The dedendum circle is a crucial feature in gear design representing the imaginary circle that defines the bottom of the tooth spaces, ensuring proper tooth clearance and avoiding interference during gear operation. It lies below the pitch circle and plays a vital role in determining the gear's tooth depth and overall efficiency. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the dedendum circle impacts gear performance and design precision.
Table of Comparison
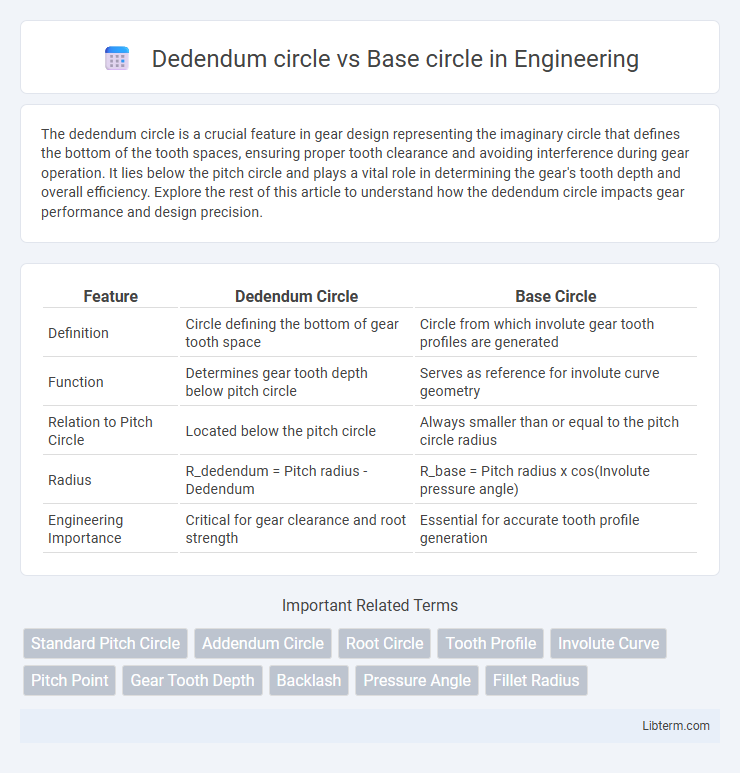
| Feature | Dedendum Circle | Base Circle |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Circle defining the bottom of gear tooth space | Circle from which involute gear tooth profiles are generated |
| Function | Determines gear tooth depth below pitch circle | Serves as reference for involute curve geometry |
| Relation to Pitch Circle | Located below the pitch circle | Always smaller than or equal to the pitch circle radius |
| Radius | R_dedendum = Pitch radius - Dedendum | R_base = Pitch radius x cos(Involute pressure angle) |
| Engineering Importance | Critical for gear clearance and root strength | Essential for accurate tooth profile generation |
Introduction to Gear Geometry
The base circle is a fundamental circle in gear geometry from which the involute tooth profile is generated, crucial for defining the gear's pitch and contact characteristics. The dedendum circle, located below the pitch circle, marks the bottom of the gear tooth spaces and determines the clearance between meshing gears, preventing interference. Understanding the distinction between the dedendum circle and base circle is essential for accurate gear design and ensuring efficient power transmission.
Understanding the Dedendum Circle
The dedendum circle is a crucial reference in gear geometry, defining the boundary at the root of the gear teeth where the clearance between mating gears is maintained. It lies beneath the base circle, which is the foundation for generating the involute tooth profile that ensures smooth transmission of motion. Understanding the dedendum circle helps in designing proper tooth depth and avoiding interference, enhancing gear performance and longevity.
Exploring the Base Circle in Gears
The base circle in gears serves as the foundational circle from which the involute tooth profile is generated, directly influencing the gear's smooth meshing and transmission efficiency. While the dedendum circle defines the root of the tooth, the base circle determines the shape and size of the involute curve, affecting contact ratio and gear strength. Precise calculation of the base circle diameter is essential for accurate involute gear design, ensuring optimal load distribution and minimizing wear.
Key Differences Between Dedendum and Base Circles
The dedendum circle defines the bottom boundary of gear teeth, marking the root of the gear tooth, while the base circle serves as the reference circle from which the involute tooth profile is generated. The dedendum circle is larger than the base circle and is critical for clearance and avoiding interference during meshing. In contrast, the base circle directly influences the gear's pressure angle and the smoothness of power transmission through its geometric construction.
Functional Roles of Dedendum Circle
The dedendum circle defines the lower boundary of the gear tooth, extending below the base circle to provide clearance for proper meshing and prevent interference. It ensures that the mating gear teeth do not collide, maintaining smooth transmission of motion and reducing wear. Functionally, the dedendum circle supports the root area of the gear tooth, safeguarding against stress concentrations and enhancing durability in gear operation.
Importance of Base Circle in Gear Design
The base circle is crucial in gear design as it serves as the foundation for generating the involute tooth profile, ensuring smooth and efficient power transmission. Unlike the dedendum circle, which defines the root depth of the gear teeth, the base circle directly influences the gear's pitch and pressure angle, affecting meshing accuracy and load distribution. Proper determination of the base circle radius is essential for minimizing friction, wear, and noise in gear operation.
Influence on Gear Tooth Profile
The dedendum circle defines the root diameter of a gear, directly influencing the depth and shape of the gear tooth's root area, while the base circle serves as the foundational reference for the involute tooth profile, determining the exact curvature of the gear tooth flanks. Variations in the dedendum circle affect clearance and potential interference at the tooth base, whereas changes in the base circle radius modify the involute angle, impacting smooth meshing and load distribution. Precise control of both circles is essential for optimizing gear tooth strength, minimizing wear, and ensuring efficient power transmission.
Calculation Methods for Dedendum and Base Circles
The base circle diameter is calculated by multiplying the pitch circle diameter by the cosine of the pressure angle, forming the reference circle for involute gear tooth profiles. The dedendum circle diameter is derived by subtracting twice the dedendum depth--typically calculated as a function of the module or diametral pitch plus addendum clearance--from the pitch circle diameter, defining the root diameter of the gear. Accurate determination of both circles is critical for precise gear geometry, ensuring proper meshing and load distribution.
Impact on Gear Performance and Efficiency
The dedendum circle, representing the root diameter, determines the clearance between mating gears and directly impacts load capacity and noise reduction during operation. The base circle is fundamental for generating the involute tooth profile, influencing transmission accuracy and smoothness of motion. Optimizing the relationship between dedendum and base circles enhances gear meshing efficiency, minimizing friction losses and wear to improve overall gear performance.
Conclusion: Dedendum Circle vs Base Circle
The dedendum circle lies below the base circle, defining the root boundary of a gear tooth, while the base circle serves as the fundamental circle from which the involute tooth profile is generated. The dedendum circle ensures sufficient clearance between meshing gears to prevent interference, whereas the base circle directly influences the gear's involute geometry and motion transfer. Understanding the spatial relationship between these circles is crucial for precise gear design, ensuring optimal strength and smooth operation.
Dedendum circle Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com