Soil-structure interaction significantly affects the performance and stability of buildings and infrastructure during seismic events and heavy loads. Understanding the complex behavior between soil and foundation materials helps optimize design for safety and cost-effectiveness. Explore this article to learn how your projects can benefit from advanced soil-structure interaction analysis techniques.
Table of Comparison
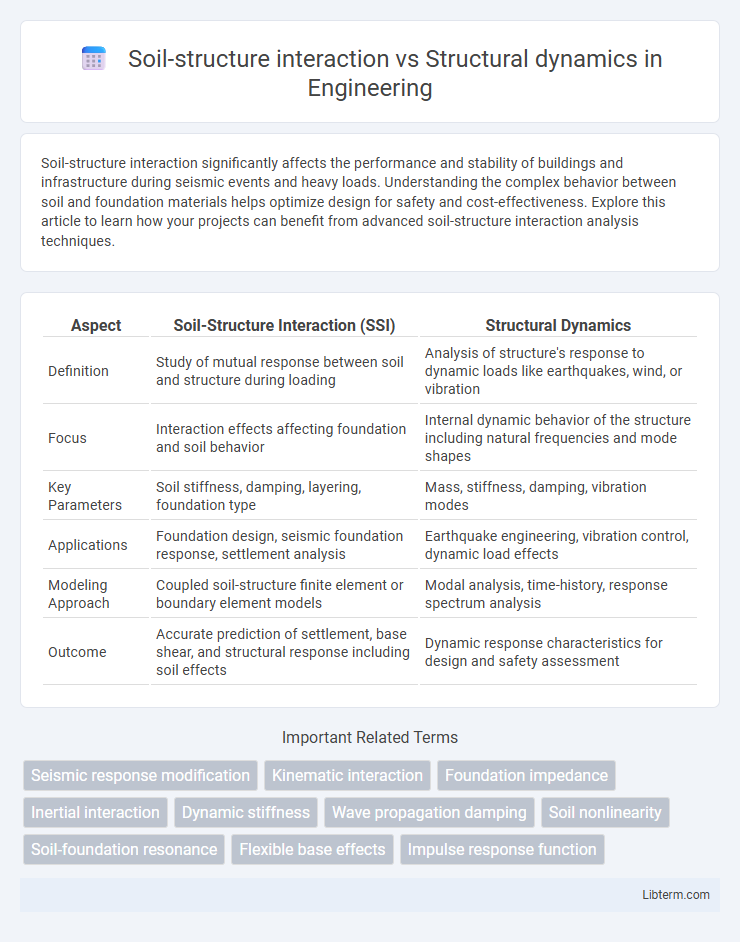
| Aspect | Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI) | Structural Dynamics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of mutual response between soil and structure during loading | Analysis of structure's response to dynamic loads like earthquakes, wind, or vibration |
| Focus | Interaction effects affecting foundation and soil behavior | Internal dynamic behavior of the structure including natural frequencies and mode shapes |
| Key Parameters | Soil stiffness, damping, layering, foundation type | Mass, stiffness, damping, vibration modes |
| Applications | Foundation design, seismic foundation response, settlement analysis | Earthquake engineering, vibration control, dynamic load effects |
| Modeling Approach | Coupled soil-structure finite element or boundary element models | Modal analysis, time-history, response spectrum analysis |
| Outcome | Accurate prediction of settlement, base shear, and structural response including soil effects | Dynamic response characteristics for design and safety assessment |
Introduction to Soil-Structure Interaction
Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI) analyzes the mutual response between soil and a structure during dynamic events such as earthquakes or wind loads, affecting the overall stability and performance of the structure. Unlike traditional Structural Dynamics, which considers structures in isolation, SSI integrates geotechnical conditions, including soil stiffness, damping, and nonlinearity, to provide a more accurate prediction of structural behavior. Understanding SSI is crucial for designing resilient foundations, optimizing seismic performance, and mitigating damage in civil infrastructure projects.
Fundamentals of Structural Dynamics
Fundamentals of structural dynamics involve analyzing how structures respond to dynamic loads such as wind, earthquakes, and machinery vibrations, focusing on parameters like natural frequencies, mode shapes, and damping. Soil-structure interaction (SSI) extends this by considering the mutual response between the structure and the supporting soil, which alters the dynamic properties and affects the structural response under seismic or dynamic excitation. Understanding SSI is critical for accurate dynamic analysis and design, ensuring safety and performance in engineering structures subjected to transient loads.
Key Differences Between Soil-Structure Interaction and Structural Dynamics
Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI) examines the mutual response between the foundation soil and the structure during seismic or dynamic loading, emphasizing how soil properties influence structural behavior. Structural Dynamics focuses solely on the response of structures to dynamic forces, including vibration and shock, without explicitly considering the supporting soil's role. Key differences lie in SSI's coupled analysis incorporating soil flexibility and damping effects, while Structural Dynamics typically assumes fixed-base conditions or simplified support models.
Physical Mechanisms of Soil-Structure Interaction
Soil-structure interaction (SSI) involves the mutual response between soil deformability and structural behavior, where soil properties such as stiffness, damping, and nonlinearities directly influence structural vibrations and load distributions. The physical mechanisms of SSI include wave propagation through soil layers, radiation damping, and soil plasticity, which alter natural frequencies and mode shapes of the structure compared to fixed-base assumptions in structural dynamics. Understanding these interactions is crucial for accurate seismic response prediction, foundation settlement assessment, and mitigating resonance effects in critical infrastructure.
Dynamic Response of Structures
Soil-structure interaction significantly influences the dynamic response of structures by altering natural frequencies and damping characteristics, leading to modified vibration modes compared to free-field conditions. Structural dynamics examines these time-dependent behaviors under dynamic loads such as earthquakes or wind, emphasizing the importance of accurately modeling foundation flexibility and soil behavior. Accurate prediction of dynamic responses ensures improved seismic resilience and serviceability of engineered structures.
Modeling Techniques for SSI and Structural Dynamics
Modeling techniques for Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI) emphasize coupled numerical methods, such as finite element and boundary element methods, to accurately simulate soil behavior and its impact on structural response under dynamic loads. Structural dynamics modeling primarily relies on modal analysis, response spectrum methods, and time-history analysis to predict structural responses to dynamic forces, often assuming fixed-base conditions. Advanced SSI modeling integrates soil nonlinearities and radiation damping, enhancing the fidelity of dynamic response predictions beyond traditional fixed-base structural dynamic models.
Influence of Soil Properties on Structural Behavior
Soil-structure interaction significantly affects structural dynamics by altering natural frequencies and damping characteristics due to soil stiffness and damping properties. Variations in soil type, density, and moisture content influence foundation settlement and lateral displacement, impacting the overall structural response under dynamic loads such as earthquakes or wind. Accurate modeling of soil properties is essential for predicting structural behavior and ensuring stability and safety in seismic design.
Seismic Analysis: SSI vs Structural Dynamics
Seismic analysis of Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI) examines the mutual response between soil and structure, significantly influencing the natural frequency and damping characteristics of the system. Structural dynamics primarily studies the behavior of structures under dynamic loads, focusing on modal properties without considering soil flexibility and inertia effects. SSI models provide more accurate predictions of seismic response by integrating soil compliance, wave scattering, and energy dissipation, whereas pure structural dynamics often assumes a rigid base, potentially underestimating seismic demands.
Design Considerations for Engineers
Soil-structure interaction (SSI) significantly influences structural dynamics by altering natural frequencies, damping, and mode shapes, requiring engineers to integrate geotechnical properties such as soil stiffness, damping ratio, and layering into dynamic response models. Design considerations include performing site-specific seismic hazard analyses and employing coupled soil-structure numerical simulations to predict performance under dynamic loads accurately. Engineers must balance structural flexibility and foundation design to mitigate resonance effects and ensure safety margins in earthquake engineering and vibration-sensitive structures.
Future Trends and Research Directions
Emerging trends in soil-structure interaction research emphasize advanced numerical modeling techniques integrating machine learning to predict seismic responses more accurately. Future directions include developing coupled simulation frameworks that address non-linear behaviors and multi-hazard scenarios, enhancing resilience in infrastructure design. Structural dynamics research increasingly focuses on real-time monitoring and adaptive control systems to mitigate dynamic loads from earthquakes and wind, promoting smarter, safer buildings.
Soil-structure interaction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com