Powder coating offers a durable and eco-friendly finish that resists chipping, fading, and scratching better than traditional paint. This technique involves applying a dry powder electrostatically and curing it under heat to form a tough protective layer. Discover how powder coating can enhance your projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
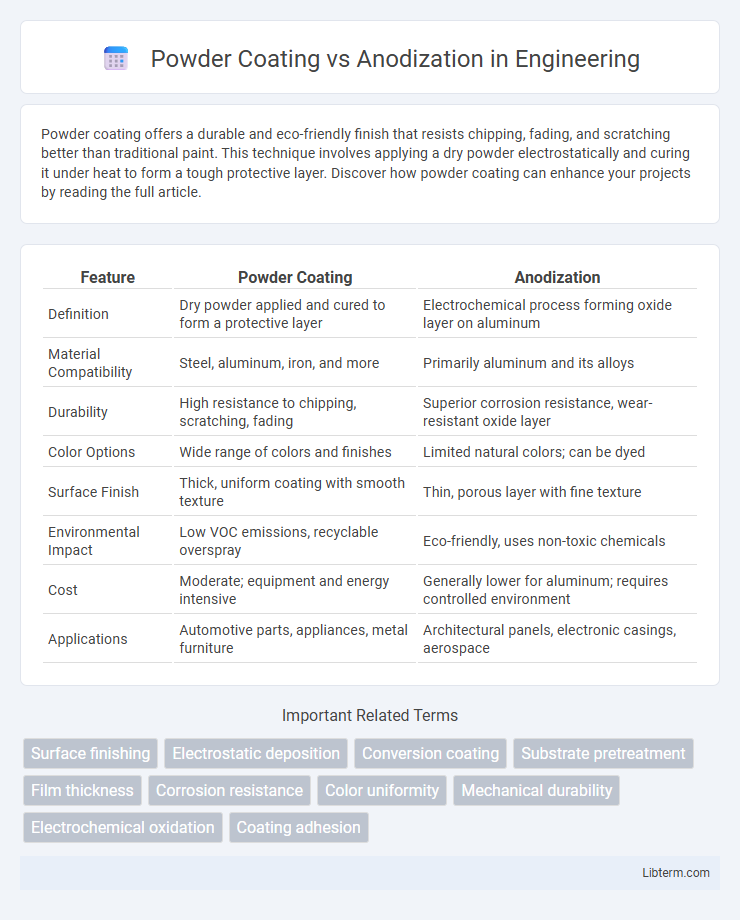
| Feature | Powder Coating | Anodization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dry powder applied and cured to form a protective layer | Electrochemical process forming oxide layer on aluminum |
| Material Compatibility | Steel, aluminum, iron, and more | Primarily aluminum and its alloys |
| Durability | High resistance to chipping, scratching, fading | Superior corrosion resistance, wear-resistant oxide layer |
| Color Options | Wide range of colors and finishes | Limited natural colors; can be dyed |
| Surface Finish | Thick, uniform coating with smooth texture | Thin, porous layer with fine texture |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, recyclable overspray | Eco-friendly, uses non-toxic chemicals |
| Cost | Moderate; equipment and energy intensive | Generally lower for aluminum; requires controlled environment |
| Applications | Automotive parts, appliances, metal furniture | Architectural panels, electronic casings, aerospace |
Introduction to Surface Finishing Techniques
Powder coating and anodization are advanced surface finishing techniques widely used to enhance durability and aesthetics of metal products. Powder coating involves applying a dry powder electrostatically, then curing it under heat to form a tough, protective layer resistant to corrosion and impact. Anodization is an electrochemical process that thickens the natural oxide layer on aluminum, improving corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and allowing for vibrant dyeing options.
What is Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a dry finishing process that involves applying a free-flowing, electrostatically charged powder onto metal surfaces, which is then cured under heat to form a durable, protective layer. This coating method offers excellent resistance to corrosion, chipping, and fading, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. The powder coating process produces a smooth, uniform finish that enhances both the aesthetic appeal and longevity of metal components compared to traditional liquid paints.
What is Anodization?
Anodization is an electrochemical process that enhances the natural oxide layer on aluminum surfaces, improving corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetic appeal. This technique creates a hard, protective coating by converting the metal surface into a decorative, durable, corrosion-resistant anodic oxide finish. Unlike powder coating, anodization penetrates the metal surface, providing long-lasting protection without chipping or peeling.
Application Processes Compared
Powder coating involves electrostatically applying a dry powder to a metal surface, followed by curing under heat to form a durable, protective layer, ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications. Anodization is an electrochemical process that converts the metal surface into a corrosion-resistant oxide layer, primarily used for aluminum to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal without adding thickness. Powder coating offers a wide range of color and texture options with higher impact resistance, while anodization provides increased surface hardness and excellent environmental protection through a natural oxide barrier.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Powder coating provides a thick, protective layer that resists chipping, scratching, and fading, making it highly durable for outdoor and industrial applications. Anodization enhances aluminum's natural oxide layer, offering exceptional corrosion resistance and increased surface hardness without adding thickness. While powder coating excels in impact resistance and color variety, anodization delivers superior wear resistance and longevity under harsh environmental conditions.
Color Options and Aesthetic Considerations
Powder coating offers a wide spectrum of vibrant and customizable color options with a durable, glossy finish that resists chipping and fading, making it ideal for decorative applications requiring bright and consistent hues. Anodization provides a more subtle, metallic appearance with limited color choices, typically in shades of silver, black, or bronze, enhancing the natural aluminum surface with a corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant layer. The choice between powder coating and anodization depends on desired aesthetic effects and color flexibility, balancing vividness and texture against a sleek, metallic look.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Powder coating produces minimal volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and generates less hazardous waste compared to liquid paints, making it environmentally friendly and safer for workers. Anodization involves electrochemical processes that consume significant energy and create acidic byproducts requiring careful disposal to avoid environmental harm. Both methods offer durable finishes, but powder coating has a lower environmental footprint and reduced health risks due to the absence of toxic chemicals and reduced solvent emissions.
Cost Comparison: Powder Coating vs Anodization
Powder coating typically costs less than anodization due to lower material and process expenses, making it more budget-friendly for large-scale or decorative applications. Anodization involves higher initial setup costs and requires specialized equipment, which increases its overall price but provides superior corrosion resistance and durable finish. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints, desired finish quality, and durability requirements.
Best Uses for Powder Coating and Anodization
Powder coating offers superior durability and resistance to chipping, corrosion, and UV damage, making it ideal for automotive parts, outdoor furniture, and industrial equipment exposed to harsh environments. Anodization enhances aluminum surfaces by creating a corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, and aesthetically appealing oxide layer, best suited for aerospace components, architectural applications, and consumer electronics. Both processes provide excellent protection, but powder coating is preferred for thicker, colorful finishes, while anodization excels in creating a hard, lightweight coating on aluminum substrates.
Choosing the Right Surface Finishing Method
Powder coating offers a durable, colorful finish ideal for outdoor applications due to its resistance to corrosion, UV rays, and impact. Anodization provides a thin, protective oxide layer that enhances metal hardness and corrosion resistance while allowing natural metallic textures to show through, especially on aluminum. Selecting between powder coating and anodization depends on factors like desired appearance, environmental exposure, and maintenance requirements to ensure optimal surface protection and longevity.
Powder Coating Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com