Modbus and DeviceNet are popular industrial communication protocols widely used for connecting automation devices and systems. Modbus offers simplicity and ease of integration in serial and Ethernet networks, while DeviceNet provides a robust solution with embedded diagnostics and network management features. Discover how these protocols can enhance your industrial automation by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
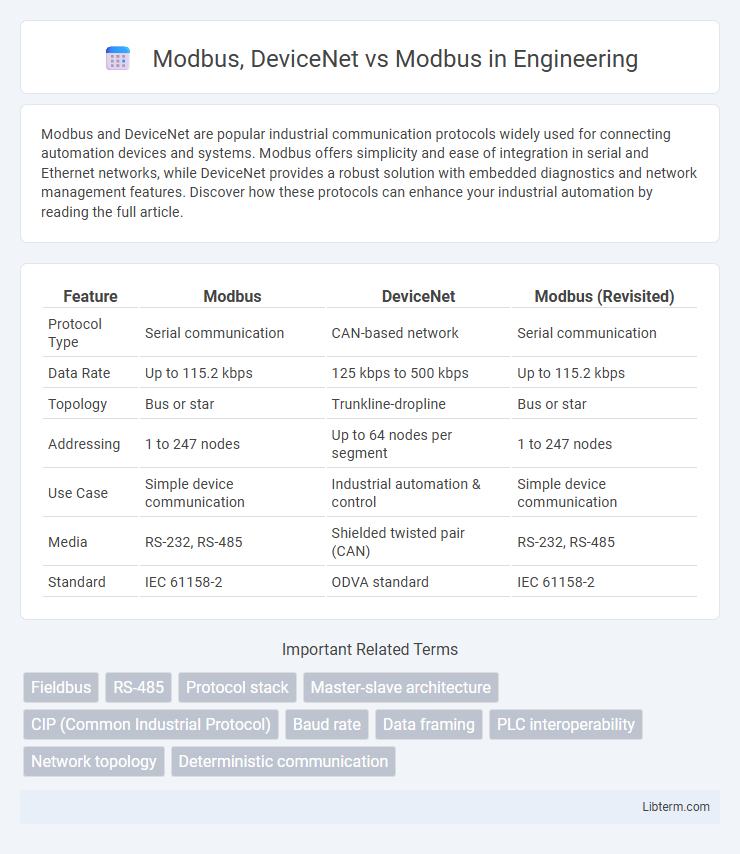
| Feature | Modbus | DeviceNet | Modbus (Revisited) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Serial communication | CAN-based network | Serial communication |
| Data Rate | Up to 115.2 kbps | 125 kbps to 500 kbps | Up to 115.2 kbps |
| Topology | Bus or star | Trunkline-dropline | Bus or star |
| Addressing | 1 to 247 nodes | Up to 64 nodes per segment | 1 to 247 nodes |
| Use Case | Simple device communication | Industrial automation & control | Simple device communication |
| Media | RS-232, RS-485 | Shielded twisted pair (CAN) | RS-232, RS-485 |
| Standard | IEC 61158-2 | ODVA standard | IEC 61158-2 |
Introduction to Modbus and DeviceNet
Modbus is a communication protocol primarily used in industrial automation for connecting electronic devices and facilitating data exchange via serial or Ethernet networks. DeviceNet, developed by ODVA, is a network protocol based on CAN (Controller Area Network) technology, designed specifically for robust communication between industrial devices and control equipment. While Modbus offers simplicity and wide adoption for basic device communication, DeviceNet provides enhanced device integration, real-time data transfer, and network diagnostics suitable for complex industrial systems.
Overview of Modbus Protocol
Modbus protocol is a widely-used communication standard in industrial automation, enabling seamless data exchange between devices such as sensors, controllers, and actuators. Compared to DeviceNet, which operates on a CAN-based network suitable for real-time control and device-level communication, Modbus excels in simplicity and interoperability across various hardware platforms and network types, including serial RS-485 and TCP/IP. Its open-standard design facilitates easy integration, troubleshooting, and scalability in monitoring and controlling industrial equipment.
Overview of DeviceNet Protocol
DeviceNet protocol is an industrial communication network based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) technology, designed for connecting industrial devices such as sensors, actuators, and controllers in automation systems. It enables real-time data transfer with efficient messaging and supports a wide range of device profiles, simplifying integration and configuration compared to Modbus, which primarily focuses on a master-slave communication model over serial or Ethernet networks. DeviceNet's event-driven architecture and built-in error checking enhance robust device-to-device communication in complex industrial environments, offering scalability and improved network diagnostics over Modbus.
Communication Architecture Comparison
Modbus employs a simple master-slave communication architecture using a single master device to control multiple slave devices over serial or TCP/IP networks, enabling straightforward and cost-effective integration. DeviceNet utilizes a more complex master-slave/token-passing architecture based on the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol, supporting peer-to-peer communication and dynamic device addressing for enhanced scalability and real-time control. The Modbus architecture favors simplicity and ease of implementation, while DeviceNet's architecture provides greater robustness, network flexibility, and faster data exchange suited for industrial automation systems.
Topology and Network Structure
Modbus operates primarily on a simple bus topology, supporting point-to-point and multi-drop communication with a master-slave network structure, which limits its scalability in large or complex industrial systems. DeviceNet, built on the CAN (Controller Area Network) protocol, uses a robust bus or trunkline-dropline topology, enabling flexible, distributed device networks with multi-master capabilities that enhance fault tolerance and data throughput. While Modbus excels in straightforward serial communication, DeviceNet provides advanced network management and real-time data exchange suitable for intricate automation environments.
Data Transmission Methods
Modbus employs a master-slave communication model using serial communication protocols such as RS-232, RS-485, or TCP/IP for data transmission, focusing on simplicity and widespread compatibility. DeviceNet utilizes a Controller Area Network (CAN) bus protocol, featuring a peer-to-peer communication method that supports real-time data exchange and automatic device addressing. Modbus is typically suited for straightforward, slower data transmission, while DeviceNet excels in fast, deterministic data transfer within complex industrial automation systems.
Device Compatibility and Integration
DeviceNet offers superior device compatibility and integration compared to Modbus due to its standardized application layer and support for a wider range of industrial devices with built-in device profiles. Modbus, while widely adopted for its simplicity and ease of implementation, often requires custom configuration for integrating diverse devices, which can limit seamless interoperability. DeviceNet's use of Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) enables automatic device configuration and robust network diagnostics, enhancing integration efficiency in complex automation systems.
Performance and Speed Analysis
Modbus and DeviceNet differ significantly in performance and speed, with DeviceNet typically offering higher data transfer rates up to 500 kbps compared to Modbus RTU's standard 19.2 kbps, making DeviceNet more suitable for applications requiring faster communication. Modbus, popular for its simplicity and broad device compatibility, operates efficiently in slower, less complex networks but may experience latency in high-demand environments. The choice between the two protocols hinges on the application's real-time data needs and network complexity, with DeviceNet excelling in robust industrial automation systems requiring rapid and deterministic communication.
Application Areas and Industry Usage
Modbus is widely used in industrial automation for simple, cost-effective communication in applications like building management, energy monitoring, and process control, particularly within legacy systems. DeviceNet, built on CAN bus technology, excels in complex automation environments requiring robust device-level networking such as automotive manufacturing, robotics, and factory floor control systems. While Modbus remains dominant in serial communication and SCADA systems, DeviceNet is preferred for real-time data exchange and diagnostics in heavy machinery and industrial equipment integration.
Choosing Between DeviceNet and Modbus
Choosing between DeviceNet and Modbus depends on the application's complexity and network requirements. DeviceNet offers higher-speed communication and built-in device profiles ideal for automation systems with multiple devices, while Modbus provides a simpler, widely supported protocol suitable for basic serial or TCP/IP communication. Evaluating factors such as network scalability, device compatibility, and communication speed helps determine the optimal protocol for industrial control systems.
Modbus, DeviceNet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com