Axial compressors are essential components in gas turbines and jet engines, designed to increase air pressure efficiently by passing air through multiple rotating and stationary blade stages. Their high performance and compact structure make them suitable for various aerospace and industrial applications, ensuring optimal engine thrust and fuel efficiency. Discover how an axial compressor can enhance Your engine's performance by exploring the detailed mechanics and benefits outlined in the rest of this article.
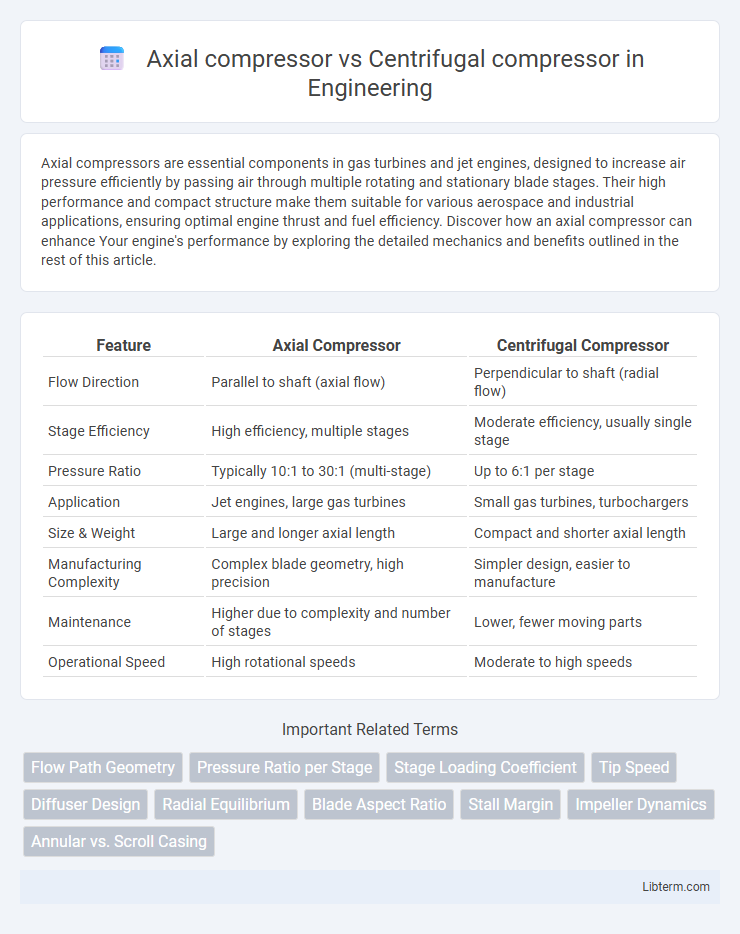
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Axial Compressor | Centrifugal Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Direction | Parallel to shaft (axial flow) | Perpendicular to shaft (radial flow) |
| Stage Efficiency | High efficiency, multiple stages | Moderate efficiency, usually single stage |
| Pressure Ratio | Typically 10:1 to 30:1 (multi-stage) | Up to 6:1 per stage |
| Application | Jet engines, large gas turbines | Small gas turbines, turbochargers |
| Size & Weight | Large and longer axial length | Compact and shorter axial length |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Complex blade geometry, high precision | Simpler design, easier to manufacture |
| Maintenance | Higher due to complexity and number of stages | Lower, fewer moving parts |
| Operational Speed | High rotational speeds | Moderate to high speeds |
Introduction to Compressors
Axial compressors use rotating airfoils to progressively increase air pressure by accelerating airflow along the axis of rotation, making them ideal for high-volume, high-pressure applications such as jet engines. Centrifugal compressors accelerate air radially outward using a spinning impeller, converting velocity into increased pressure, commonly utilized in smaller-scale applications like turbochargers and industrial blowers. Both compressor types are essential components in gas turbine engines and HVAC systems, differing primarily in flow direction, pressure ratio capabilities, and design complexity.
Overview of Axial Compressors
Axial compressors consist of multiple rotating blades arranged in a series that progressively compresses air by increasing velocity and pressure through axial flow. They offer high efficiency and are commonly used in large-scale applications such as jet engines and gas turbines due to their ability to handle high flow rates and achieve significant pressure ratios. The aerodynamic design of axial compressors allows for continuous flow compression, making them ideal for systems requiring stable, high-volume air compression.
Overview of Centrifugal Compressors
Centrifugal compressors utilize a rotating impeller to increase the velocity of the air or gas before converting this kinetic energy into pressure through a diffuser, making them ideal for applications requiring moderate pressure ratios. These compressors are compact with high efficiency at small to medium flow rates and are commonly used in turbochargers, refrigeration systems, and small gas turbines. Unlike axial compressors that handle large volumes of air with multiple stages, centrifugal compressors achieve pressure rise in a single or few stages, offering simpler design and robust performance.
Working Principle: Axial vs Centrifugal Compressors
Axial compressors operate by continuously accelerating air along the axis of rotation through multiple stages of rotating and stationary blades, increasing pressure incrementally with each stage. Centrifugal compressors use a rotating impeller to draw air inward and propel it outward radially, converting velocity into pressure in a volute or diffuser. The axial design is favored for high flow rates and efficiency in large gas turbines, while the centrifugal type excels in compact applications with moderate pressure increases.
Key Design Differences
Axial compressors feature multiple stages of rotating and stationary blades that compress air by gradually reducing its axial velocity, ideal for high flow rates and efficiency in large gas turbines. Centrifugal compressors use a single impeller to accelerate air radially outward into a diffuser, offering a compact design with high pressure ratios per stage suitable for smaller engines and turbochargers. The axial design requires precise blade aerodynamics for optimal performance, while centrifugal compressors rely on robust impeller geometry to manage higher mechanical stress and thermal loads.
Efficiency Comparison
Axial compressors typically achieve higher efficiency in large-scale applications due to their ability to handle greater mass flow rates with lower pressure ratios per stage, resulting in lower energy losses. Centrifugal compressors, while generally more compact and better suited for smaller flow rates, often exhibit slightly lower overall efficiency because of higher aerodynamic losses and increased flow turbulence at the impeller. Efficiency differences between axial and centrifugal compressors become less pronounced when comparing multi-stage axial designs with high-pressure single-stage centrifugal compressors, depending on operating conditions and design optimization.
Applications and Industry Uses
Axial compressors are primarily utilized in large-scale applications such as jet engines, power plants, and industrial gas turbines due to their high flow rates and efficiency at high speeds. Centrifugal compressors find extensive use in smaller, lower flow rate applications including HVAC systems, turbochargers, and refrigeration units because of their compact design and strong pressure rise capabilities. Industries such as aerospace, energy production, chemical processing, and automotive manufacturing leverage these compressors based on the required pressure ratio, flow rate, and spatial constraints.
Advantages of Axial Compressors
Axial compressors offer higher efficiency and greater air flow capacity, making them ideal for large-scale applications such as jet engines and power plants. Their design allows for multiple stages, enabling higher pressure ratios and smoother performance under varying operating conditions. These compressors also maintain better aerodynamic stability and lower energy losses compared to centrifugal compressors.
Advantages of Centrifugal Compressors
Centrifugal compressors offer a compact design with a high pressure ratio per stage, making them highly efficient for applications requiring moderate flow rates and pressures. Their robust construction results in greater reliability and lower maintenance costs compared to axial compressors. They excel in delivering stable performance with less sensitivity to flow variations, which is advantageous in industrial and HVAC systems.
Choosing the Right Compressor for Your Needs
Selecting the right compressor involves understanding the operational differences between axial and centrifugal compressors. Axial compressors excel in high-flow, low-pressure applications such as jet engines and large-scale power plants, providing high efficiency and continuous airflow. Centrifugal compressors are ideal for lower flow rates with higher pressure ratios, commonly used in HVAC systems and turbochargers, offering compact design and robust performance.
Axial compressor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com