Modular action enhances efficiency by breaking down complex tasks into manageable, interchangeable components that can be easily adapted or replaced. This approach streamlines processes and improves flexibility, allowing you to customize workflows to meet specific needs. Discover how modular action can transform your project management in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
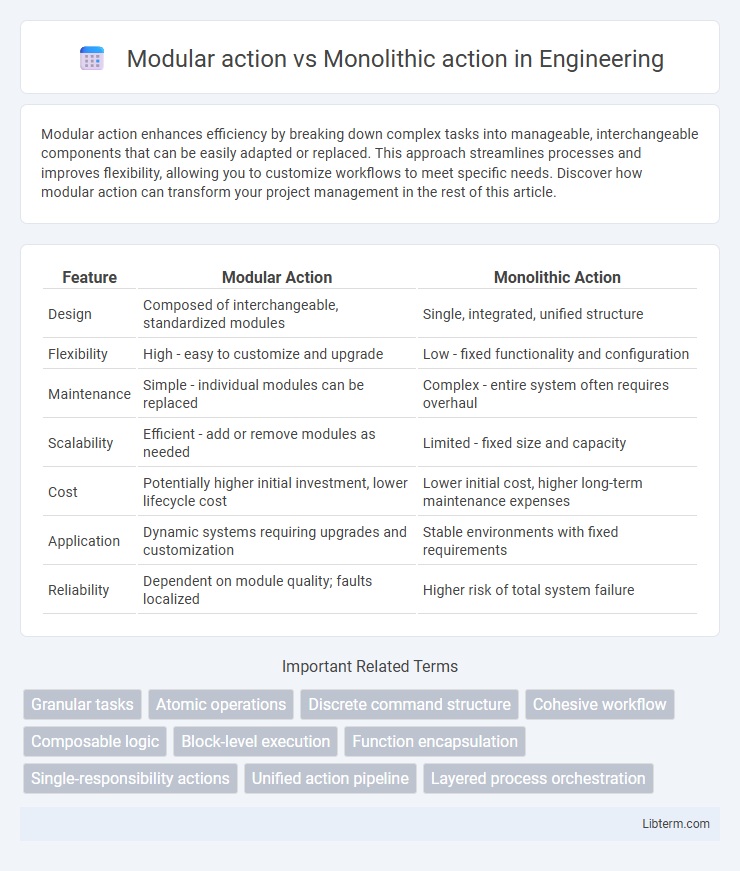
| Feature | Modular Action | Monolithic Action |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Composed of interchangeable, standardized modules | Single, integrated, unified structure |
| Flexibility | High - easy to customize and upgrade | Low - fixed functionality and configuration |
| Maintenance | Simple - individual modules can be replaced | Complex - entire system often requires overhaul |
| Scalability | Efficient - add or remove modules as needed | Limited - fixed size and capacity |
| Cost | Potentially higher initial investment, lower lifecycle cost | Lower initial cost, higher long-term maintenance expenses |
| Application | Dynamic systems requiring upgrades and customization | Stable environments with fixed requirements |
| Reliability | Dependent on module quality; faults localized | Higher risk of total system failure |
Understanding Modular Action: Definition and Key Concepts
Modular action refers to breaking down complex tasks into smaller, independent components that can be developed, tested, and maintained separately, enhancing flexibility and scalability. Key concepts include encapsulation, reusability, and clear interfaces between modules, which reduce interdependencies and improve system robustness. This contrasts with monolithic action, where all functionalities are tightly integrated, potentially causing challenges in updates, debugging, and scalability.
What Is Monolithic Action? A Comprehensive Overview
Monolithic action refers to a programming approach where all functionalities are tightly integrated into a single unified codebase, making the entire system dependent on one large, indivisible structure. This method contrasts with modular action, which breaks down functionality into smaller, independent modules or components for better scalability and maintenance. Monolithic action often leads to challenges in debugging, upgrading, and scaling applications due to its rigid and interwoven structure.
Major Differences Between Modular and Monolithic Actions
Modular actions are designed as independent, reusable components that allow for greater flexibility and scalability, while monolithic actions are tightly integrated within a single codebase, resulting in less adaptability and more complexity. Modular approaches enhance maintainability by isolating functionalities, making updates and testing more efficient compared to monolithic structures where changes can impact the entire system. Performance optimization and collaborative development are more streamlined in modular actions, whereas monolithic actions often face challenges with scalability and slower deployment cycles.
Advantages of Adopting Modular Action Approaches
Modular action approaches enhance system scalability by enabling independent development and deployment of components, reducing complexity and facilitating easier maintenance. These approaches promote reusability and faster iteration cycles, leading to improved flexibility in adapting to changing requirements. Enhanced fault isolation within modular designs minimizes system-wide failures, ensuring higher reliability and robustness compared to monolithic architectures.
Limitations and Challenges of Monolithic Actions
Monolithic actions pose significant limitations such as scalability issues due to their tightly coupled structure, making updates and maintenance complex and time-consuming. These actions often suffer from reduced flexibility, as changes in one component can inadvertently affect the entire system, leading to increased risk of errors and downtime. The difficulty in isolating failures in monolithic architectures hinders efficient debugging and can result in prolonged system outages.
Application Scenarios: Modular vs. Monolithic Action
Modular action architectures excel in complex, large-scale applications requiring flexibility, scalability, and maintainability, such as microservices or multi-team development environments. Monolithic actions are better suited for simpler, smaller applications with tightly integrated components needing faster initial development and deployment. Enterprises benefit from modular designs when frequent updates and independent scaling are necessary, while monolithic approaches remain efficient for straightforward use cases with limited resource constraints.
Scalability and Flexibility: Modular Action Benefits
Modular action architectures enhance scalability by enabling independent component scaling based on demand, reducing resource wastage and improving system responsiveness. Flexibility is increased through modularity, allowing developers to update, replace, or add features without impacting the entire system. This approach fosters faster iteration, easier maintenance, and better adaptability to evolving business requirements compared to monolithic action structures.
Performance and Efficiency: Comparing Action Structures
Modular actions enhance performance by isolating specific tasks, reducing code redundancy, and enabling parallel execution, which leads to faster processing times compared to monolithic actions. Monolithic actions often suffer from slower execution and maintenance overhead due to tightly coupled logic and larger codebases, impacting overall efficiency. Optimizing action structures with modular design improves scalability and resource utilization, making systems more responsive and easier to debug.
Real-World Examples of Modular and Monolithic Actions
Modular actions, such as microservices in Netflix's architecture, enable independent deployment and scalability of specific features, improving resilience and development speed. Monolithic actions, exemplified by early versions of Amazon's platform, involve a single unified codebase where all functionalities are interdependent, often resulting in slower updates and harder maintenance. Real-world shifts from monolithic to modular designs showcase enhanced agility and fault isolation, as seen in Spotify's transition to a modular system facilitating rapid feature iterations.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between modular action and monolithic action depends on factors such as scalability, maintainability, and complexity of the project. Modular action offers flexibility by enabling independent updates and easier debugging, ideal for large, evolving systems. Monolithic action suits simpler projects where performance optimization and tight integration are critical, minimizing overhead from inter-module communication.
Modular action Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com