Jib cranes provide flexible lifting solutions ideal for workshops, garages, and manufacturing floors. Their compact design allows easy rotation and precise load handling, enhancing workplace safety and efficiency. Discover how a jib crane can improve your operations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
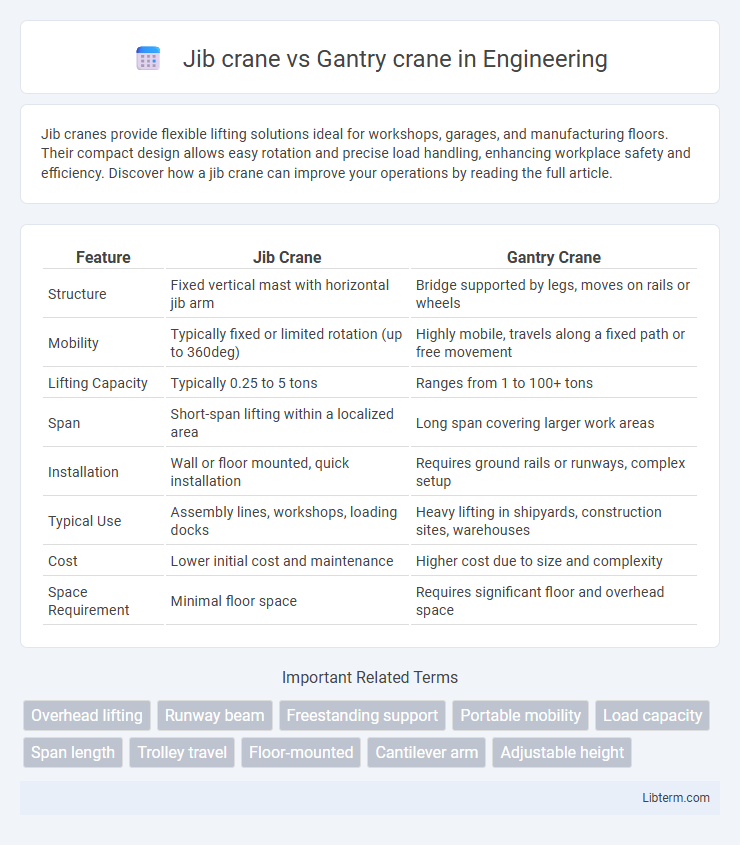
| Feature | Jib Crane | Gantry Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fixed vertical mast with horizontal jib arm | Bridge supported by legs, moves on rails or wheels |
| Mobility | Typically fixed or limited rotation (up to 360deg) | Highly mobile, travels along a fixed path or free movement |
| Lifting Capacity | Typically 0.25 to 5 tons | Ranges from 1 to 100+ tons |
| Span | Short-span lifting within a localized area | Long span covering larger work areas |
| Installation | Wall or floor mounted, quick installation | Requires ground rails or runways, complex setup |
| Typical Use | Assembly lines, workshops, loading docks | Heavy lifting in shipyards, construction sites, warehouses |
| Cost | Lower initial cost and maintenance | Higher cost due to size and complexity |
| Space Requirement | Minimal floor space | Requires significant floor and overhead space |
Introduction to Jib Cranes and Gantry Cranes
Jib cranes feature a horizontal arm fixed to a vertical mast or wall, enabling rotation and localized lifting, ideal for small workshops and assembly lines. Gantry cranes consist of a bridge supported by two or more legs running on tracks, designed for heavy-duty lifting in outdoor yards and shipping docks. Both cranes optimize workflow by facilitating material handling, but jib cranes excel in confined spaces while gantry cranes manage larger, heavier loads across wider areas.
Key Differences Between Jib and Gantry Cranes
Jib cranes feature a fixed vertical mast with a horizontal jib arm that pivots to lift and move loads within a limited radius, ideal for localized material handling. Gantry cranes consist of a bridge supported by two or more legs that move on wheels or rails, enabling them to handle much heavier loads over larger areas such as shipyards and warehouses. The primary differences lie in their structure, mobility, load capacity, and operational range, with jib cranes being compact and suited for shorter reach, while gantry cranes offer broad coverage and higher lifting power.
Design and Structural Comparison
Jib cranes feature a horizontal arm fixed to a vertical mast, allowing rotational movement within a limited radius, ideal for localized lifting tasks, while gantry cranes possess a bridge supported by two vertical legs on wheels or rails, enabling full overhead coverage and heavy-duty lifting. Structurally, jib cranes are compact and mounted either on walls, floors, or ceilings, making them space-efficient but limited in reach and load capacity; gantry cranes require larger footprints and robust framework designed to handle wider spans and significantly heavier loads. The design differences influence their applications: jib cranes excel in confined or fixed workstations, whereas gantry cranes serve expansive areas such as shipyards or construction sites demanding versatile and high-capacity lifting solutions.
Load Capacity and Lifting Capabilities
Jib cranes typically handle load capacities ranging from 500 kg to 5 tons, ideal for localized lifting in confined spaces, while gantry cranes support much heavier loads, often exceeding 20 tons, making them suitable for large-scale industrial lifting tasks. The jib crane's lifting radius is limited by its cantilever arm, whereas gantry cranes provide a broader range of motion with their overhead bridge structure, enabling the movement of heavier loads over larger areas. Load capacity and lifting capabilities directly influence the choice between jib and gantry cranes based on operational requirements and spatial constraints.
Installation and Space Requirements
Jib cranes require minimal installation space due to their wall or floor-mounted design, making them ideal for tight workplaces and localized lifting tasks. Gantry cranes demand a larger footprint for setup, as their overhead beam and supporting legs must span the entire working area, offering greater coverage for heavy or bulk materials. The installation of gantry cranes is more complex and time-consuming compared to jib cranes, often involving anchoring heavy rail systems or wheels on the ground.
Mobility and Flexibility
Jib cranes offer limited mobility as they are usually fixed to a single location, making them ideal for repetitive tasks within a confined workspace. Gantry cranes provide superior mobility and flexibility, featuring wheels or tracks that allow them to move heavy loads across larger work areas or multiple locations. This mobility advantage makes gantry cranes highly suitable for outdoor projects and dynamic industrial environments requiring versatile lifting solutions.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Jib cranes are ideal for localized, repetitive lifting tasks in manufacturing, workshops, and warehouses, providing flexibility for loading and unloading materials within a confined radius. Gantry cranes are suited for heavy-duty, large-scale operations such as shipyards, construction sites, and container yards, where they handle bulk materials and large containers across wide spans. Industries like automotive, metal fabrication, and logistics commonly use jib cranes, while gantry cranes find extensive application in ports, rail yards, and heavy manufacturing.
Safety Considerations and Guidelines
Jib cranes require secure mounting and regular inspection of the swing mechanism to prevent accidents, while gantry cranes demand thorough checks of rail alignment and load capacity to avoid tipping hazards. Both crane types must adhere to OSHA regulations, including operator training, proper signaling, and routine maintenance schedules. Implementing comprehensive load testing and ensuring clear operational zones are critical for minimizing risks associated with overhead lifting equipment.
Cost Analysis and Maintenance
Jib cranes typically have lower initial costs and simpler installation compared to gantry cranes, making them ideal for localized lifting tasks in smaller workspaces. Gantry cranes require higher upfront investment due to their larger size and more complex structure but offer greater load capacity and versatility for outdoor or heavy-duty applications. Maintenance costs for jib cranes are generally lower, involving routine inspections and lubrication, while gantry cranes demand more intensive upkeep, including structural inspections and potential component replacements to ensure operational safety and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Crane for Your Needs
Jib cranes excel in localized lifting tasks with limited workspace, offering 360-degree rotation and ease of installation, making them ideal for repetitive, short-distance material handling. Gantry cranes provide greater lifting capacity and span, suited for outdoor or large-scale operations requiring mobility across wider areas and heavy load movement. Choosing the right crane depends on factors like load weight, workspace size, operational frequency, and mobility requirements to ensure efficiency and safety.
Jib crane Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com