Rope drive systems transmit power efficiently using ropes wrapped around pulleys, offering flexibility and smooth operation in various mechanical applications. They are especially useful in industries where long-distance power transmission is required without significant energy loss. Discover how rope drive technology can enhance your machinery performance by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
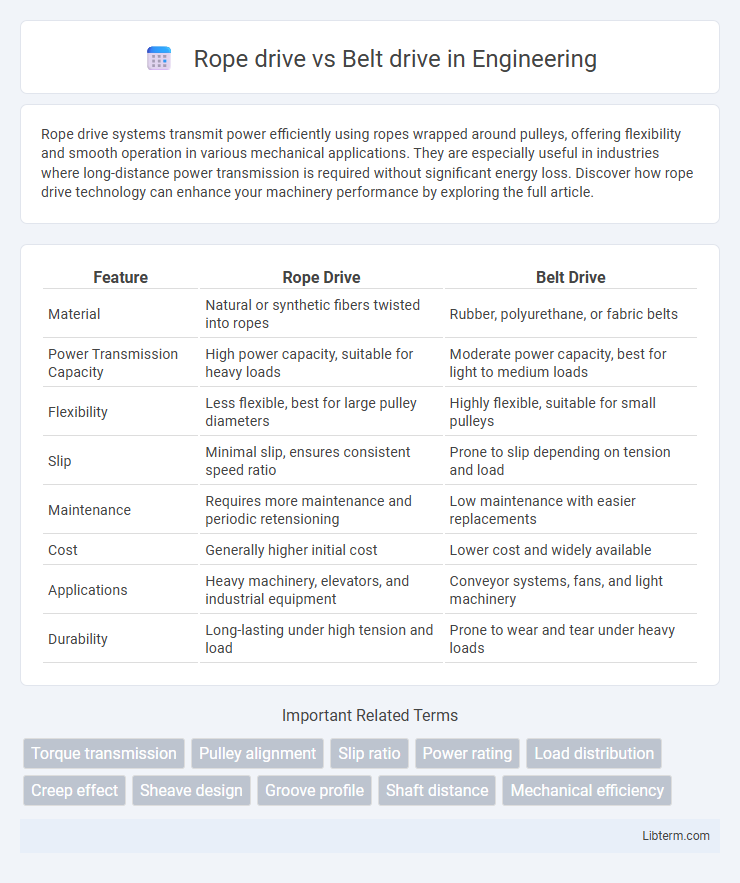
| Feature | Rope Drive | Belt Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Natural or synthetic fibers twisted into ropes | Rubber, polyurethane, or fabric belts |
| Power Transmission Capacity | High power capacity, suitable for heavy loads | Moderate power capacity, best for light to medium loads |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, best for large pulley diameters | Highly flexible, suitable for small pulleys |
| Slip | Minimal slip, ensures consistent speed ratio | Prone to slip depending on tension and load |
| Maintenance | Requires more maintenance and periodic retensioning | Low maintenance with easier replacements |
| Cost | Generally higher initial cost | Lower cost and widely available |
| Applications | Heavy machinery, elevators, and industrial equipment | Conveyor systems, fans, and light machinery |
| Durability | Long-lasting under high tension and load | Prone to wear and tear under heavy loads |
Introduction to Rope and Belt Drives
Rope drives utilize multiple ropes running over grooved pulleys to transmit mechanical power efficiently, offering high flexibility and durability for long-distance power transmission. Belt drives employ flat or V-shaped belts made from materials like rubber or leather, providing smooth and quiet operation in various industrial applications. Both systems serve crucial roles in machinery, with rope drives excelling in heavy-duty, high-tension environments and belt drives favored for moderate power transmission with minimal maintenance.
Key Components of Rope Drives
Rope drives consist of multiple ropes running over grooved pulleys, with key components including the ropes themselves, which are typically made from natural fibers or synthetic materials for high tensile strength and flexibility. Grooved pulleys enhance friction and grip, ensuring efficient power transmission and minimal slippage. The tensioning device maintains proper rope tension, reducing wear and extending the system's operational lifespan compared to belt drives.
Key Components of Belt Drives
Belt drives consist of key components including the belt, pulleys, and tensioners, which work together to transmit power efficiently between rotating shafts. The belt, typically made from rubber or synthetic materials, wraps around the pulleys to create friction that drives motion. Proper tension maintained by adjustable tensioners ensures minimal slippage and optimal performance in various mechanical applications.
Working Principles: Rope vs Belt Drive
Rope drives transmit power through multiple intertwined ropes stretched over grooved pulleys, relying on friction and tensile strength to transfer motion efficiently, particularly in heavy load applications with long distances. Belt drives operate by looping a flexible belt around pulleys, using frictional force between belt surfaces and pulley grooves to transmit rotational motion smoothly and with minimal slip. Both systems convert input torque into mechanical power, but rope drives excel in high-tension, low-speed environments, whereas belt drives are preferred for high-speed, moderate-load transmissions.
Efficiency Comparison: Rope vs Belt Drive
Rope drives exhibit higher efficiency than belt drives, often achieving 95-98% efficiency due to reduced slippage and better power transmission over long distances. Belt drives typically show efficiencies ranging from 85-95%, influenced by factors like belt tension, alignment, and materials. The minimal elongation and friction loss in rope drives make them favorable for heavy-duty applications requiring consistent speed and power.
Applications and Suitability
Rope drives excel in transmitting power over long distances with minimal slip, making them ideal for applications like elevators, cranes, and mining hoists where high load capacity and durability are critical. Belt drives suit lighter loads and moderate distances, commonly used in automotive engines, conveyor systems, and agricultural machinery due to their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation. Rope drives are preferred in heavy industrial settings requiring robust tension maintenance and minimal elongation, whereas belt drives are optimal for moderate power transmission where flexibility and quieter operation are important.
Advantages of Rope Drives
Rope drives offer superior flexibility and reduced slippage compared to belt drives, enhancing power transmission efficiency in varying load conditions. They provide excellent durability and resistance to wear and tear, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications in industries like mining and manufacturing. The ability to maintain consistent tension and accommodate long distances between pulleys further distinguishes rope drives as a reliable choice for high-torque mechanical systems.
Advantages of Belt Drives
Belt drives offer advantages such as smoother and quieter operation compared to rope drives, reducing noise pollution in mechanical systems. They provide flexibility in design by accommodating larger distances between shafts and can handle misalignment more effectively. Belt drives also require less maintenance due to their simple construction and do not necessitate lubrication, improving overall system reliability and reducing operational costs.
Limitations and Challenges
Rope drives face limitations such as lower power transmission capacity and increased maintenance due to rope wear and slippage under heavy loads. Belt drives encounter challenges including stretch, slip, and wear, which reduce efficiency and require frequent tension adjustments and replacements. Both systems struggle with high-speed applications and can suffer from environmental factors like temperature and moisture affecting durability and performance.
Selecting the Right Drive for Industrial Needs
Rope drives provide high power transmission efficiency and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring minimal stretch and maintenance. Belt drives offer greater flexibility, quieter operation, and cost-effective installation, suitable for moderate power and speed variations in manufacturing settings. Selecting the right drive depends on factors like load capacity, operational environment, maintenance intervals, and torque requirements to optimize performance and longevity.
Rope drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com