A digital manometer provides precise pressure measurements by converting air or gas pressure into an electronic signal displayed on a digital screen. It offers high accuracy, ease of use, and is essential for applications in HVAC systems, medical equipment, and industrial processes. Discover how choosing the right digital manometer can enhance your pressure monitoring by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
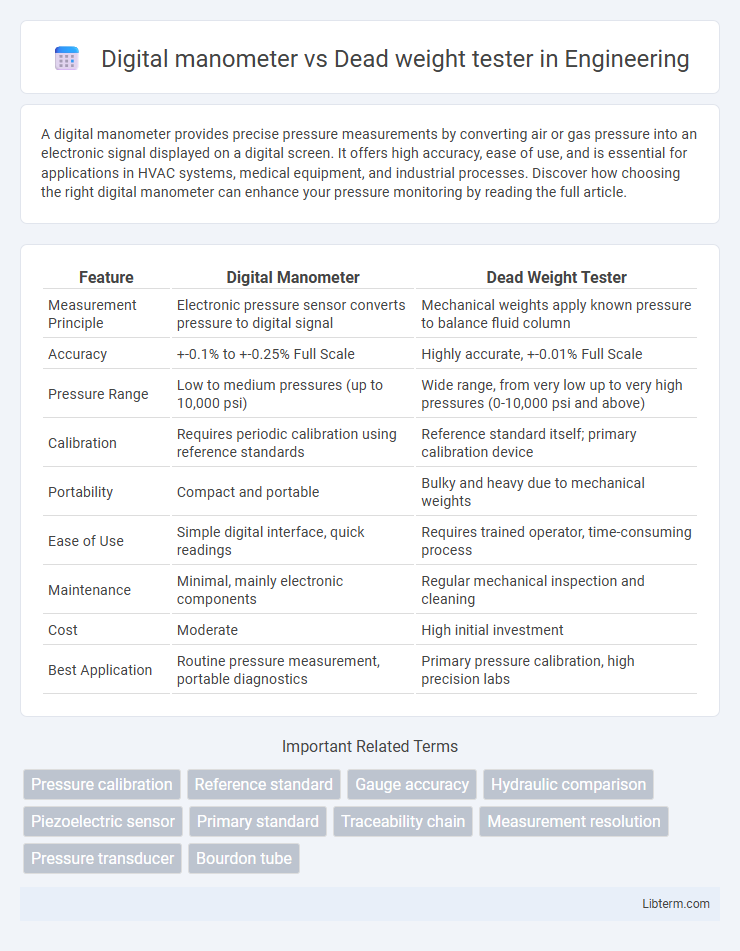
| Feature | Digital Manometer | Dead Weight Tester |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Electronic pressure sensor converts pressure to digital signal | Mechanical weights apply known pressure to balance fluid column |
| Accuracy | +-0.1% to +-0.25% Full Scale | Highly accurate, +-0.01% Full Scale |
| Pressure Range | Low to medium pressures (up to 10,000 psi) | Wide range, from very low up to very high pressures (0-10,000 psi and above) |
| Calibration | Requires periodic calibration using reference standards | Reference standard itself; primary calibration device |
| Portability | Compact and portable | Bulky and heavy due to mechanical weights |
| Ease of Use | Simple digital interface, quick readings | Requires trained operator, time-consuming process |
| Maintenance | Minimal, mainly electronic components | Regular mechanical inspection and cleaning |
| Cost | Moderate | High initial investment |
| Best Application | Routine pressure measurement, portable diagnostics | Primary pressure calibration, high precision labs |
Introduction to Pressure Measurement Tools
Digital manometers provide precise and immediate pressure readings using electronic sensors, ideal for quick diagnostics and real-time monitoring in various industrial applications. Dead weight testers offer superior accuracy by applying known calibration weights to measure pressure, serving as a standard for calibrating other pressure meters. Both tools are essential in ensuring accurate pressure measurement, with digital manometers favored for convenience and dead weight testers preferred for laboratory calibration.
What is a Digital Manometer?
A digital manometer is an electronic device designed to measure pressure accurately by converting pressure levels into electrical signals displayed on a digital screen. It offers high precision, portability, and easy readability, making it ideal for applications requiring quick and reliable pressure measurements in HVAC, laboratory, and industrial settings. Unlike a dead weight tester, which uses calibrated weights to provide direct pressure measurement, a digital manometer relies on sensor technology such as piezoresistive or capacitive sensors for real-time monitoring.
What is a Dead Weight Tester?
A Dead Weight Tester is a precision calibration device used to generate accurate pressure standards by applying known weights to a piston-cylinder assembly, ensuring traceable pressure measurements. It is commonly employed to calibrate pressure instruments such as digital manometers, providing a reliable comparison against known pressure values. Unlike digital manometers that provide electronic pressure readings, Dead Weight Testers offer mechanical accuracy through controlled weight application for precise pressure calibration.
Key Differences Between Digital Manometers and Dead Weight Testers
Digital manometers offer real-time, precise pressure readings through electronic sensors and digital displays, making them ideal for quick diagnostics and portable applications. Dead weight testers provide highly accurate, primary standard calibration by applying known weights to generate precise pressures, ensuring traceability and reliability in calibration labs. Unlike digital manometers, dead weight testers require manual setup and physical weights, but they excel in measurement accuracy and certification for calibration standards.
Accuracy Comparison: Digital Manometer vs Dead Weight Tester
Digital manometers offer high-resolution readings ideal for real-time pressure monitoring but may experience slight accuracy drift due to electronic components and calibration intervals. Dead weight testers provide exceptional accuracy and traceability by using calibrated masses to apply known pressure, making them the gold standard for primary pressure calibration. While digital manometers provide faster, user-friendly measurements, dead weight testers maintain superior long-term accuracy with minimal uncertainty, typically within +-0.01% of reading.
Applications and Use Cases
Digital manometers are widely used in HVAC systems, laboratory measurements, and industrial process monitoring due to their portability and real-time pressure readings. Dead weight testers find applications in calibration laboratories and metrology institutes where precise and traceable pressure calibration is essential for validating other pressure instruments. Both devices serve critical roles in ensuring accurate pressure measurements, with digital manometers favored for convenience and dead weight testers valued for calibration accuracy.
Pros and Cons of Digital Manometers
Digital manometers offer high precision measurements with easy-to-read digital displays, making them ideal for quick and accurate pressure monitoring in various industrial applications. Their portability, compact size, and ability to store data digitally enhance convenience, but they may be limited by battery life and susceptibility to electronic malfunctions compared to the mechanical reliability of dead weight testers. Despite these drawbacks, digital manometers provide faster setup times and greater versatility in field use, although dead weight testers remain the gold standard for calibration due to their unmatched accuracy and robustness.
Pros and Cons of Dead Weight Testers
Dead weight testers provide highly accurate and traceable pressure calibration, making them ideal for lab environments requiring precision standards. However, they are bulkier and less convenient for field use compared to digital manometers, which offer portability and faster readings. The main drawback of dead weight testers lies in their complexity and maintenance requirements, including regular calibration of weights and susceptibility to environmental factors like temperature and vibration.
Choosing the Right Pressure Measurement Device
Choosing the right pressure measurement device depends on accuracy requirements and application context; digital manometers offer quick readings and ease of use, ideal for routine monitoring and fieldwork. Dead weight testers provide superior calibration precision and traceability, making them essential for laboratory standards and calibration of other instruments. Understanding the trade-offs between portability and calibration accuracy ensures optimal performance in pressure measurement tasks.
Conclusion: Which is Better for Your Needs?
Digital manometers offer precise, real-time pressure measurements with easy-to-read displays and portability, making them ideal for routine monitoring and troubleshooting in various applications. Dead weight testers provide highly accurate calibration standards and are preferred when traceability and certification are critical, especially in laboratory or calibration environments. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prioritize convenience and speed (digital manometer) or ultimate accuracy and calibration reliability (dead weight tester).
Digital manometer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com