CANopen is a communication protocol designed for embedded systems used in automation, enabling reliable and efficient data exchange between devices on a Controller Area Network (CAN). It provides standardized communication objects and device profiles to ensure interoperability and streamlined network configuration. Discover how CANopen can enhance your system's performance and why it's a leading choice in industrial automation throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
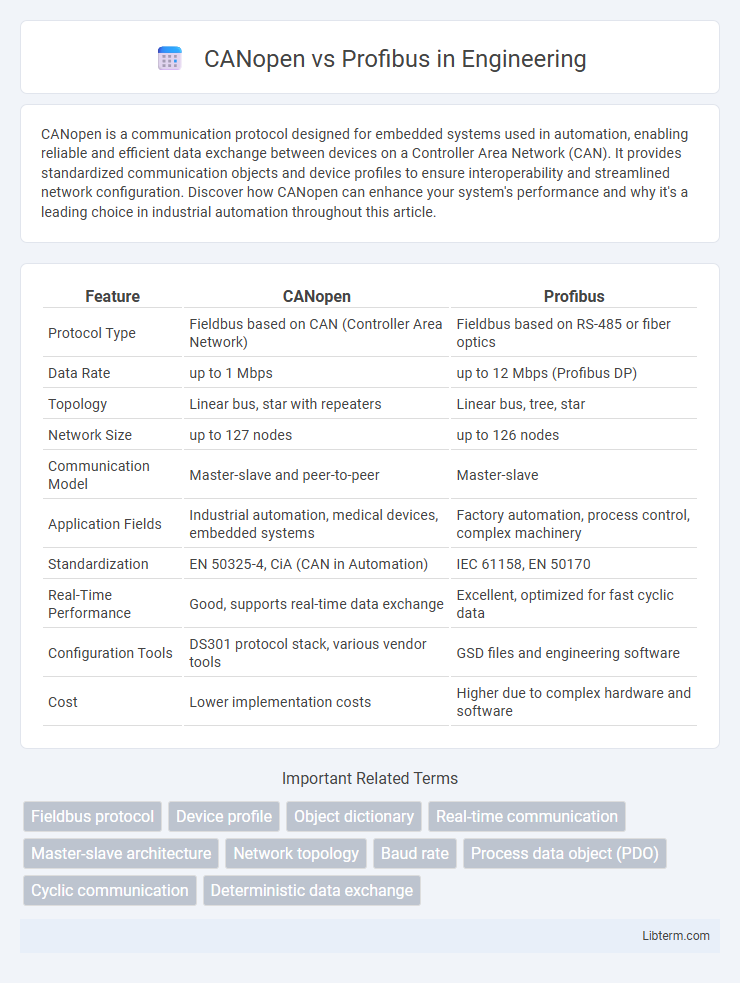
| Feature | CANopen | Profibus |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Fieldbus based on CAN (Controller Area Network) | Fieldbus based on RS-485 or fiber optics |
| Data Rate | up to 1 Mbps | up to 12 Mbps (Profibus DP) |
| Topology | Linear bus, star with repeaters | Linear bus, tree, star |
| Network Size | up to 127 nodes | up to 126 nodes |
| Communication Model | Master-slave and peer-to-peer | Master-slave |
| Application Fields | Industrial automation, medical devices, embedded systems | Factory automation, process control, complex machinery |
| Standardization | EN 50325-4, CiA (CAN in Automation) | IEC 61158, EN 50170 |
| Real-Time Performance | Good, supports real-time data exchange | Excellent, optimized for fast cyclic data |
| Configuration Tools | DS301 protocol stack, various vendor tools | GSD files and engineering software |
| Cost | Lower implementation costs | Higher due to complex hardware and software |
Introduction to CANopen and Profibus
CANopen is a robust communication protocol designed for embedded control systems in automation, offering high-speed data exchange and device interoperability via the CAN bus network. Profibus, primarily used in industrial automation, provides real-time data transmission with two main variants: Profibus DP for fast device communication and Profibus PA for process automation. Both protocols enable reliable networked control but differ in application scope, with CANopen excelling in modular, decentralized systems and Profibus favored for complex plant-wide automation.
Overview of CANopen Protocol
CANopen is a communication protocol based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) designed for embedded control systems in automation. It provides standardized device profiles and a flexible communication model supporting real-time data exchange, device configuration, and diagnostics. Widely used in industrial environments, CANopen emphasizes simplicity, scalability, and interoperability for applications such as motion control, medical devices, and building automation.
Overview of Profibus Protocol
Profibus, developed by Siemens in the 1980s, is a widely adopted industrial communication protocol designed for high-speed, real-time data exchange in automation systems. It supports a variety of physical layers, including RS-485 and fiber optics, and offers robust error detection mechanisms to ensure reliable performance in harsh industrial environments. Profibus networks facilitate seamless integration of sensors, actuators, and controllers, making it ideal for complex factory automation and process control applications.
Key Differences Between CANopen and Profibus
CANopen operates on a Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol primarily designed for motion control and embedded systems, offering real-time communication with deterministic behavior and lightweight data frames. Profibus utilizes a fieldbus communication standard suitable for complex automation systems, supporting a larger network size with higher data throughput and diverse device profiles including DP, PA, and FMS. The key differences lie in their network topologies, data rates, device interoperability, and typical application environments where CANopen excels in smaller, time-critical systems, while Profibus is favored for extensive industrial automation with robust diagnostics.
Communication Speed and Performance Comparison
CANopen supports communication speeds up to 1 Mbps, optimized for real-time control in embedded systems, while Profibus offers higher speeds reaching up to 12 Mbps, suitable for complex automation networks. Profibus provides faster data throughput and better support for large-scale industrial environments, enhancing performance for extensive device communication. CANopen excels in lightweight, deterministic communication with lower latency, ideal for time-critical applications requiring precise synchronization.
Network Topology and Scalability
CANopen supports flexible network topologies including linear, star, and tree configurations, allowing easy expansion with up to 127 devices per network segment, which enhances scalability in industrial automation. Profibus typically employs a linear bus topology with limited branching, supporting up to 126 devices per segment but requiring repeaters for extended network length and device count, impacting scalability. The inherent flexibility of CANopen's topology options provides superior scalability and adaptability compared to the more rigid Profibus infrastructure.
Device Compatibility and Interoperability
CANopen offers superior device compatibility due to its widespread use in embedded control systems and support for standardized device profiles, facilitating seamless integration across various manufacturers. Profibus provides strong interoperability in process automation with its flexible communication protocols and extensive device library, though it may require more complex configuration for mixed-device environments. Both protocols support multi-vendor ecosystems, but CANopen typically ensures faster integration and easier scalability in distributed automation networks.
Application Areas for CANopen and Profibus
CANopen excels in embedded control systems for automotive, industrial automation, and medical equipment due to its real-time communication and device management capabilities. Profibus is widely used in factory automation, process control, and building automation, supporting complex networks with higher data throughput and robustness. Both protocols serve distinct industrial sectors where CANopen suits distributed control with smaller data loads, while Profibus handles large-scale, complex automation systems.
Installation, Maintenance, and Cost Considerations
CANopen offers simplified installation with flexible wiring over standard CAN bus, reducing complexity and labor costs compared to Profibus's more rigid cabling requirements. Maintenance is easier in CANopen networks due to built-in diagnostics and fault-tolerant features, while Profibus systems often require specialized tools and expertise, increasing downtime and service expenses. Cost considerations favor CANopen for smaller to mid-sized automation projects due to cheaper hardware and lower training needs, whereas Profibus is typically more expensive but justified in large-scale industrial environments demanding high data throughput and extensive device integration.
Choosing the Right Protocol: CANopen vs Profibus
Choosing between CANopen and Profibus hinges on the specific application requirements and network complexity. CANopen excels in decentralized control systems with lower data rates and simpler wiring, ideal for embedded automation. Profibus offers higher data throughput and extensive device interoperability, making it suitable for complex industrial environments demanding real-time communication and robust diagnostics.
CANopen Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com