Rotameters measure flow rate by indicating the position of a float inside a tapered tube, providing precise and simple flow measurement without external power. Venturi meters use a converging section to create a pressure drop proportional to flow velocity, ideal for measuring fluids with minimal energy loss. Explore the rest of the article to discover which flow measurement device best suits your needs and applications.
Table of Comparison
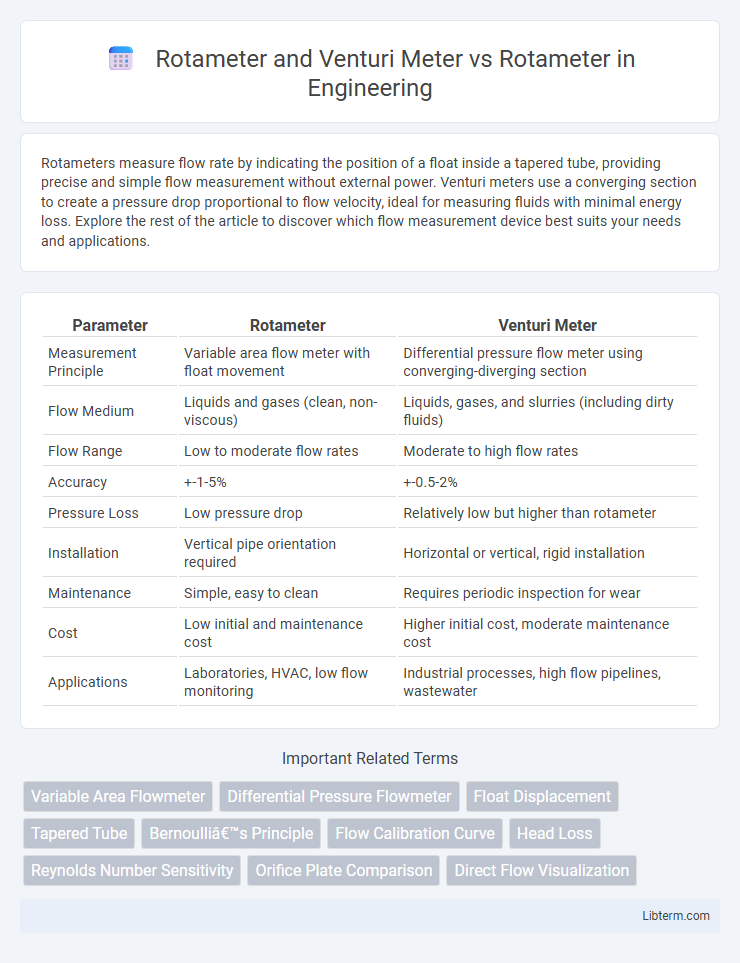
| Parameter | Rotameter | Venturi Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Variable area flow meter with float movement | Differential pressure flow meter using converging-diverging section |
| Flow Medium | Liquids and gases (clean, non-viscous) | Liquids, gases, and slurries (including dirty fluids) |
| Flow Range | Low to moderate flow rates | Moderate to high flow rates |
| Accuracy | +-1-5% | +-0.5-2% |
| Pressure Loss | Low pressure drop | Relatively low but higher than rotameter |
| Installation | Vertical pipe orientation required | Horizontal or vertical, rigid installation |
| Maintenance | Simple, easy to clean | Requires periodic inspection for wear |
| Cost | Low initial and maintenance cost | Higher initial cost, moderate maintenance cost |
| Applications | Laboratories, HVAC, low flow monitoring | Industrial processes, high flow pipelines, wastewater |
Introduction to Flow Measurement Devices
Rotameters and Venturi meters are essential flow measurement devices used in various industrial applications to determine fluid flow rates accurately. Rotameters operate on the variable area principle, where a float rises in a tapered tube with increasing flow, providing direct visual measurement; Venturi meters utilize differential pressure created by a narrowed throat to calculate flow based on Bernoulli's equation. Both devices offer reliable flow measurement, with Rotameters suited for low to moderate flows and clear fluids, while Venturi meters handle higher flow rates and offer minimal pressure loss, making the choice dependent on specific application requirements.
Overview of Rotameter: Principle and Applications
Rotameters operate based on the variable area flow measurement principle, where a float rises and falls within a tapered tube to indicate flow rate, offering precise readings without external power sources. Common applications include water treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, where reliable, low-maintenance flow measurement is essential. Compared to Venturi meters, rotameters provide direct visual flow indication and simpler installation but are generally better suited for lower flow rates and less turbulent conditions.
Venturi Meter: Working Principle and Uses
Venturi Meter operates on the principle of Bernoulli's equation, measuring flow rate by detecting pressure differences between a converging inlet and a diverging outlet, ensuring minimal energy loss. It is widely used in large-scale applications like water supply systems, wastewater treatment, and chemical processing due to its high accuracy and low maintenance. Compared to Rotameters, Venturi Meters provide reliable measurements for high flow rates and heavy fluids, making them suitable for industrial environments.
Key Differences Between Rotameter and Venturi Meter
Rotameters measure flow rate using a float that rises in a tapered tube, providing direct visual indication, while Venturi meters use differential pressure in a converging-diverging pipe section to calculate flow rate. Rotameters are suitable for low to moderate flow rates and are simpler, whereas Venturi meters handle high flow rates with minimal pressure loss and greater accuracy. The key difference lies in the measurement principle: Rotameters rely on variable area flow measurement, whereas Venturi meters depend on pressure differential for flow calculation.
Advantages of Rotameter in Flow Measurement
Rotameters offer distinct advantages in flow measurement, including visual flow indication through a simple float mechanism and the absence of external power requirements, making them ideal for low-pressure applications. Unlike Venturi meters, Rotameters provide real-time, direct flow readings without complex calibration, reducing maintenance and operational costs. Their compact design and ease of installation enable versatile use across various industries, enhancing accuracy and reliability in measuring liquids and gases.
Benefits of Using Venturi Meter
Venturi meters offer higher accuracy and lower pressure loss compared to rotameters, making them ideal for high-flow and high-pressure applications. Their robust design allows for measuring flow rates in fluids with suspended solids or varying viscosities, which can be challenging for rotameters. Venturi meters also provide consistent performance in large-diameter pipes and are less affected by flow disturbances, enhancing overall measurement reliability.
Limitations of Rotameter vs Venturi Meter
Rotameters have limitations such as sensitivity to fluid viscosity, requiring vertical installation, and reduced accuracy in turbulent or low-flow conditions, whereas Venturi meters offer better accuracy with less pressure loss and can handle a wider range of flow conditions. The Venturi meter's design minimizes flow disturbances, making it more suitable for high-pressure and high-flow applications compared to the Rotameter's reliance on gravity and a float mechanism. However, Venturi meters tend to be bulkier and more expensive, which can limit their use in compact or budget-conscious setups.
Comparative Analysis: Accuracy and Reliability
Rotameters provide moderate accuracy and are suitable for clear, clean fluids, but their reliability decreases with turbulent or dirty flow conditions. Venturi meters offer higher accuracy and better reliability in measuring flow rates, especially in industrial applications with varying fluid types and pressures. Comparative analysis reveals Venturi meters have superior precision due to minimal energy loss and reduced susceptibility to flow profile changes compared to Rotameters.
Selection Criteria: Rotameter or Venturi Meter?
Selection between a Rotameter and a Venturi Meter depends on factors like fluid type, accuracy requirements, and installation conditions. Rotameters are preferred for low flow rates, transparent liquids, and easy visual readouts, while Venturi Meters are suited for high flow rates, dirty or corrosive fluids, and applications needing minimal pressure loss. Consider flow range, fluid properties, installation space, and maintenance needs to choose the optimal flow measurement device.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Flow Meter
Selecting the appropriate flow meter depends on the specific application requirements such as fluid type, accuracy, and installation constraints. Rotameters offer simplicity and affordability for clear liquids with moderate accuracy, whereas Venturi meters provide high accuracy and low pressure drop, suitable for large-scale or industrial flows. Evaluating factors like maintenance needs, flow range, and cost-efficiency ensures the optimal choice between Rotameter and Venturi meter.
Rotameter and Venturi Meter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com