Rotary clubs bring together professionals and community leaders dedicated to making a positive impact through service projects and humanitarian efforts worldwide. Emphasizing fellowship, integrity, and diversity, Rotary fosters connections that empower local and global change. Discover how your involvement with Rotary can transform lives and communities in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
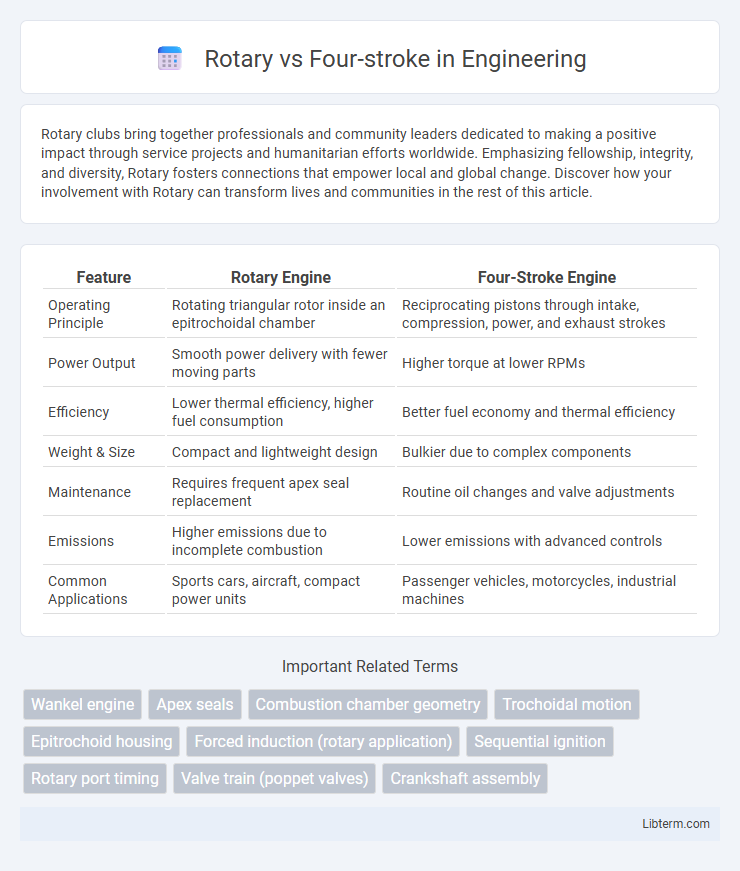
| Feature | Rotary Engine | Four-Stroke Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Rotating triangular rotor inside an epitrochoidal chamber | Reciprocating pistons through intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes |
| Power Output | Smooth power delivery with fewer moving parts | Higher torque at lower RPMs |
| Efficiency | Lower thermal efficiency, higher fuel consumption | Better fuel economy and thermal efficiency |
| Weight & Size | Compact and lightweight design | Bulkier due to complex components |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent apex seal replacement | Routine oil changes and valve adjustments |
| Emissions | Higher emissions due to incomplete combustion | Lower emissions with advanced controls |
| Common Applications | Sports cars, aircraft, compact power units | Passenger vehicles, motorcycles, industrial machines |
Overview of Rotary and Four-Stroke Engines
Rotary engines, also known as Wankel engines, utilize a triangular rotor spinning inside an epitrochoid-shaped housing to convert pressure into rotational motion, offering smooth power delivery with fewer moving parts. Four-stroke engines operate through intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes involving pistons moving reciprocally within cylinders, providing efficient fuel combustion and widespread application across vehicles. The compact design and high power-to-weight ratio characterize rotary engines, while four-stroke engines are favored for their fuel efficiency and reliability in diverse performance ranges.
Key Differences in Engine Design
Rotary engines feature a triangular rotor that spins within an epitrochoidal chamber, unlike four-stroke engines that use pistons moving up and down in cylinders. The rotary design enables smooth, high-revving operation with fewer moving parts, resulting in a compact and lightweight engine structure. In contrast, four-stroke engines rely on intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust strokes, providing higher fuel efficiency and easier emission control.
Performance Comparison: Power and Efficiency
Rotary engines deliver higher power-to-weight ratios due to their compact design and fewer moving parts, enabling quicker acceleration and smoother high-RPM performance compared to traditional four-stroke engines. Four-stroke engines typically achieve better fuel efficiency and emissions control through more precise combustion cycles, making them ideal for everyday driving and regulatory compliance. Despite the rotary engine's superior power density, four-stroke engines maintain an edge in reliability and overall energy efficiency across diverse operating conditions.
Maintenance and Longevity
Rotary engines feature fewer moving parts, resulting in simpler maintenance but generally shorter lifespan due to rotor apex seal wear. Four-stroke engines benefit from established maintenance routines and durable components, which contribute to their longer operational longevity. Regular oil changes and timely part replacements extend the lifespan of both engine types, but four-strokes typically offer greater reliability over time.
Fuel Consumption and Emissions
Rotary engines typically exhibit higher fuel consumption compared to four-stroke engines due to their continuous combustion cycle and less efficient sealing, leading to increased fuel usage. Emissions from rotary engines are generally higher, as incomplete combustion results in elevated levels of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. Four-stroke engines offer better fuel efficiency and lower emissions by employing separate intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust strokes, optimizing fuel burn and reducing pollutants.
Applications in Modern Vehicles
Rotary engines are commonly found in specialized sports cars and aircraft due to their compact size and high power-to-weight ratio, offering smooth high-rev performance ideal for racing and aviation applications. Four-stroke engines dominate mainstream vehicles, including sedans, trucks, and motorcycles, thanks to their fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and durability, making them suitable for everyday use and mass production. Modern electric and hybrid vehicles increasingly integrate four-stroke engines as range extenders, while rotary engines remain niche due to limited fuel economy and emissions challenges.
Advantages of Rotary Engines
Rotary engines offer a compact, lightweight design that delivers a high power-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications where space and weight are critical. Their smooth operation results from fewer moving parts, reducing vibration and wear compared to traditional four-stroke engines. Additionally, rotary engines achieve high RPM capabilities and produce consistent power output, enhancing performance in sports cars and aviation.
Benefits of Four-Stroke Engines
Four-stroke engines offer superior fuel efficiency and lower emissions compared to rotary engines, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective for long-term use. Their complex valve system provides better torque and power control, enhancing vehicle performance and reliability. Additionally, four-stroke engines have a more widespread infrastructure for maintenance and repair, increasing their practicality and lifespan.
Common Issues and Reliability
Rotary engines commonly face issues such as apex seal wear and overheating, which can lead to reduced compression and engine failure, whereas four-stroke engines primarily encounter problems like valve wear, timing chain issues, and oil consumption. Reliability in four-stroke engines is generally higher due to their simpler mechanical design and widespread use, leading to easier maintenance and availability of parts. Despite rotary engines offering high power-to-weight ratios, their complex sealing systems and cooling requirements make them less reliable over long-term use compared to the robust and well-understood four-stroke configurations.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Rotary engines offer advantages in compact size and high power-to-weight ratio, making them promising for lightweight, high-performance applications and hybrid electric systems. Four-stroke engines benefit from decades of technological advancements in fuel efficiency, emissions control, and durability, supporting their continued dominance in automotive and industrial sectors. Innovations such as advanced materials, variable valve timing, and integration with alternative fuels are shaping the future of four-stroke engines, while research into improving rotary engine thermal efficiency and sealing technology aims to overcome past limitations.
Rotary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com