Reactive maintenance focuses on repairing equipment only after a failure occurs, minimizing upfront costs but risking unexpected downtimes and higher long-term expenses. It is a straightforward approach but often leads to inefficiencies and increased disruption in operations. Discover how reactive maintenance compares to proactive strategies and which approach best suits your maintenance needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
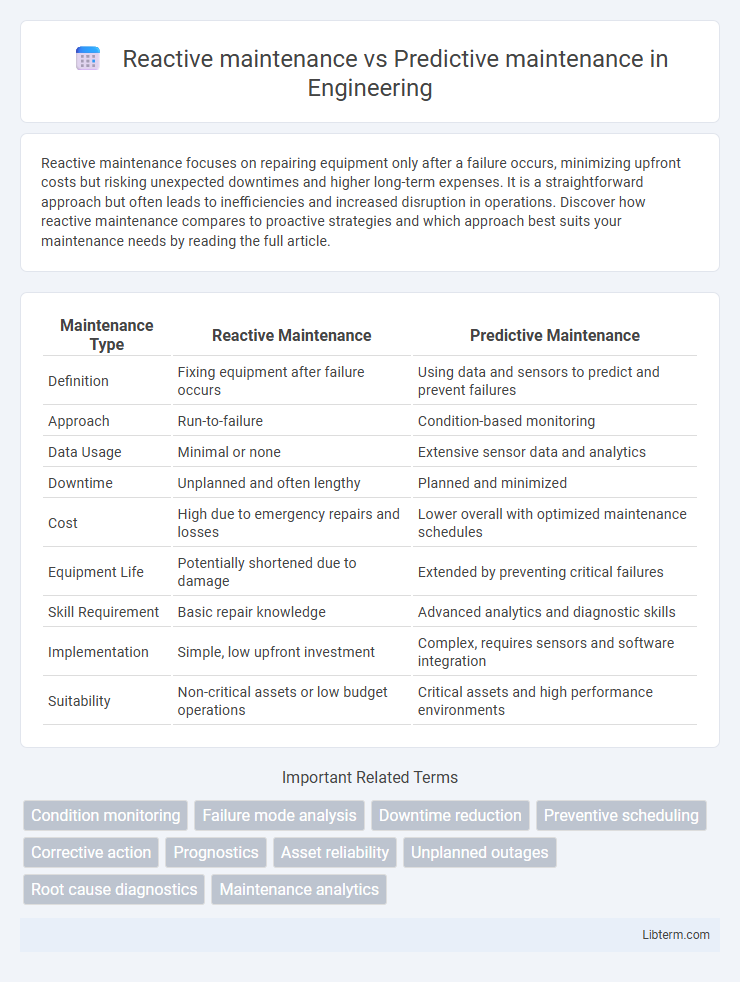
| Maintenance Type | Reactive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fixing equipment after failure occurs | Using data and sensors to predict and prevent failures |
| Approach | Run-to-failure | Condition-based monitoring |
| Data Usage | Minimal or none | Extensive sensor data and analytics |
| Downtime | Unplanned and often lengthy | Planned and minimized |
| Cost | High due to emergency repairs and losses | Lower overall with optimized maintenance schedules |
| Equipment Life | Potentially shortened due to damage | Extended by preventing critical failures |
| Skill Requirement | Basic repair knowledge | Advanced analytics and diagnostic skills |
| Implementation | Simple, low upfront investment | Complex, requires sensors and software integration |
| Suitability | Non-critical assets or low budget operations | Critical assets and high performance environments |
Introduction to Maintenance Strategies
Reactive maintenance involves repairing equipment only after a failure occurs, often leading to unexpected downtime and higher repair costs. Predictive maintenance relies on real-time data and condition monitoring technologies, such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging, to forecast equipment failures before they happen. Implementing predictive maintenance improves asset lifespan, reduces unplanned outages, and optimizes maintenance schedules for better operational efficiency.
Defining Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance involves repairing equipment only after a failure occurs, emphasizing immediate response to breakdowns without pre-planned interventions. This approach often leads to increased downtime, higher repair costs, and unpredictable operational disruptions. In contrast, predictive maintenance uses data-driven insights and condition monitoring to anticipate equipment failures before they happen, enabling timely maintenance actions that minimize downtime and extend asset lifespan.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data from sensors and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures before they occur, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. Unlike reactive maintenance, which addresses issues after breakdowns happen, predictive approaches extend asset life and optimize maintenance schedules. Machine learning algorithms and IoT technology play a critical role in accurately predicting equipment health and enabling proactive interventions.
Key Differences Between Reactive and Predictive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance responds to equipment failures after they occur, leading to unplanned downtime and potentially higher repair costs. Predictive maintenance uses data analytics, sensor monitoring, and machine learning to forecast equipment issues before failure, enabling proactive interventions that minimize downtime and extend asset life. The key difference lies in reactive maintenance being break-fix oriented, while predictive maintenance focuses on condition-based actions driven by real-time performance data.
Advantages of Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance offers the advantage of lower initial costs since repairs are only performed when equipment fails, reducing unnecessary expenditures on routine inspections or parts replacements. This approach minimizes downtime in systems where failures are infrequent, allowing organizations to concentrate resources on critical operations. It also simplifies maintenance scheduling by eliminating the need for complex predictive analytics or monitoring systems.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance leverages real-time data and advanced analytics to identify potential equipment failures before they occur, significantly reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. By enabling targeted interventions, it extends asset lifespan and optimizes resource allocation compared to reactive maintenance, which only addresses issues after breakdowns. This proactive approach improves operational efficiency and enhances overall reliability in industrial environments.
Cost Comparison: Reactive vs Predictive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance typically incurs higher costs due to unexpected equipment failures, emergency repairs, and production downtime, leading to substantial financial losses. Predictive maintenance leverages condition-monitoring technologies and data analytics to identify potential issues early, significantly reducing unplanned outages and minimizing repair expenses. Over time, predictive maintenance proves more cost-effective by optimizing resource allocation and extending asset lifespan, resulting in lower total maintenance costs compared to reactive approaches.
Impact on Equipment Lifespan and Downtime
Reactive maintenance often leads to increased equipment downtime and accelerates wear and tear, reducing overall equipment lifespan due to unplanned breakdowns. Predictive maintenance utilizes condition-monitoring technologies and data analytics to detect issues early, extending equipment lifespan by preventing severe failures and minimizing downtime. Implementing predictive maintenance results in optimized asset performance, reduced repair costs, and improved operational reliability.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Approach
Choosing the right maintenance approach depends on balancing asset criticality, operational costs, and risk tolerance. Reactive maintenance suits non-critical equipment with low failure impact, minimizing upfront investments but risking unexpected downtime. Predictive maintenance leverages condition-monitoring technologies and data analytics to forecast failures, optimizing resource allocation and reducing unplanned outages in high-value assets.
Future Trends in Maintenance Strategies
Future trends in maintenance strategies emphasize the integration of AI-driven predictive analytics and IoT-enabled sensors to enhance predictive maintenance accuracy, reducing downtime and operational costs significantly. Reactive maintenance remains prevalent in urgent failure scenarios but is increasingly supplemented by real-time condition monitoring technologies that enable proactive interventions. Advances in machine learning algorithms and digital twin simulations are projected to further optimize maintenance schedules and asset life cycles in industrial sectors.
Reactive maintenance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com