Mechanical seals are critical components designed to prevent leakage between rotating shafts and stationary housings in pumps and compressors, ensuring efficient operation. Their reliable performance extends equipment lifespan, reduces maintenance costs, and enhances safety in various industrial applications. Explore the rest of the article to learn how selecting the right mechanical seal can optimize Your system's performance.
Table of Comparison
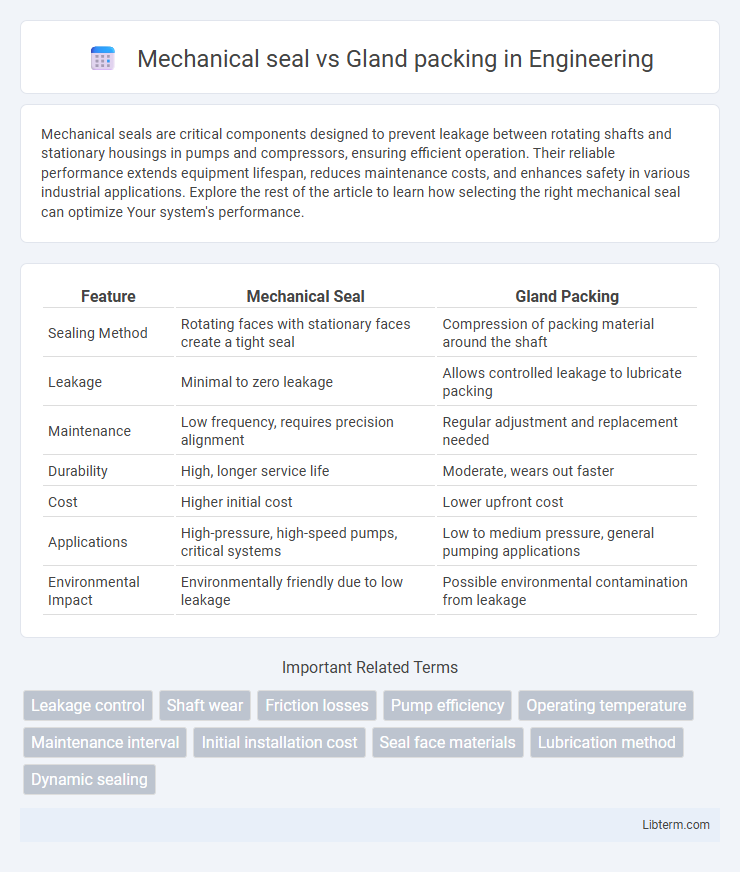
| Feature | Mechanical Seal | Gland Packing |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Method | Rotating faces with stationary faces create a tight seal | Compression of packing material around the shaft |
| Leakage | Minimal to zero leakage | Allows controlled leakage to lubricate packing |
| Maintenance | Low frequency, requires precision alignment | Regular adjustment and replacement needed |
| Durability | High, longer service life | Moderate, wears out faster |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Applications | High-pressure, high-speed pumps, critical systems | Low to medium pressure, general pumping applications |
| Environmental Impact | Environmentally friendly due to low leakage | Possible environmental contamination from leakage |
Introduction to Mechanical Seal and Gland Packing
Mechanical seals and gland packing are essential components used to prevent leakage in rotating equipment such as pumps and compressors. Mechanical seals offer a modern sealing solution by using precisely engineered faces that maintain a tight seal through controlled contact and lubrication, increasing reliability and reducing maintenance. Gland packing, a traditional sealing method, involves compressible materials packed into a stuffing box, relying on friction to create a seal but often requiring frequent adjustments and producing more wear.
Understanding the Basics: How Each System Works
Mechanical seals use a rotating seal face and a stationary seal face pressed together by a spring or bellows, creating a tight barrier that prevents fluid leakage in pumps and rotating equipment. Gland packing consists of braided fibers compressed into a stuffing box around a shaft, forming a seal by controlling the leakage through friction and pressure. Mechanical seals provide superior leak control and longer service life, while gland packing offers a simpler, cost-effective solution requiring regular maintenance and adjustment.
Key Components of Mechanical Seals vs. Gland Packing
Mechanical seals consist of primary sealing rings, secondary seals, a gland plate, and a spring mechanism to maintain contact and prevent leakage. Gland packing relies on braided or woven packing material compressed by a gland follower to create a seal around the shaft. The mechanical seal's precision components enable superior sealing performance and reduced maintenance compared to the simpler, more wear-prone components of gland packing.
Main Applications and Industries
Mechanical seals are predominantly used in high-pressure and high-speed applications such as pumps, compressors, and mixers within the chemical, petrochemical, and pharmaceutical industries due to their superior leak prevention and durability. Gland packing finds extensive use in industries like water treatment, pulp and paper, and general manufacturing where moderate pressure and lower-speed operations benefit from its cost-effectiveness and ease of maintenance. Both sealing methods are critical in industries requiring fluid containment but differ substantially in their suitability based on operational conditions and regulatory standards.
Performance Efficiency: Mechanical Seal vs. Gland Packing
Mechanical seals offer superior performance efficiency compared to gland packing by providing a more reliable, leak-free seal that reduces friction and wear. Unlike gland packing, mechanical seals minimize fluid leakage and require less maintenance, resulting in lower operating costs and prolonged equipment life. The enhanced sealing capability of mechanical seals allows for higher pressure and temperature handling, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Mechanical seals require precise alignment and clean installation environments to ensure optimal performance, with components often needing specialist tools and trained personnel for fitting. Maintenance involves routine inspections and occasional seal face replacement, offering longer service intervals compared to gland packing. Gland packing installation is simpler, involving manual adjustment of packing rings around the shaft, but demands frequent tightening and lubrication to prevent leakage and wear, resulting in higher maintenance frequency.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Mechanical seals typically require a higher initial investment compared to gland packing due to their complex design and advanced materials. However, mechanical seals offer lower long-term maintenance costs and reduced downtime, leading to greater overall cost efficiency. Gland packing demands frequent replacement and more labor-intensive maintenance, resulting in higher cumulative expenses over time despite its lower upfront cost.
Leakage Control and Environmental Impact
Mechanical seals offer superior leakage control by providing a tight, reliable barrier that minimizes fluid escape, reducing operational downtime and product loss. In contrast, gland packing tends to allow more leakage due to its reliance on compression and wear, leading to higher maintenance and environmental pollution. The reduced leakage of mechanical seals significantly lowers the environmental impact by preventing hazardous fluid emissions and promoting sustainable industrial practices.
Reliability and Operational Lifespan
Mechanical seals offer superior reliability and longer operational lifespan compared to gland packing due to their precise design, which minimizes leakage and wear under high-pressure and high-speed conditions. Gland packing requires frequent adjustments and often leads to higher maintenance costs and downtime as it wears unevenly and degrades faster in harsh environments. For industries prioritizing consistent performance and reduced maintenance intervals, mechanical seals provide a more durable and dependable sealing solution.
Choosing the Right Sealing Solution: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right sealing solution between mechanical seal and gland packing depends on factors such as operating pressure, temperature, and fluid type. Mechanical seals offer superior leak prevention and lower maintenance for high-speed, high-pressure applications, while gland packing is cost-effective and simpler to install for low-pressure systems with less critical sealing needs. Evaluating equipment specifications, operational conditions, and long-term maintenance costs is essential for optimal seal performance and reliability.
Mechanical seal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com