Gear drives efficiently transmit power between rotating shafts through interlocking toothed wheels, ensuring precise speed and torque control in mechanical systems. They are essential in applications ranging from industrial machinery to automotive transmissions, providing durability and reliability under varying load conditions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how gear drives can enhance your mechanical designs.
Table of Comparison
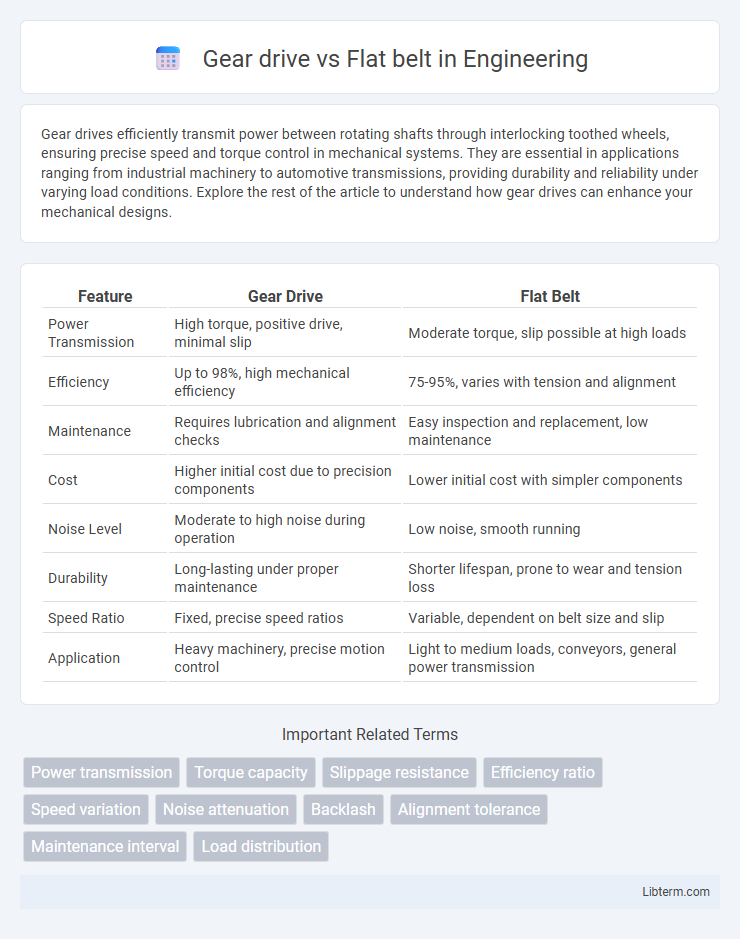
| Feature | Gear Drive | Flat Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | High torque, positive drive, minimal slip | Moderate torque, slip possible at high loads |
| Efficiency | Up to 98%, high mechanical efficiency | 75-95%, varies with tension and alignment |
| Maintenance | Requires lubrication and alignment checks | Easy inspection and replacement, low maintenance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to precision components | Lower initial cost with simpler components |
| Noise Level | Moderate to high noise during operation | Low noise, smooth running |
| Durability | Long-lasting under proper maintenance | Shorter lifespan, prone to wear and tension loss |
| Speed Ratio | Fixed, precise speed ratios | Variable, dependent on belt size and slip |
| Application | Heavy machinery, precise motion control | Light to medium loads, conveyors, general power transmission |
Introduction to Gear Drives and Flat Belts
Gear drives transmit mechanical power through meshing teeth, offering precise speed ratios and high torque capacity, ideal for heavy-duty applications and compact machinery. Flat belts function by friction between the belt surface and pulleys, providing smooth, flexible power transmission suitable for moderate load and high-speed operations. Both systems serve distinct roles in mechanical design, with gear drives excelling in accuracy and flat belts favored for simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Key Differences Between Gear Drive and Flat Belt
Gear drives transmit power through interlocking teeth on gears, offering precise speed ratios and higher torque capacity, suitable for heavy-duty applications. Flat belts transfer power via friction between the belt and pulleys, providing smoother operation and flexibility but generally lower torque transmission. Gear drives excel in accuracy and durability, whereas flat belts are preferred for quieter, low-maintenance, and cost-effective power transmission in lighter machinery.
Working Mechanism of Gear Drives
Gear drives transmit torque through interlocking teeth on meshing gears, ensuring precise speed ratios and synchronized motion with minimal slip. Unlike flat belts that rely on friction to transfer power, gear drives provide direct mechanical engagement, resulting in higher efficiency and load capacity. This mechanism enables gear drives to maintain consistent rotational speed and torque even under high load conditions.
Working Mechanism of Flat Belt Drives
Flat belt drives transmit power through friction between the flat belt and pulleys, relying on tension to maintain grip and prevent slippage. The belt wraps around the driving and driven pulleys, creating a frictional force that transfers rotational motion and torque efficiently over variable center distances. Unlike gear drives that engage through interlocking teeth, flat belt drives offer smoother, quieter operation and accommodate slight misalignments in machinery.
Efficiency Comparison: Gear Drive vs Flat Belt
Gear drives typically exhibit higher efficiency, often exceeding 95%, due to direct mechanical engagement that minimizes power loss. Flat belts, while offering smoother and quieter operation, generally achieve efficiency levels around 90-93% due to slip and friction losses. The choice between gear drives and flat belts depends on application requirements for precision, load capacity, and maintenance priorities.
Load Capacity and Durability
Gear drives offer superior load capacity due to their rigid tooth engagement, allowing them to transmit high torque efficiently without slipping. Their durability is enhanced by the use of hardened materials and precise manufacturing, resulting in long-lasting performance even under heavy and continuous loads. In contrast, flat belts provide lower load capacity and are more prone to wear, stretching, and slippage, which limits their durability in high-torque applications.
Maintenance Requirements
Gear drives require regular lubrication, periodic inspection for wear, and proper alignment to ensure efficient operation and prevent premature failure. Flat belts demand frequent tension adjustments, regular checking for cracks or fraying, and alignment of pulleys to maintain optimal performance. Compared to flat belts, gear drives generally have higher maintenance intensity due to lubrication needs and potential gear tooth wear.
Applications in Industry
Gear drives are preferred in heavy machinery and precision equipment due to their ability to transmit high torque with minimal slip and consistent speed ratios, making them ideal for automotive transmissions and industrial robots. Flat belts are commonly used in light to medium load applications such as conveyors, agricultural machinery, and textile production where flexibility, ease of maintenance, and low cost are prioritized. Industries requiring high-speed power transmission with lower noise levels often select flat belts, while gear drives dominate in environments demanding durability and compact design.
Cost Analysis: Gear Drive vs Flat Belt
Gear drives typically involve higher initial costs due to precision manufacturing and materials, but offer greater durability and lower maintenance expenses over time. Flat belts are generally less expensive upfront and easier to install, yet they may require more frequent replacement and tension adjustments, increasing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership often favors gear drives for heavy-duty applications, while flat belts remain cost-effective for light to moderate power transmission needs.
Choosing the Right Power Transmission System
Gear drives deliver precise, high-torque power transmission with minimal slippage, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring exact speed ratios and high efficiency. Flat belt drives offer quieter operation, flexibility in design, and cost-effectiveness for moderate power transmission and applications with variable center distances. Selecting the right system depends on factors such as load capacity, torque requirements, speed consistency, maintenance needs, and environmental conditions.
Gear drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com