Axonometric projection is a technique used in technical drawing and engineering to represent three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane, maintaining scale along each axis without distortion. This form of projection allows for clear visualization of complex structures by displaying multiple sides simultaneously, aiding in accurate design and comprehension. Explore the rest of the article to understand how axonometric projection can enhance your technical illustrations.
Table of Comparison
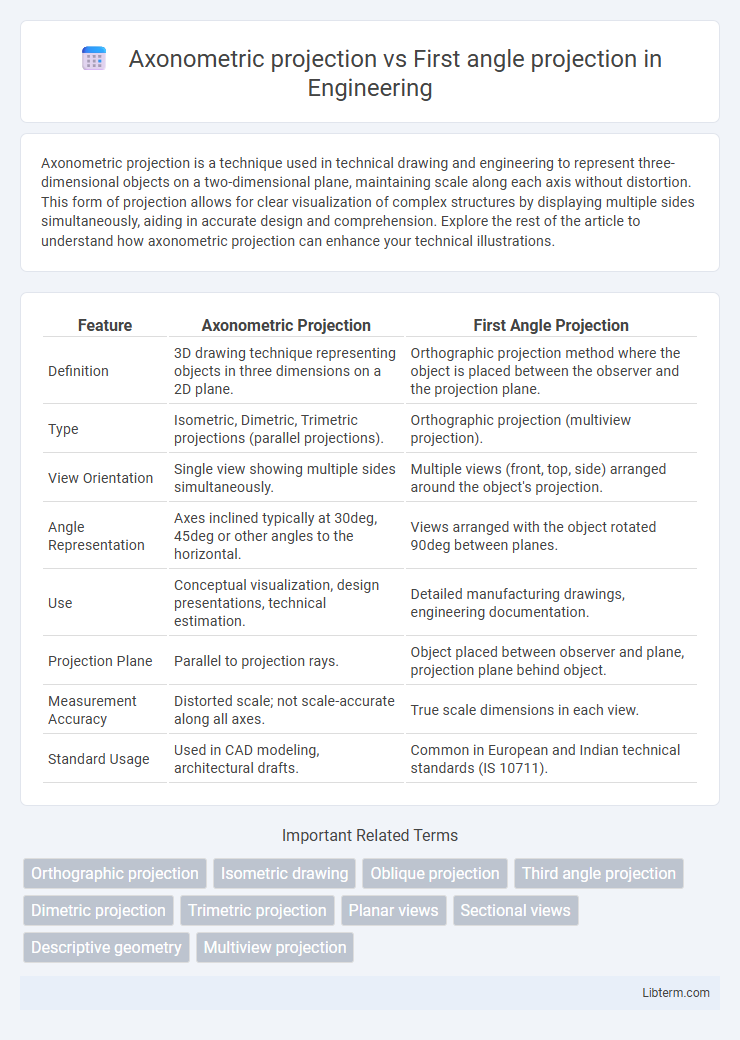
| Feature | Axonometric Projection | First Angle Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 3D drawing technique representing objects in three dimensions on a 2D plane. | Orthographic projection method where the object is placed between the observer and the projection plane. |
| Type | Isometric, Dimetric, Trimetric projections (parallel projections). | Orthographic projection (multiview projection). |
| View Orientation | Single view showing multiple sides simultaneously. | Multiple views (front, top, side) arranged around the object's projection. |
| Angle Representation | Axes inclined typically at 30deg, 45deg or other angles to the horizontal. | Views arranged with the object rotated 90deg between planes. |
| Use | Conceptual visualization, design presentations, technical estimation. | Detailed manufacturing drawings, engineering documentation. |
| Projection Plane | Parallel to projection rays. | Object placed between observer and plane, projection plane behind object. |
| Measurement Accuracy | Distorted scale; not scale-accurate along all axes. | True scale dimensions in each view. |
| Standard Usage | Used in CAD modeling, architectural drafts. | Common in European and Indian technical standards (IS 10711). |
Introduction to Projection Methods
Axonometric projection is a type of orthographic projection where the object is depicted with its axes tilted relative to the plane of projection, allowing three dimensions to be displayed simultaneously without distortion of scale along the axes. First angle projection, a principal method used in technical drawing primarily in Europe and Asia, involves placing the object between the observer and the projection plane, resulting in views projected opposite to their actual positions relative to the object. Understanding these projection methods is crucial for accurate interpretation and representation of spatial relationships in engineering and architectural designs.
Understanding Axonometric Projection
Axonometric projection is a type of orthographic projection where the object is depicted with its axes tilted relative to the plane of projection, allowing multiple sides to be visible simultaneously, unlike first angle projection which shows one view per plane. In axonometric projection, scale and dimensions along each axis are preserved, aiding in precise measurements and spatial visualization. This method is widely used in engineering and architecture for its ability to represent three-dimensional objects clearly without perspective distortion.
Fundamentals of First Angle Projection
First angle projection is a method used in technical drawing where the object is placed between the observer and the plane of projection, resulting in views projected onto planes opposite the object's faces. This technique forms the basis of many European and international drafting standards and emphasizes clear spatial relationships by projecting views in a specific sequence: front, top, and side. Axonometric projection differs fundamentally by representing three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane without distortion, maintaining scale along each axis and allowing simultaneous visualization of multiple faces.
Key Differences Between Axonometric and First Angle Projection
Axonometric projection offers a three-dimensional representation where scale is maintained along all axes, enabling clear visualization of an object's spatial structure without perspective distortion. First angle projection is a 2D orthographic technique primarily used in European engineering, where the object is placed between the observer and the plane, producing views arranged around the object's front view according to standardized layout conventions. Key differences include dimensionality--axonometric being 3D vs. first angle's 2D nature--and projection method, with axonometric preserving scale across axes, while first angle focuses on accurate, separate orthographic views for technical clarity.
Advantages of Axonometric Projection
Axonometric projection offers a clear advantage in visualizing objects by presenting three dimensions simultaneously without distortion of scale, making measurements directly from the drawing more accurate. It facilitates better spatial understanding and communication of complex designs in engineering and architecture compared to first angle projection, which only depicts two dimensions at a time. This method enhances clarity in technical documentation and supports efficient design analysis and modification.
Benefits of First Angle Projection
First Angle Projection offers clear visualization by placing the object between the viewer and the plane, making it easier for engineers to interpret views intuitively. It reduces confusion in technical drawings by maintaining consistent placement of views, which enhances communication across international teams familiar with ISO standards. This method simplifies dimensioning and reduces the risk of errors during manufacturing due to its standardized approach.
Applications in Engineering and Design
Axonometric projection, commonly used in engineering and design, enables the visualization of three-dimensional objects on two-dimensional media without distortion in scale, making it ideal for detailed technical drawings in mechanical and architectural fields. First angle projection, primarily applied in European engineering industries, provides standardized orthographic views that facilitate precise manufacturing and quality control by representing different object orientations clearly. Both projection methods are essential for accurately interpreting design specifications and ensuring effective communication between engineers, designers, and manufacturers.
Visual Representation: Axonometric vs First Angle
Axonometric projection offers a three-dimensional visual representation where the object is rotated along one or more of its axes, providing a clear view of multiple sides simultaneously without perspective distortion. First angle projection presents views as flat, orthogonal planes, arranging the object's front, top, and side views around the primary view to accurately depict dimensions but lacks a true 3D appearance. Axonometric views are valuable for visualizing spatial relationships, while first angle projection is essential for precise dimensional interpretation in technical drawings.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Axonometric projection faces challenges in accurately representing true dimensions, as scale distortion occurs due to the parallelogram shape of the projection, complicating measurements and spatial interpretation. First angle projection can lead to confusion because it reverses the placement of views compared to third angle projection, making it difficult for users unfamiliar with this standard to correctly interpret object orientation. Both methods have limitations in visual clarity; axonometric projection sacrifices realistic depth perception, while first angle projection may cause ambiguity in complex assemblies due to its layout conventions.
Choosing the Right Projection for Your Project
Selecting between axonometric projection and first angle projection depends on the project's visualization needs and industry standards. Axonometric projection offers a clear 3D representation without perspective distortion, ideal for technical and engineering drawings requiring spatial understanding. First angle projection, widely used in Europe, provides precise orthographic views for manufacturing and detailed component layout, ensuring accuracy in dimensions and assembly.
Axonometric projection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com