Modbus and Profibus are widely used industrial communication protocols that enable efficient data exchange between devices in manufacturing environments. Modbus is known for its simplicity and ease of integration, while Profibus offers high-speed communication and robust performance for complex automation systems. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these protocols can enhance your industrial network solutions.
Table of Comparison
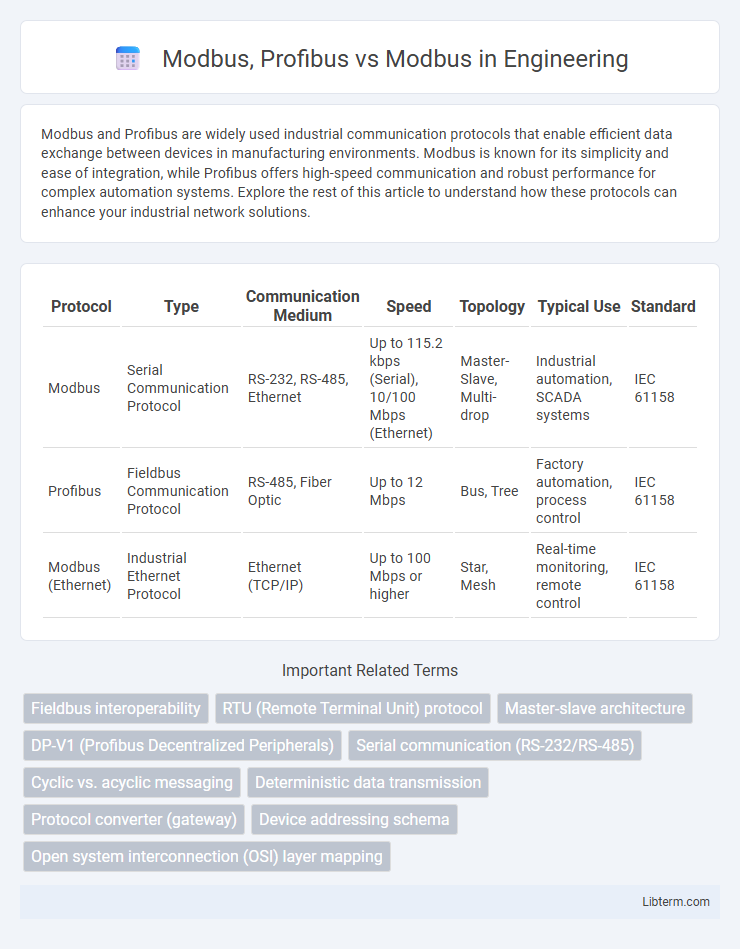
| Protocol | Type | Communication Medium | Speed | Topology | Typical Use | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modbus | Serial Communication Protocol | RS-232, RS-485, Ethernet | Up to 115.2 kbps (Serial), 10/100 Mbps (Ethernet) | Master-Slave, Multi-drop | Industrial automation, SCADA systems | IEC 61158 |
| Profibus | Fieldbus Communication Protocol | RS-485, Fiber Optic | Up to 12 Mbps | Bus, Tree | Factory automation, process control | IEC 61158 |
| Modbus (Ethernet) | Industrial Ethernet Protocol | Ethernet (TCP/IP) | Up to 100 Mbps or higher | Star, Mesh | Real-time monitoring, remote control | IEC 61158 |
Introduction to Industrial Communication Protocols
Modbus and Profibus are widely used industrial communication protocols designed to enable data exchange between devices in automation systems. Modbus, known for its simplicity and open standard, operates primarily in serial communication environments, making it ideal for basic device networking. Profibus offers higher speed and more complex data handling capabilities, supporting both serial and Ethernet-based communication, which suits advanced industrial applications requiring real-time control and robustness.
What is Modbus?
Modbus is a widely used communication protocol in industrial automation that facilitates data exchange between electronic devices, primarily programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and sensors. It operates on a master-slave architecture, allowing a master device to query multiple slave devices for information or control commands over serial lines or Ethernet networks. Unlike Profibus, which supports more complex communication and faster data rates with a focus on process automation, Modbus is valued for its simplicity, ease of implementation, and broad compatibility in monitoring and control applications.
Key Features of Modbus
Modbus is a widely used communication protocol known for its simplicity, open standard, and ease of implementation in industrial automation. Its key features include a master-slave architecture, support for serial and TCP/IP communication, and efficient data structuring with function codes for reading and writing registers. Compared to Profibus, Modbus offers greater flexibility in terms of network topology and device compatibility but typically operates at lower speeds and supports fewer advanced diagnostics.
What is Profibus?
Profibus is an industrial communication protocol designed for high-speed data exchange in automation systems, primarily used in manufacturing and process control. Unlike Modbus, which is a simpler, serial communication protocol ideal for basic device networking, Profibus supports complex fieldbus structures with real-time capabilities and robust error handling. Profibus networks connect sensors, actuators, and controllers, enabling efficient and reliable automation in large-scale industrial environments.
Key Features of Profibus
Profibus offers advanced features such as real-time communication, high data transfer rates up to 12 Mbps, and robust error detection mechanisms, making it suitable for complex industrial automation systems. Unlike Modbus, which primarily supports simple master-slave communication and lower speeds, Profibus facilitates decentralized peripherals and seamless integration with various field devices. Its ability to handle both cyclic and acyclic data exchange enhances process control efficiency and system diagnostics.
Modbus vs Profibus: Protocol Architecture Comparison
Modbus operates on a master-slave architecture with a simple, application-layer protocol primarily designed for serial communication, while Profibus employs a more complex, hierarchical structure supporting multiple device classes and real-time data exchange through its DP and PA variants. Modbus's lightweight implementation is ideal for straightforward data acquisition with limited overhead, whereas Profibus provides enhanced features such as token-passing for deterministic bus access and built-in diagnostics for advanced network management. The protocol architecture differentiation positions Modbus as suitable for less demanding industrial environments and Profibus for more complex automation systems requiring higher reliability and speed.
Performance and Speed: Modbus vs Profibus
Profibus offers higher data transfer rates up to 12 Mbps compared to Modbus's typical rates of 9600 bps to 115.2 kbps, resulting in superior communication speed and real-time performance. Modbus, while simpler and widely supported, is limited in bandwidth and slower in handling complex automation tasks. For applications requiring rapid data exchange and deterministic timing, Profibus outperforms Modbus in overall system responsiveness and efficiency.
Application Areas: Where to Use Each Protocol
Modbus is widely used in industrial automation for simple, low-speed communication between devices such as PLCs, sensors, and meters, making it suitable for applications like HVAC systems, water treatment, and building automation. Profibus offers high-speed, deterministic communication ideal for complex manufacturing processes, robotics, and real-time control systems in automotive and pharmaceutical industries. Choosing Modbus suits cost-effective, less time-critical setups, while Profibus excels in environments demanding precise synchronization and extensive device networking.
Integration Challenges and Compatibility
Modbus and Profibus differ significantly in integration challenges and compatibility due to their distinct communication protocols; Modbus operates primarily on serial and TCP/IP networks, making it widely compatible with simpler device architectures, while Profibus relies on deterministic fieldbus technology suited for complex automation systems. Integration challenges with Modbus often involve handling diverse device data formats and ensuring efficient polling mechanisms, whereas Profibus integration requires managing combined cyclic and acyclic data exchange with strict timing constraints. Compatibility issues arise as Modbus favors open, broadly supported standards ideal for multi-vendor environments, whereas Profibus demands specialized hardware and protocol stacks, limiting interoperability in heterogeneous networks.
Choosing the Right Protocol: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Modbus and Profibus protocols depends on factors such as network size, communication speed, and device compatibility. Modbus is favored for simple, cost-effective implementations with wide device support, while Profibus excels in complex industrial environments requiring high-speed data transfer and deterministic communication. Consider system requirements, scalability, and integration capabilities to select the optimal protocol for reliable industrial automation.
Modbus, Profibus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com