Layer of Protection Analysis (LOPA) is a risk assessment method used to evaluate the effectiveness of safety layers in preventing hazardous events. It provides a systematic approach to quantify risk by combining initiating event frequency with the probability of failure for independent protection layers. Explore the rest of the article to understand how LOPA can enhance your process safety management strategy.
Table of Comparison
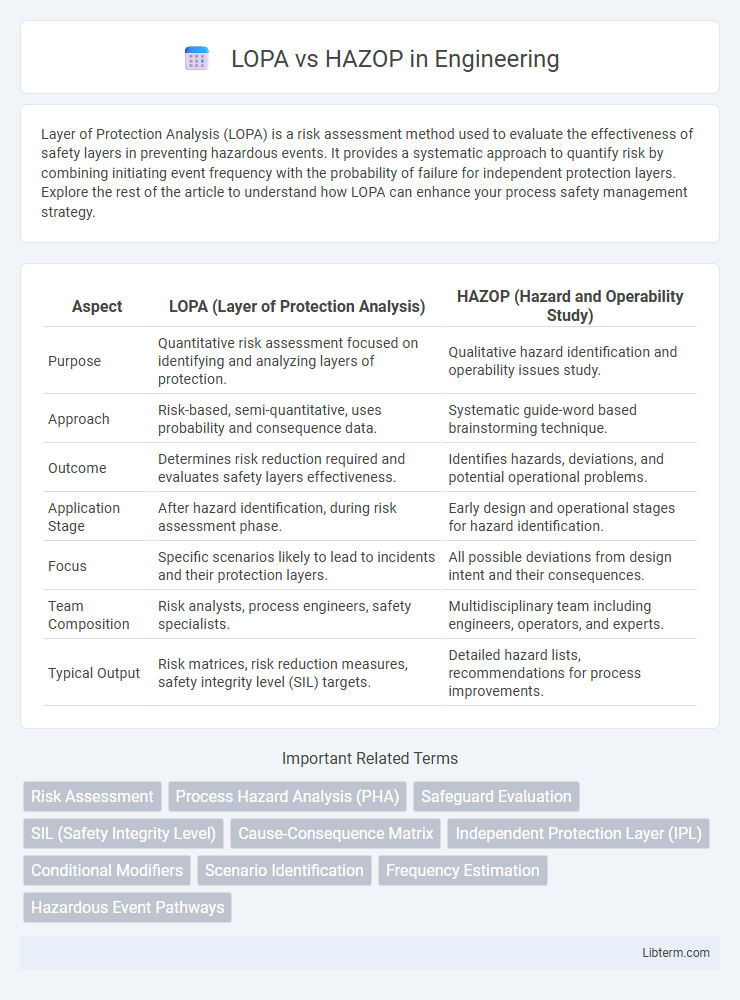
| Aspect | LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) | HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Quantitative risk assessment focused on identifying and analyzing layers of protection. | Qualitative hazard identification and operability issues study. |
| Approach | Risk-based, semi-quantitative, uses probability and consequence data. | Systematic guide-word based brainstorming technique. |
| Outcome | Determines risk reduction required and evaluates safety layers effectiveness. | Identifies hazards, deviations, and potential operational problems. |
| Application Stage | After hazard identification, during risk assessment phase. | Early design and operational stages for hazard identification. |
| Focus | Specific scenarios likely to lead to incidents and their protection layers. | All possible deviations from design intent and their consequences. |
| Team Composition | Risk analysts, process engineers, safety specialists. | Multidisciplinary team including engineers, operators, and experts. |
| Typical Output | Risk matrices, risk reduction measures, safety integrity level (SIL) targets. | Detailed hazard lists, recommendations for process improvements. |
Introduction to LOPA and HAZOP
LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) is a semi-quantitative risk assessment method used to evaluate the effectiveness of safety layers in preventing hazardous events. HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) is a systematic qualitative technique designed to identify potential hazards and operability problems in process plants through structured brainstorming sessions. Both LOPA and HAZOP are critical tools in process safety management, with HAZOP focusing on hazard identification and LOPA on risk mitigation verification.
Definitions: What Are LOPA and HAZOP?
LOPA, or Layers of Protection Analysis, is a risk assessment method used to evaluate the effectiveness of independent protection layers in preventing hazardous events and quantifying risk levels. HAZOP, or Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic technique aimed at identifying potential hazards and operational issues through detailed examination of process deviations within industrial systems. Both methods serve distinct roles in safety management, with LOPA focusing on risk quantification and HAZOP emphasizing hazard identification and process review.
Core Objectives of LOPA and HAZOP
LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) focuses on quantifying risk by evaluating independent protection layers to prevent hazardous events, ensuring that risk is reduced to a tolerable level. HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) systematically identifies process hazards and operability problems by analyzing deviations in process parameters through guide words. Both methodologies aim to enhance process safety but LOPA emphasizes risk assessment and mitigation effectiveness, while HAZOP centers on hazard identification and process design review.
Methodology: Step-by-Step Processes
LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) involves identifying initiating events, estimating risk levels, and evaluating the effectiveness of existing protection layers to determine if additional safeguards are needed. HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) systematically examines process deviations by applying guide words to assess potential hazards and operability issues within process parameters. Both methodologies require multidisciplinary teams, but LOPA quantifies risk through scenario analysis while HAZOP emphasizes qualitative identification of hazards and causes during detailed process reviews.
Key Differences Between LOPA and HAZOP
LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) quantifies risk reduction by evaluating independent protection layers, while HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) systematically identifies hazards and operability problems through structured brainstorming. LOPA provides semi-quantitative analysis focusing on risk scenarios, whereas HAZOP emphasizes qualitative identification of deviations in process parameters. Key differences include LOPA's risk quantification role in risk management compared to HAZOP's detailed hazard identification and process design improvement.
When to Use LOPA vs. HAZOP
LOPA is most effective during risk assessment phases to quantify the risk of specific hazardous events by analyzing independent protection layers, making it suitable when clear scenarios and risk tolerance criteria are defined. HAZOP excels in the early design stage or process review by systematically identifying potential deviations from design intent and uncovering unknown hazards through detailed guide word analysis. Use LOPA when objective risk evaluation is needed for decision-making on safety layers, and deploy HAZOP when comprehensive hazard identification and process safety optimization are priorities.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) offers a quantitative risk assessment method, providing clear criteria for risk tolerance and the effectiveness of safety layers, which facilitates decision-making in process safety. HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) excels in qualitative hazard identification by systematically examining deviations from design intent, allowing for comprehensive identification of potential operability issues and process hazards. LOPA's limitation lies in its reliance on predefined scenarios and probability data, potentially overlooking unknown hazards, while HAZOP can be time-consuming and may generate less precise risk quantification, impacting prioritization of safety measures.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) and HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) are critical safety assessment tools widely applied in chemical, oil and gas, and manufacturing industries. HAZOP systematically identifies potential hazards and operability issues in process designs, often serving as a foundation for LOPA, which quantifies risk levels and evaluates the effectiveness of independent protection layers. Case studies demonstrate HAZOP's role in uncovering design flaws early in chemical plants, while LOPA is extensively used in refining and petrochemical sectors to ensure compliance with safety integrity level (SIL) requirements and optimize risk reduction measures.
Integration of LOPA and HAZOP in Risk Management
LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis) and HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) integrate in risk management by combining qualitative hazard identification with quantitative risk assessment to enhance safety decision-making. HAZOP systematically identifies potential deviations and hazards in process systems, while LOPA evaluates the effectiveness of existing safeguards and estimates risk levels using independent protection layers. This integration enables organizations to prioritize risk reduction measures efficiently, ensuring comprehensive hazard analysis and robust safety management.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Plant
LOPA provides a semi-quantitative risk assessment that identifies layered protection systems, making it ideal for prioritizing safety measures based on risk tolerance. HAZOP offers a systematic qualitative analysis to detect process deviations and hazards through detailed guidewords, excelling in early design phase evaluations. Selecting the right approach depends on the plant's risk management objectives, project stage, and depth of analysis required to ensure optimal process safety.
LOPA Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com