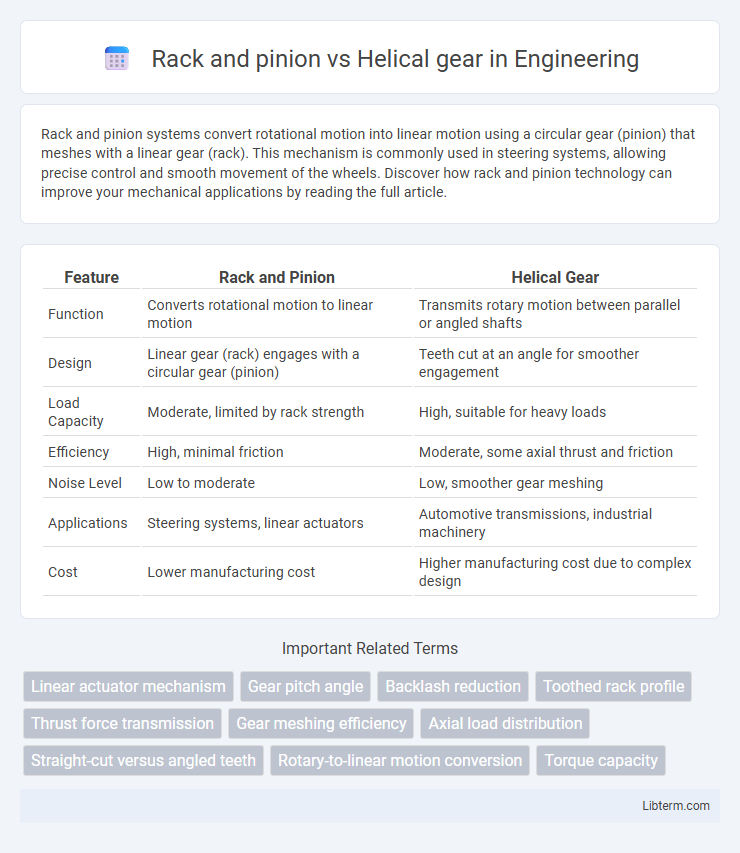
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion using a circular gear (pinion) that meshes with a linear gear (rack). This mechanism is commonly used in steering systems, allowing precise control and smooth movement of the wheels. Discover how rack and pinion technology can improve your mechanical applications by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rack and Pinion | Helical Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts rotational motion to linear motion | Transmits rotary motion between parallel or angled shafts |
| Design | Linear gear (rack) engages with a circular gear (pinion) | Teeth cut at an angle for smoother engagement |
| Load Capacity | Moderate, limited by rack strength | High, suitable for heavy loads |
| Efficiency | High, minimal friction | Moderate, some axial thrust and friction |
| Noise Level | Low to moderate | Low, smoother gear meshing |
| Applications | Steering systems, linear actuators | Automotive transmissions, industrial machinery |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost due to complex design |
Introduction to Rack and Pinion and Helical Gears
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion through a circular gear (pinion) engaging a linear gear (rack), offering precise control and high efficiency in steering mechanisms and machinery. Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, providing smoother operation, higher load capacity, and reduced noise compared to spur gears, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Both gear types optimize motion transfer but serve distinct functions in mechanical design based on the directional movement and load requirements.
Fundamental Working Principles
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion of the pinion into linear motion of the rack by meshing a circular gear with a linear toothed bar, enabling precise linear displacement. Helical gears operate through angled teeth that engage gradually along the gear face, which provides smoother and quieter transmission of rotational motion between parallel or crossed shafts. The fundamental difference lies in the rack and pinion's linear output versus the helical gear's rotational motion transfer, influencing their application in steering mechanisms versus high-speed machinery.
Key Design Differences
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion using a flat rack and a circular pinion gear, emphasizing straightforward design and precise linear movement. Helical gears feature angled teeth that engage gradually, offering quieter operation and higher load capacity, making them ideal for transmitting rotary motion between parallel or crossed shafts. Key design differences include the linear versus rotational output, tooth geometry--straight for rack and pinion versus angled for helical gears--and application suitability for linear motion control versus torque transmission.
Efficiency Comparison
Rack and pinion systems typically offer higher mechanical efficiency due to their straightforward design and direct linear motion, minimizing energy loss. Helical gears, while providing smoother and quieter operation with greater load capacity, experience slightly lower efficiency because of increased friction from angled teeth engagement. Efficiency rates for rack and pinion systems often reach around 95%, whereas helical gears generally operate around 90-94%, depending on load and lubrication quality.
Load Capacity and Durability
Rack and pinion systems generally provide higher load capacity in linear motion applications due to direct tooth engagement, allowing efficient transmission of force with minimal backlash. Helical gears offer superior durability with angled teeth that produce smoother, quieter operation and better load distribution, reducing wear and extending service life. For heavy-duty or continuous operation, helical gears excel in longevity, whereas rack and pinion mechanisms balance load capacity with straightforward design for linear actuation.
Noise Levels and Smoothness of Operation
Rack and pinion systems generally produce higher noise levels due to their linear-to-rotary motion mechanism and direct tooth engagement, whereas helical gears operate more quietly thanks to their angled teeth that provide gradual contact. Helical gears offer smoother operation with less vibration and reduced backlash, enhancing precision in high-speed applications. Noise reduction and operational smoothness make helical gears preferable in automotive transmissions, while rack and pinion remains common in steering systems where precise linear motion is required.
Applications in Various Industries
Rack and pinion systems are widely used in automotive steering and CNC machinery for precise linear motion conversion. Helical gears are favored in heavy machinery, industrial conveyors, and automotive transmissions due to their ability to handle high loads and operate quietly. Industries such as robotics, aerospace, and manufacturing rely on these components for efficient power transmission and motion control.
Maintenance Requirements
Rack and pinion systems require regular lubrication and periodic inspection for wear on the teeth to maintain smooth linear motion, with simpler maintenance due to fewer components. Helical gears demand more intensive maintenance, including precise lubrication practices and frequent monitoring for alignment and backlash to prevent noise and wear from the angled teeth interaction. Both systems benefit from condition monitoring technologies, but helical gears typically incur higher maintenance complexity and costs due to their intricate geometry.
Cost Considerations
Rack and pinion systems generally offer lower initial costs due to simpler design and manufacturing processes, making them ideal for applications requiring linear motion with budget constraints. Helical gears, while more expensive because of complex geometry and higher precision machining, provide greater load capacity and smoother, quieter operation, justifying the investment in high-performance settings. Maintenance costs also differ, with rack and pinion components typically easier and cheaper to replace, whereas helical gears demand more specialized upkeep to preserve efficiency.
Choosing the Right Gear System
Rack and pinion systems provide precise linear motion ideal for steering and positioning applications, while helical gears excel in transmitting torque smoothly in high-speed industrial machinery. Selecting the right gear system depends on factors like load capacity, desired motion type, and noise levels, with rack and pinion favored for linear accuracy and helical gears preferred for quiet, efficient rotary power transfer. Considering maintenance requirements and space constraints also guides the decision between these gear options.
Rack and pinion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com