Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) and Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) are widely used in applications requiring high efficiency and precise control. PMSMs offer smooth torque and high power density, making them ideal for industrial automation, while BLDC motors are known for their reliability and low maintenance in electric vehicles and consumer electronics. Explore the rest of the article to understand which motor technology best suits Your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
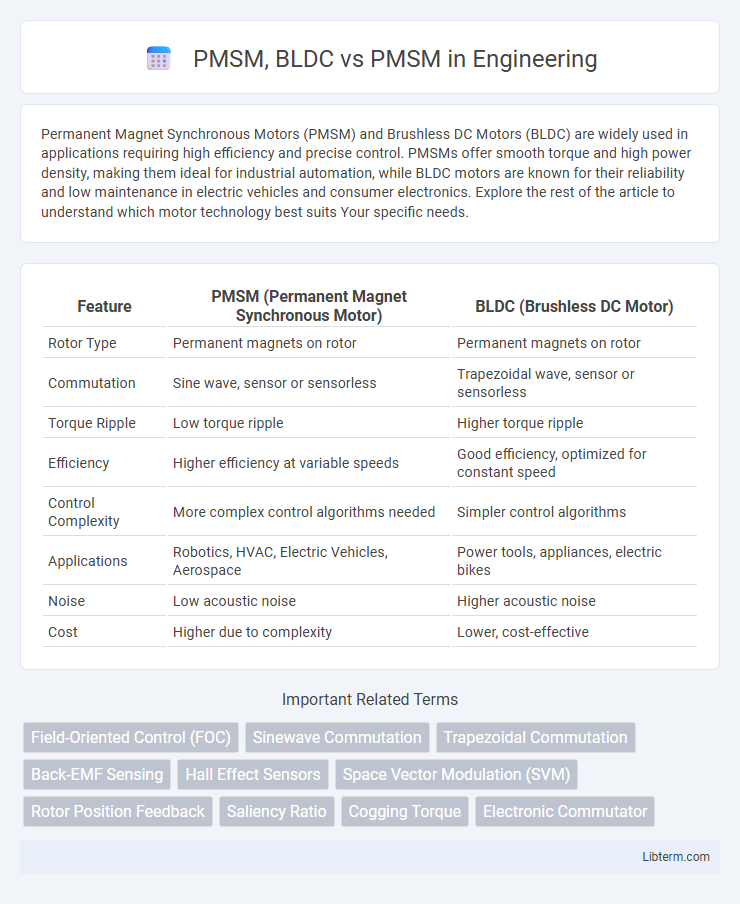
| Feature | PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) | BLDC (Brushless DC Motor) |
|---|---|---|
| Rotor Type | Permanent magnets on rotor | Permanent magnets on rotor |
| Commutation | Sine wave, sensor or sensorless | Trapezoidal wave, sensor or sensorless |
| Torque Ripple | Low torque ripple | Higher torque ripple |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency at variable speeds | Good efficiency, optimized for constant speed |
| Control Complexity | More complex control algorithms needed | Simpler control algorithms |
| Applications | Robotics, HVAC, Electric Vehicles, Aerospace | Power tools, appliances, electric bikes |
| Noise | Low acoustic noise | Higher acoustic noise |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity | Lower, cost-effective |
Introduction to PMSM and BLDC Motors
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) utilize permanent magnets embedded in the rotor, providing high efficiency, precise control, and smooth torque output ideal for applications requiring high performance and reliability. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) feature electronically commutated stators with permanent magnet rotors, delivering low maintenance, high power density, and excellent speed-torque characteristics suitable for various industrial and automotive uses. Both PMSM and BLDC motors rely on permanent magnets for rotor excitation but differ in rotor design and control strategies, influencing their respective efficiency, noise levels, and application suitability.
Understanding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM)
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) utilize permanent magnets embedded in the rotor, providing high efficiency and precise speed control in various industrial applications. Compared to Brushless DC Motors (BLDC), PMSMs offer smoother torque output and better performance at high speeds due to their sinusoidal back-EMF waveform and vector control compatibility. The advanced control strategies employed in PMSM optimize energy consumption and reduce acoustic noise, making them ideal for electric vehicles and advanced robotics.
Fundamentals of Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) utilize electronic commutation, relying on sensors or sensorless control methods to switch current in stator windings, which generates a rotating magnetic field. Unlike Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) that use sinusoidal current waveforms for smooth torque, BLDC motors employ trapezoidal current waveforms, resulting in simpler control and higher efficiency at low speeds. Fundamental characteristics of BLDC motors include high power density, low maintenance due to the absence of brushes, and precise speed control, making them ideal for applications requiring reliable and efficient motor performance.
Key Differences: PMSM vs. BLDC
PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) utilizes sinusoidal back EMF waveforms, resulting in smoother torque and quieter operation, while BLDC (Brushless DC Motor) uses trapezoidal back EMF, producing more torque ripple and commutation noise. PMSMs require sophisticated control algorithms like Field-Oriented Control (FOC) for efficient performance, whereas BLDC motors can operate with simpler trapezoidal commutation methods. PMSMs offer higher efficiency and better thermal management, making them suitable for precision applications, while BLDC motors are favored for cost-effective and robust solutions in industrial and consumer products.
Operating Principles of PMSM and BLDC
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) operate using sinusoidal back-EMF generated by permanent magnets on the rotor, synchronized with a three-phase sinusoidal current in the stator for smooth torque production. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) utilize trapezoidal back-EMF and are commutated electronically with rectangular current waveforms, resulting in a simpler control scheme but higher torque ripple compared to PMSMs. The key operational difference lies in PMSM's sinusoidal waveform and synchronous operation versus BLDC's trapezoidal waveform and sector-based electronic commutation.
Efficiency Comparison: PMSM versus BLDC
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) generally exhibit higher efficiency than Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) due to their sinusoidal back-EMF waveform, which reduces torque ripple and power losses. PMSMs offer improved performance at variable speeds, making them more suitable for applications requiring precise control and energy savings. In contrast, BLDC motors, with their trapezoidal back-EMF, often experience higher core and copper losses, resulting in slightly lower overall efficiency under comparable operating conditions.
Control Strategies for PMSM and BLDC Motors
PMSM and BLDC motors demand distinct control strategies due to their differing rotor constructions and back-EMF waveforms. PMSM motors require precise vector control methods, such as Field-Oriented Control (FOC), to achieve sinusoidal current waveforms and optimal torque production, enhancing efficiency and dynamic response. BLDC motors typically utilize trapezoidal commutation with Hall effect sensors or sensorless back-EMF detection, focusing on simpler control schemes that emphasize robustness and cost-effectiveness.
Applications of PMSM and BLDC in Industry
PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors) and BLDC (Brushless DC Motors) are both prevalent in industrial applications, with PMSMs favored for high-precision and high-efficiency roles such as robotics, CNC machines, and electric vehicles due to their smooth torque and superior speed control. BLDC motors are commonly used in applications requiring simple control and high reliability, including HVAC systems, home appliances, and small electric tools. The choice between PMSM and BLDC depends on specific industrial requirements for torque density, efficiency, and control complexity.
Pros and Cons: PMSM vs. BLDC Motors
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) offer higher efficiency, smooth torque, and better power density compared to Brushless DC (BLDC) motors, making them ideal for precision applications like electric vehicles and robotics. BLDC motors, however, benefit from simpler control algorithms and lower cost, but exhibit torque ripple and reduced efficiency at low speeds. PMSM requires complex controllers and is costlier due to rare earth magnets, while BLDC motors provide robust performance with simpler maintenance and control.
Future Trends: PMSM and BLDC Motor Technologies
PMSM and BLDC motor technologies are rapidly evolving with a strong focus on improving energy efficiency, power density, and thermal management for future applications in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Advanced control algorithms and sensorless techniques are enhancing performance and reducing maintenance requirements in both motor types. Integration of wide-bandgap semiconductors and IoT connectivity is enabling smarter, more reliable motor systems tailored for Industry 4.0 and sustainable energy solutions.
PMSM, BLDC Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com