Fuzzy logic control enhances system performance by mimicking human reasoning through approximate data rather than precise measurements, making it highly effective in handling uncertainty and imprecision. This approach improves decision-making in complex environments where traditional binary logic falls short. Discover how fuzzy logic control can optimize your system by exploring the detailed mechanisms and applications in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
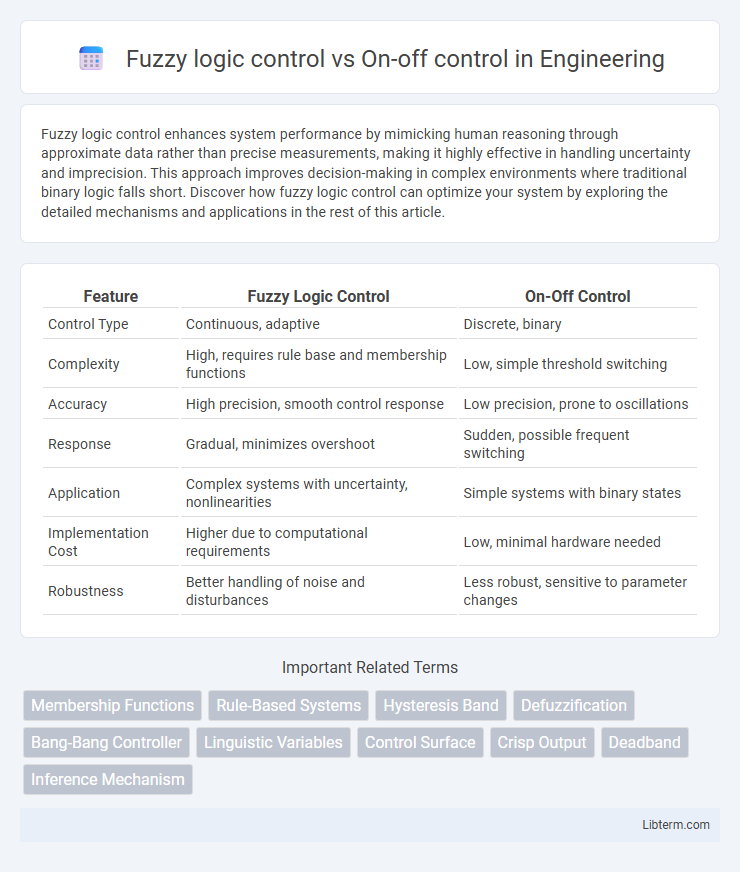
| Feature | Fuzzy Logic Control | On-Off Control |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Continuous, adaptive | Discrete, binary |
| Complexity | High, requires rule base and membership functions | Low, simple threshold switching |
| Accuracy | High precision, smooth control response | Low precision, prone to oscillations |
| Response | Gradual, minimizes overshoot | Sudden, possible frequent switching |
| Application | Complex systems with uncertainty, nonlinearities | Simple systems with binary states |
| Implementation Cost | Higher due to computational requirements | Low, minimal hardware needed |
| Robustness | Better handling of noise and disturbances | Less robust, sensitive to parameter changes |
Introduction to Control Systems
Fuzzy logic control offers a flexible approach to managing systems with uncertainty and imprecision by mimicking human reasoning through linguistic variables and rule-based algorithms. On-off control operates on a binary principle, switching devices fully on or off to maintain setpoints, often resulting in simpler implementation but potential oscillations. In control system introduction, fuzzy logic excels in handling nonlinear processes and improving stability, while on-off control remains ideal for basic, cost-effective applications with clear threshold boundaries.
Fundamentals of On-Off Control
On-off control operates by switching a system fully on or off based on whether the measured variable crosses a set threshold, providing simple and cost-effective regulation for binary systems like thermostats. The fundamental principle involves hysteresis to prevent rapid switching, ensuring system stability by introducing a dead band around the set point. In contrast to fuzzy logic control, which handles continuous inputs with degrees of truth, on-off control relies solely on discrete states, limiting its application to processes requiring basic, straightforward control.
Basics of Fuzzy Logic Control
Fuzzy logic control utilizes a rule-based approach that mimics human reasoning by handling uncertainty and imprecision through degrees of truth rather than binary states. Unlike on-off control, which switches abruptly between two states based on fixed thresholds, fuzzy logic control processes input variables with membership functions to produce smooth and adaptive output responses. This method improves system performance in complex or nonlinear environments where precise mathematical models are unavailable or impractical.
Key Differences Between Fuzzy Logic and On-Off Control
Fuzzy logic control uses degrees of truth rather than binary states, allowing for more precise and smooth control responses compared to the simple on-off control that switches fully on or off based on preset thresholds. Fuzzy logic handles uncertainties and nonlinearities by applying linguistic variables and rule-based inference, whereas on-off control relies solely on fixed setpoint comparisons leading to potential oscillations and wear on mechanical components. This makes fuzzy logic control more suitable for complex systems requiring gradual adjustments, while on-off control remains effective for basic, low-cost applications with clear-cut operational boundaries.
Advantages of On-Off Control Systems
On-off control systems provide simplicity and ease of implementation, making them cost-effective for basic applications requiring binary decisions. Their rapid response time and straightforward design allow efficient management of devices like thermostats and simple mechanical systems. The minimal computational resources required make on-off controllers highly reliable and suitable for environments where precision is less critical.
Strengths of Fuzzy Logic Controllers
Fuzzy Logic Controllers excel in handling systems with uncertainty and imprecision by mimicking human reasoning and providing smooth control actions, unlike On-off control which only switches between two states. They offer superior adaptability in nonlinear and complex systems without requiring precise mathematical models, enhancing robustness and stability. This leads to improved performance in temperature regulation, robotics, and automotive applications where traditional On-off control often causes oscillations and wear on components.
Limitations of On-Off Control
On-off control systems often suffer from frequent cycling and excessive wear on mechanical components due to their binary operation, causing inefficiencies in maintaining precise system conditions. This simplistic approach lacks the ability to handle system nonlinearities or continuous variations, resulting in oscillations around setpoints and reduced stability. Fuzzy logic control overcomes these limitations by providing smooth and adaptive control through approximate reasoning, better managing uncertainties and system dynamics.
Weaknesses of Fuzzy Logic Control
Fuzzy logic control can struggle with computational complexity and the need for extensive rule sets, which may increase design time and processing power requirements. It often lacks guaranteed stability and robustness compared to traditional on-off control, making it less reliable in highly dynamic or safety-critical systems. The subjective nature of rule creation can also lead to inconsistent performance and difficulty in tuning the controller for optimal results.
Real-World Applications: Fuzzy Logic vs On-Off Control
Fuzzy logic control excels in real-world applications requiring smooth, adaptive responses such as climate control systems and automotive transmissions, offering nuanced adjustments that improve efficiency and comfort. On-off control remains prevalent in simpler systems like household thermostats and basic motor controls, where binary decisions suffice and cost-effectiveness is prioritized. The choice between fuzzy logic and on-off control depends on application complexity, precision requirements, and response smoothness.
Choosing the Right Control Strategy
Fuzzy logic control offers superior adaptability and precision in managing complex, nonlinear systems by using linguistic rules and gradual membership functions, whereas on-off control provides simple, binary operation suited for straightforward applications with minimal processing requirements. Selecting the right control strategy depends on system dynamics, desired accuracy, and the complexity of the control environment; fuzzy logic excels in scenarios demanding smooth transitions and tolerance to uncertainty, while on-off control is ideal for cost-effective, less sensitive systems. Understanding the trade-offs between computational complexity and control quality is essential for optimizing performance and energy efficiency in industrial automation or HVAC systems.
Fuzzy logic control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com