Independent action empowers you to take control of your decisions and outcomes without relying on others. This approach fosters self-reliance, confidence, and accountability in both personal and professional settings. Discover how embracing independent action can transform your life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
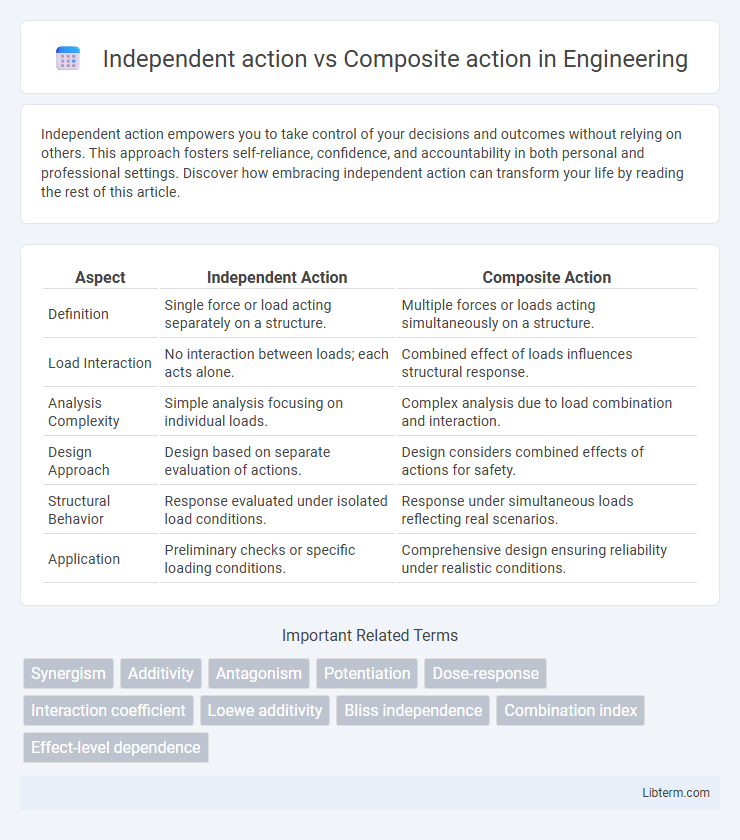
| Aspect | Independent Action | Composite Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single force or load acting separately on a structure. | Multiple forces or loads acting simultaneously on a structure. |
| Load Interaction | No interaction between loads; each acts alone. | Combined effect of loads influences structural response. |
| Analysis Complexity | Simple analysis focusing on individual loads. | Complex analysis due to load combination and interaction. |
| Design Approach | Design based on separate evaluation of actions. | Design considers combined effects of actions for safety. |
| Structural Behavior | Response evaluated under isolated load conditions. | Response under simultaneous loads reflecting real scenarios. |
| Application | Preliminary checks or specific loading conditions. | Comprehensive design ensuring reliability under realistic conditions. |
Understanding Independent Action
Understanding independent action involves recognizing actions taken by a single actor without collaboration or influence from others, often emphasizing individual responsibility and decision-making. Independent actions are analyzed separately to determine their direct effects, distinguishing them from composite actions, which combine multiple actors' contributions into a unified process. This distinction is crucial for accurately attributing outcomes and responsibilities in legal, organizational, and social contexts.
Defining Composite Action
Composite action refers to a complex task composed of multiple interrelated independent actions that collectively achieve a broader objective. It involves the orchestration of individual actions in a sequence or parallel structure, often requiring synchronization and state management to ensure coherent execution. In fields like robotics and software engineering, defining composite actions enhances modularity and scalability by encapsulating functionality within hierarchical task frameworks.
Key Differences Between Independent and Composite Actions
Independent actions operate as singular, discrete events that achieve specific outcomes without relying on other processes, making them simpler and easier to manage. Composite actions, in contrast, consist of multiple interconnected steps or sub-actions that work together to perform complex tasks, offering greater flexibility and coordination. Key differences include their structural complexity, dependency on internal components, and the scope of tasks they can accomplish autonomously.
Real-World Examples of Independent Action
Independent actions refer to individual tasks or decisions executed without relying on other processes, frequently seen in real-world scenarios such as single-step online purchases where a customer completes payment without additional system dependencies. Autonomous vehicle obstacle detection operates as an independent action by processing sensor data locally to make immediate navigation decisions. Simple sensor-triggered home automation systems, like motion-activated lights, perform independent actions by activating devices based solely on detected inputs.
Use Cases for Composite Action
Composite actions in GitHub workflows enable the reuse and combination of multiple steps into a single action, streamlining complex automation processes. Use cases for composite actions include creating standardized deployment pipelines, encapsulating environment setup procedures, and simplifying multi-step testing workflows. These actions improve maintainability by reducing code duplication and enhancing modularity across repositories.
Advantages of Independent Action
Independent action in structural engineering allows elements to function autonomously, which enhances design flexibility and simplifies analysis. It enables easier identification and isolation of failures, improving safety and maintenance efficiency. This approach reduces complexity in construction and material usage by allowing targeted reinforcement only where necessary.
Benefits of Composite Action
Composite action combines the strengths of multiple structural elements, resulting in increased load-bearing capacity and enhanced stiffness compared to independent action. This integrated approach optimizes material usage, reduces deformation, and improves overall structural efficiency. Engineers favor composite action for its ability to deliver cost-effective, durable solutions in building and bridge construction.
Challenges with Independent and Composite Actions
Challenges with independent actions often include difficulties in coordinating multiple discrete tasks that lack integration, leading to inefficiencies and increased risk of errors. Composite actions face complexity in managing interdependencies between sub-actions, which can cause synchronization issues, increased processing time, and potential failure points in automated systems. Both action types require robust error handling and monitoring mechanisms to maintain performance and reliability in dynamic environments.
Decision Criteria: When to Choose Each Approach
Choosing between independent action and composite action depends on task complexity and dependency. Independent actions suit scenarios requiring isolated, straightforward decisions with minimal interrelation, enhancing modularity and ease of debugging. Composite actions are ideal for complex workflows needing coordinated multi-step processes and are selected when tasks have sequential dependencies or require unified result evaluation.
Future Trends in Action Management
Future trends in action management reveal a shift towards integrating independent actions and composite actions within AI systems to enhance adaptability and efficiency. Advances in machine learning and natural language processing enable more sophisticated orchestration of composite actions, allowing seamless execution of complex tasks by combining multiple independent actions. Emerging frameworks emphasize dynamic action composition and real-time decision-making to optimize performance in evolving environments such as autonomous systems and intelligent assistants.
Independent action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com