Shot blasting is a surface treatment process that uses high-velocity steel abrasives to clean, strengthen, or polish metal surfaces. This method enhances adhesion for coatings, removes rust, and improves metal fatigue resistance, making it essential in manufacturing and maintenance. Discover how shot blasting can optimize your metal preparation by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
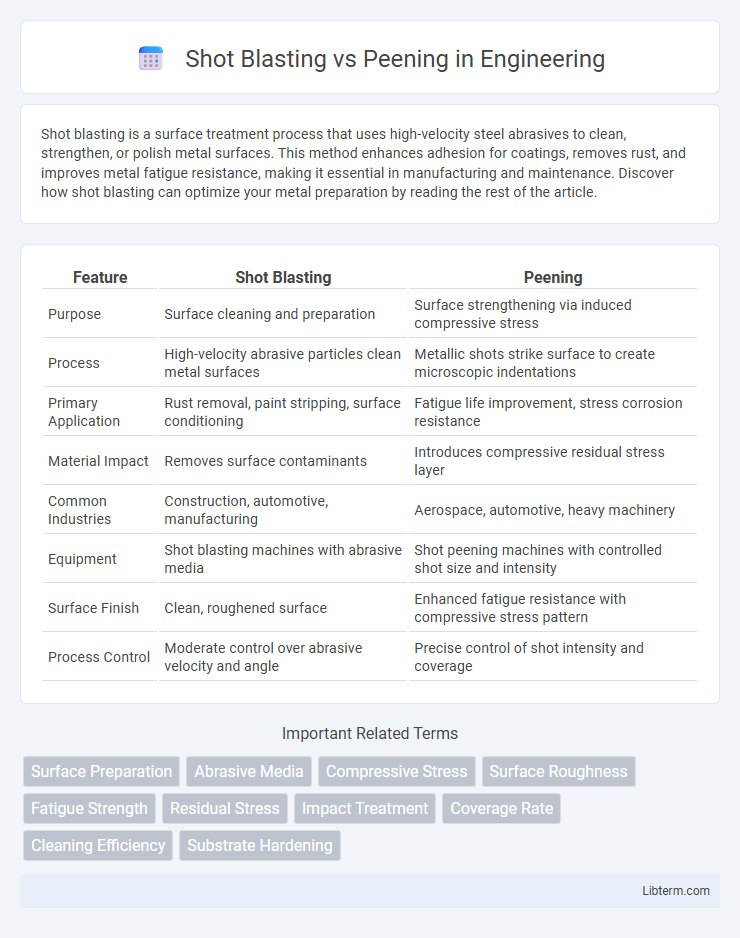
| Feature | Shot Blasting | Peening |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Surface cleaning and preparation | Surface strengthening via induced compressive stress |
| Process | High-velocity abrasive particles clean metal surfaces | Metallic shots strike surface to create microscopic indentations |
| Primary Application | Rust removal, paint stripping, surface conditioning | Fatigue life improvement, stress corrosion resistance |
| Material Impact | Removes surface contaminants | Introduces compressive residual stress layer |
| Common Industries | Construction, automotive, manufacturing | Aerospace, automotive, heavy machinery |
| Equipment | Shot blasting machines with abrasive media | Shot peening machines with controlled shot size and intensity |
| Surface Finish | Clean, roughened surface | Enhanced fatigue resistance with compressive stress pattern |
| Process Control | Moderate control over abrasive velocity and angle | Precise control of shot intensity and coverage |
Introduction to Shot Blasting and Peening
Shot blasting is a surface treatment process that propels abrasive materials at high velocity to clean, strengthen, or prepare metal surfaces for further processing. Peening, on the other hand, is a mechanical process that induces compressive residual stresses on a metal surface by impacting it with small spherical media, enhancing fatigue resistance and preventing crack propagation. Both techniques play crucial roles in industrial applications by improving surface durability and performance.
Understanding Surface Preparation Techniques
Shot blasting and peening are critical surface preparation techniques used to enhance metal durability and performance; shot blasting removes rust, scale, and contaminants by propelling abrasive particles at high velocity, improving surface cleanliness and texture. Peening involves impacting the metal surface with small spherical media to induce compressive residual stresses, which increases fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Selecting between shot blasting and peening depends on the specific application requirements, such as surface finish quality and mechanical property enhancement.
Shot Blasting: Process and Applications
Shot blasting is a surface treatment process that propels abrasive media, such as steel or glass beads, at high velocity to clean, strengthen, or polish metal surfaces. This method effectively removes rust, scale, and old coatings, preparing metals for further processing like painting or coating. Primarily used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction, shot blasting enhances surface durability and adhesion, ensuring improved performance and longevity of metal components.
Shot Peening: Process and Benefits
Shot peening is a surface enhancement process using small spherical media to impart compressive stresses on metal components, improving fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. This technique is commonly applied in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery industries to extend the service life of critical parts such as gears, springs, and turbine blades. Unlike shot blasting, which primarily cleans surfaces, shot peening enhances mechanical properties by creating a hardened, more durable surface layer.
Key Differences Between Shot Blasting and Peening
Shot blasting uses high-velocity abrasive particles to clean or prepare metal surfaces, primarily removing rust, scale, or debris. Peening involves impacting the metal surface with small spherical media to induce compressive stresses, enhancing fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. The key difference lies in shot blasting's focus on surface cleaning, while peening aims to improve mechanical properties through surface hardening.
Equipment and Materials Used in Each Method
Shot blasting utilizes high-velocity steel or abrasive grit propelled by centrifugal wheels or compressed air to clean or prepare surfaces, commonly employing equipment such as wheel blast machines or air blasting cabinets. Peening involves ceramic, glass, or steel shots delivered at controlled speeds via pneumatic or mechanical systems, using equipment like shot peening turbines or blast cabinets designed to induce compressive stresses to improve material fatigue strength. The key difference lies in the shot media and equipment calibration tailored for surface cleaning in shot blasting versus surface strengthening in peening processes.
Surface Finish Outcomes: Blasting vs Peening
Shot blasting produces a uniform, rough surface finish ideal for cleaning, descaling, and preparing metal surfaces for further coating or painting processes. Peening induces a smoother, more controlled surface with compressive residual stress, enhancing fatigue resistance and reducing the risk of crack initiation. The choice between blasting and peening directly affects surface morphology, durability, and the functional performance of metal components in industrial applications.
Industrial Applications: When to Use Each Technique
Shot blasting is ideal for heavy-duty surface preparation in industrial applications such as removing rust, scale, and old coatings from metal parts before painting or welding. Peening is primarily used for enhancing fatigue strength and stress resistance in critical components like automotive springs, aircraft landing gear, and turbine blades by inducing compressive residual stresses. Selecting shot blasting or peening depends on whether surface cleaning or mechanical property improvement is the primary goal in manufacturing or maintenance processes.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Shot blasting uses high-velocity abrasive particles to clean or prepare metal surfaces, requiring stringent protective gear and dust control systems to prevent inhalation hazards and environmental contamination. Peening involves mechanical impact to improve metal fatigue resistance, generating less airborne debris but still necessitates proper ventilation and personal protective equipment to ensure operator safety. Both processes must adhere to regulatory standards for noise, dust emissions, and waste disposal to minimize environmental impact and protect worker health.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Choosing between shot blasting and peening depends on the specific surface treatment goals and material requirements of your project. Shot blasting is ideal for cleaning and preparing surfaces by removing rust, scale, and contaminants, resulting in a smooth finish, while peening enhances mechanical properties by inducing compressive residual stresses that improve fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Evaluate factors such as desired surface texture, material hardness, and performance needs to select the method that balances cost-effectiveness with achieving optimal durability and quality.
Shot Blasting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com