest rate central banks charge commercial banks for short-term loans. This rate affects borrowing costs, consumer spending, and overall economic growth. Explore the rest of the article to understand how changes in the discount rate policy impact your financial decisions and market stability.
Table of Comparison
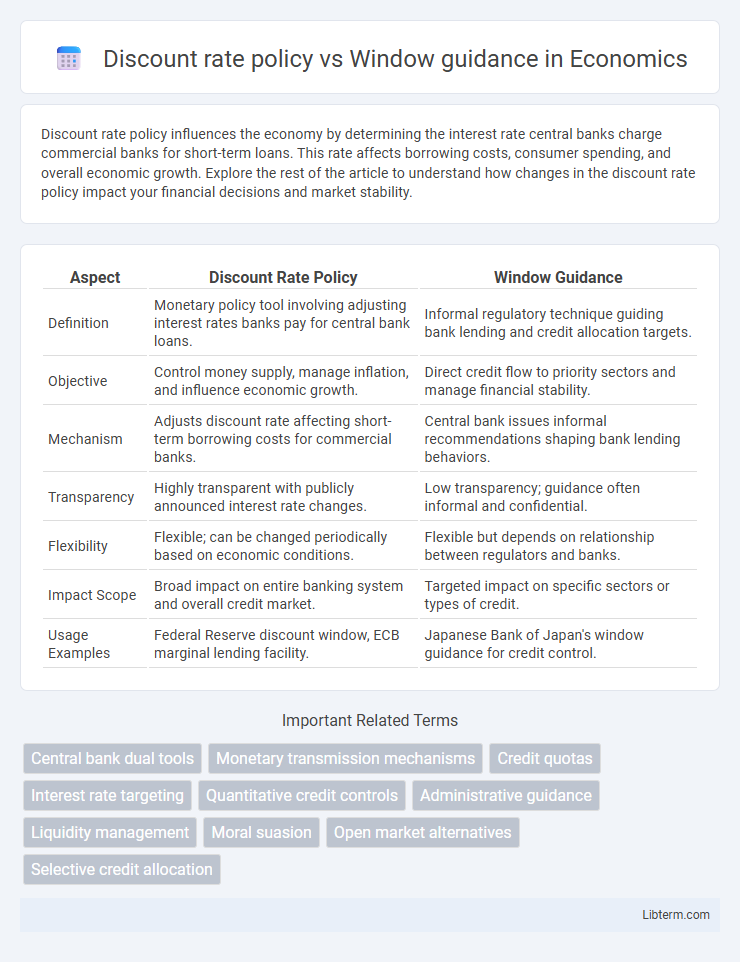
| Aspect | Discount Rate Policy | Window Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary policy tool involving adjusting interest rates banks pay for central bank loans. | Informal regulatory technique guiding bank lending and credit allocation targets. |
| Objective | Control money supply, manage inflation, and influence economic growth. | Direct credit flow to priority sectors and manage financial stability. |
| Mechanism | Adjusts discount rate affecting short-term borrowing costs for commercial banks. | Central bank issues informal recommendations shaping bank lending behaviors. |
| Transparency | Highly transparent with publicly announced interest rate changes. | Low transparency; guidance often informal and confidential. |
| Flexibility | Flexible; can be changed periodically based on economic conditions. | Flexible but depends on relationship between regulators and banks. |
| Impact Scope | Broad impact on entire banking system and overall credit market. | Targeted impact on specific sectors or types of credit. |
| Usage Examples | Federal Reserve discount window, ECB marginal lending facility. | Japanese Bank of Japan's window guidance for credit control. |
Introduction to Discount Rate Policy and Window Guidance
Discount rate policy involves the central bank setting the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow funds, influencing liquidity and overall economic activity. Window guidance refers to a regulatory tool where central banks provide informal directives to financial institutions about credit expansion targets to control lending behavior. Both mechanisms serve to steer monetary policy but differ in transparency and directness of intervention.
Historical Evolution of Monetary Policy Tools
The historical evolution of monetary policy tools reveals that discount rate policy originated as a primary mechanism for central banks to influence liquidity by adjusting the interest rates charged to commercial banks. Over time, window guidance emerged as a more direct, qualitative tool, particularly in East Asian economies, guiding credit allocation through informal directives rather than formal rate adjustments. This shift reflects a transition from price-based interventions to quantity- and guidance-based measures aimed at achieving targeted economic outcomes.
Key Principles of Discount Rate Policy
The discount rate policy centers on setting the interest rate at which central banks lend to commercial banks, influencing liquidity and credit conditions in the economy. It aims to manage inflation and stimulate growth by adjusting borrowing costs, reflecting monetary policy stances such as tightening or easing. Unlike window guidance, which directs credit allocation more discreetly, discount rate policy operates transparently through interest rate signals affecting overall market behavior.
Mechanisms and Application of Window Guidance
Window guidance operates as a non-market tool where central banks directly instruct financial institutions on lending volumes and targets, influencing credit allocation without altering interest rates. Discount rate policy adjusts the cost of borrowing for banks through interest rate changes, affecting liquidity and overall economic activity by making credit more or less expensive. Window guidance emphasizes quantitative credit control and sector-specific lending priorities, commonly applied in economies with strong central bank intervention to manage credit growth and direct funds to strategic industries.
Comparative Analysis: Objectives and Approaches
Discount rate policy primarily aims to influence overall economic activity by adjusting the cost of borrowing for commercial banks, thereby affecting liquidity and inflation. Window guidance involves direct instructions from central banks to financial institutions regarding credit allocation to targeted sectors, emphasizing credit quantity and direction rather than price. While discount rate policy operates through market-driven interest rate mechanisms, window guidance relies on administrative controls to achieve monetary and industrial policy objectives.
Impact on Banking Sector and Credit Allocation
Discount rate policy directly influences the cost of borrowing for banks, affecting their lending rates and overall liquidity, which can tighten or ease credit supply depending on the rate adjustments. Window guidance serves as a regulatory tool used primarily by central banks to steer financial institutions toward preferential credit allocation, often targeting strategic sectors without altering market interest rates. The combined use of these tools shapes banking sector behavior by balancing market-driven lending incentives with directive credit allocation priorities, impacting both the quantity and quality of credit distribution in the economy.
Effectiveness During Economic Cycles
Discount rate policy directly influences borrowing costs and consumer spending by altering central bank interest rates, showing high effectiveness during economic expansions by controlling inflation and stimulating investment. Window guidance, a more direct and qualitative tool used mainly by some Asian central banks, effectively channels credit toward priority sectors during downturns, supporting targeted economic recovery without broad market disruptions. Both policies demonstrate cyclical efficacy: discount rates provide broad monetary stimulus or restraint, while window guidance ensures strategic credit allocation aligned with economic cycle needs.
Case Studies: Global Applications and Outcomes
Discount rate policy and window guidance are pivotal tools for central banks in steering monetary conditions and credit allocation. Case studies from Japan illustrate how window guidance effectively directed bank lending during the post-bubble period, preventing excessive risk-taking, while U.S. reliance on discount rate adjustments influenced short-term interest rates to manage economic cycles. China's use of window guidance alongside selective discount rate cuts has balanced growth incentives with financial stability, showcasing the nuanced outcomes of combining these policies globally.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Policy
The discount rate policy, which adjusts the interest rate at which central banks lend to commercial banks, faces limitations such as delayed transmission to the broader economy and potential market misinterpretation causing unintended liquidity shocks. Window guidance, a form of informal credit control directing banks' lending behaviors, encounters challenges including lack of transparency, reliance on regulatory discretion, and difficulties in measuring its effectiveness across diverse financial institutions. Both tools present hurdles in balancing monetary control with market stability, often requiring complementary measures for precise economic targeting.
Future Trends in Monetary Policy Frameworks
Discount rate policy remains a crucial tool for central banks to influence short-term interest rates and signal monetary stance, while window guidance provides qualitative directives to banks, shaping credit allocation and financial stability. Future trends in monetary policy frameworks emphasize integrating these tools with advanced digital currencies and real-time data analytics to enhance precision and responsiveness. Central banks are increasingly adopting hybrid approaches that combine traditional discount rate adjustments with nuanced window guidance to balance inflation control and economic growth sustainably.
Discount rate policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com