Condition-based maintenance enhances equipment reliability by monitoring real-time data to predict failures before they occur, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Sensors and diagnostic tools track parameters such as vibration, temperature, and pressure to optimize maintenance schedules. Explore the rest of the article to discover how this strategy can improve your operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
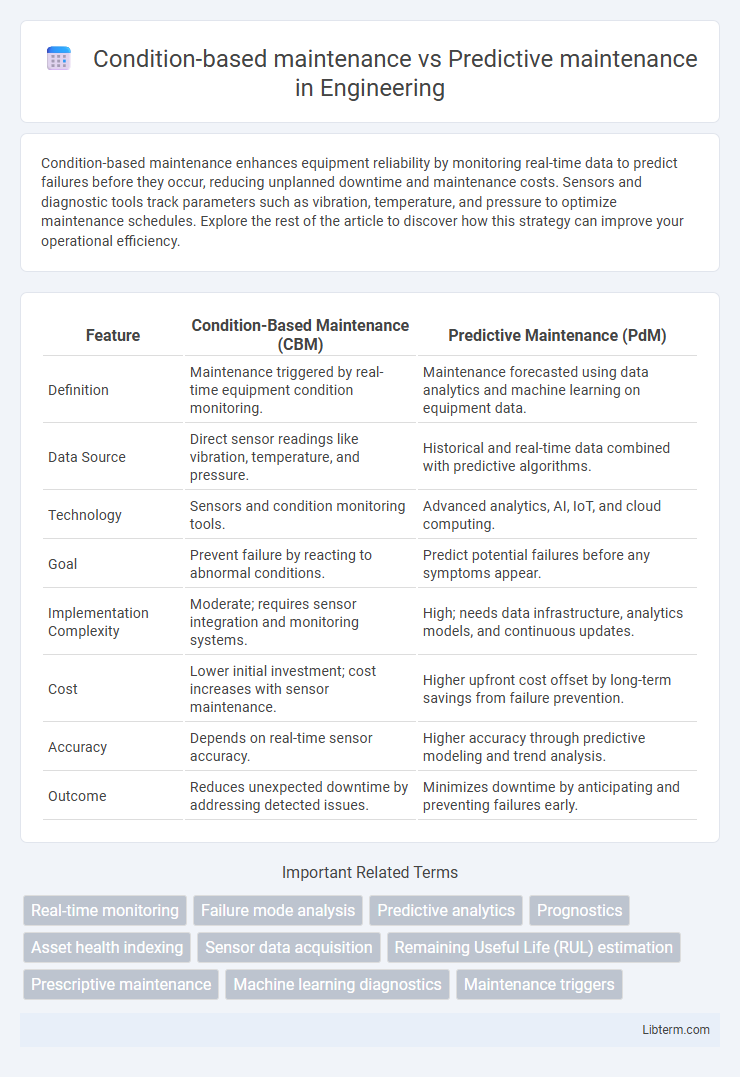
| Feature | Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) | Predictive Maintenance (PdM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance triggered by real-time equipment condition monitoring. | Maintenance forecasted using data analytics and machine learning on equipment data. |
| Data Source | Direct sensor readings like vibration, temperature, and pressure. | Historical and real-time data combined with predictive algorithms. |
| Technology | Sensors and condition monitoring tools. | Advanced analytics, AI, IoT, and cloud computing. |
| Goal | Prevent failure by reacting to abnormal conditions. | Predict potential failures before any symptoms appear. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate; requires sensor integration and monitoring systems. | High; needs data infrastructure, analytics models, and continuous updates. |
| Cost | Lower initial investment; cost increases with sensor maintenance. | Higher upfront cost offset by long-term savings from failure prevention. |
| Accuracy | Depends on real-time sensor accuracy. | Higher accuracy through predictive modeling and trend analysis. |
| Outcome | Reduces unexpected downtime by addressing detected issues. | Minimizes downtime by anticipating and preventing failures early. |
Understanding Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM)
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) relies on real-time data from sensors monitoring equipment health to trigger maintenance actions only when necessary, minimizing unnecessary interventions and reducing downtime. CBM emphasizes the continuous assessment of machine conditions such as vibration, temperature, and pressure, enabling proactive decision-making based on actual asset performance. This approach contrasts with predictive maintenance by prioritizing condition thresholds rather than forecasting future failures through advanced analytics.
What Is Predictive Maintenance (PdM)?
Predictive Maintenance (PdM) utilizes advanced data analytics, machine learning, and IoT sensors to monitor equipment condition in real-time, enabling precise prediction of potential failures before they occur. Unlike Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM), which triggers maintenance based on current equipment condition or specific thresholds, PdM forecasts future issues by analyzing trends and patterns in operational data. This proactive approach maximizes asset lifespan, reduces unexpected downtime, and optimizes maintenance scheduling through timely, data-driven interventions.
Key Differences Between CBM and PdM
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) relies on real-time data from equipment sensors to trigger repairs only when specific conditions indicate potential failure, optimizing maintenance schedules based on actual asset status. Predictive maintenance (PdM) uses advanced analytics, machine learning models, and historical data trends to forecast when equipment failures might occur, enabling preemptive actions before any signs of degradation are visible. Key differences include CBM's reactive approach to current conditions versus PdM's proactive prediction of future failures, with PdM often requiring more complex data integration and algorithmic analysis for accurate forecasting.
Data Requirements: CBM vs Predictive Maintenance
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) relies on real-time sensor data and threshold limits to trigger maintenance actions, requiring continuous monitoring of equipment parameters such as vibration, temperature, and pressure. Predictive maintenance utilizes advanced analytics, machine learning models, and historical data to predict future failures, demanding large datasets encompassing operational history, failure modes, and environmental conditions. The data requirements for predictive maintenance are more extensive and complex, integrating multiple data sources to enable accurate remaining useful life (RUL) estimations and early fault detection.
Technology Involved in Each Approach
Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time data from sensors monitoring equipment parameters such as vibration, temperature, and pressure to detect anomalies, utilizing technologies like IoT devices and condition monitoring software. Predictive maintenance employs advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and big data processing to analyze historical and real-time sensor data, forecasting potential failures before they occur. Both approaches integrate cloud computing and data acquisition systems, but predictive maintenance emphasizes AI-driven prediction models for proactive decision-making.
Cost Implications: Which Is More Economical?
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) relies on real-time data and thresholds to trigger maintenance activities, often resulting in lower immediate costs and reduced downtime by avoiding unnecessary repairs. Predictive maintenance (PdM) uses advanced analytics and machine learning to forecast failures, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses through precise intervention and extended asset life. While CBM offers cost-efficiency for simpler systems, PdM proves more economical for complex machinery where accurate prediction minimizes catastrophic failures and optimizes resource allocation.
Implementation Challenges for CBM and PdM
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) faces implementation challenges such as the need for continuous sensor data collection and the integration of real-time monitoring systems, which can result in high initial costs and complex infrastructure requirements. Predictive maintenance (PdM) implementation is hindered by the necessity for advanced data analytics, machine learning algorithms, and accurate historical data to forecast equipment failures effectively, demanding specialized expertise and robust IT infrastructure. Both CBM and PdM require seamless data integration from various sources, standardized protocols, and skilled personnel to interpret data, presenting significant barriers in transitioning from traditional maintenance strategies.
Industry Applications: When to Use CBM vs PdM
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) is ideal for industries with equipment that experiences sudden failures, such as manufacturing plants and power generation, where maintenance is triggered by real-time data indicating degradation. Predictive maintenance (PdM) suits industries like aerospace and automotive, where advanced analytics and machine learning models forecast failures before symptoms appear, enabling optimized maintenance scheduling. Choosing between CBM and PdM depends on the criticality of equipment, data availability, and the complexity of failure modes within the industry context.
Impact on Equipment Reliability and Uptime
Condition-based maintenance relies on real-time equipment data to perform maintenance only when specific wear indicators exceed thresholds, directly improving equipment reliability by preventing unexpected failures. Predictive maintenance uses advanced analytics and machine learning models to forecast failures before symptoms appear, significantly increasing uptime through timely interventions and optimized maintenance scheduling. Both strategies enhance equipment performance, but predictive maintenance offers a higher potential for maximizing uptime by anticipating issues earlier than condition-based methods.
Future Trends in Maintenance Strategies
Condition-based maintenance leverages real-time sensor data to perform repairs only when equipment shows signs of deterioration, optimizing resource use. Predictive maintenance advances this approach by employing machine learning algorithms and AI-driven analytics to forecast failures before symptoms appear, enabling proactive interventions. Future trends emphasize integration with IoT platforms, enhanced digital twins, and autonomous decision-making systems to boost accuracy, reduce downtime, and lower maintenance costs.
Condition-based maintenance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com