A rectifier converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), providing a stable power source for electronic devices. Regulators maintain a consistent voltage level, protecting circuits from fluctuations that could cause damage. Discover how these essential components work together to ensure your electronics perform reliably by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
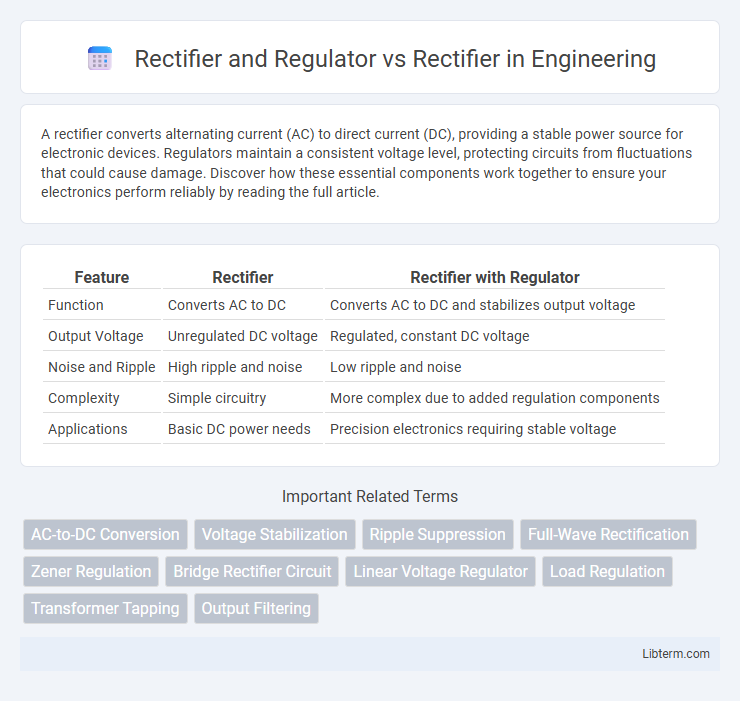
| Feature | Rectifier | Rectifier with Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts AC to DC | Converts AC to DC and stabilizes output voltage |
| Output Voltage | Unregulated DC voltage | Regulated, constant DC voltage |
| Noise and Ripple | High ripple and noise | Low ripple and noise |
| Complexity | Simple circuitry | More complex due to added regulation components |
| Applications | Basic DC power needs | Precision electronics requiring stable voltage |
Introduction to Rectifiers and Regulators
Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in one direction, which is essential for DC-powered devices. Regulators maintain a constant output voltage regardless of input voltage fluctuations or load variations, ensuring stable performance in electronic circuits. Combining rectifiers with regulators provides a steady and reliable DC power supply critical for sensitive electronic components.
Understanding Rectifiers: Definition and Function
Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction, essential for powering DC devices from AC sources. Regulators maintain a stable output voltage by compensating for fluctuations in the input voltage or load conditions, ensuring consistent electrical performance. While rectifiers shape the current type, regulators stabilize voltage, both crucial in electronic power supply systems.
Types of Rectifiers: Half-Wave vs Full-Wave
Half-wave rectifiers convert only one half-cycle of AC input into DC output, resulting in lower efficiency and higher ripple voltage, suitable for low-power applications. Full-wave rectifiers utilize both half-cycles, significantly improving output smoothness and efficiency by reducing ripple, ideal for high-power circuits. Bridge rectifiers and center-tap full-wave rectifiers represent common full-wave configurations, offering reliable performance in various electronic devices.
What is a Voltage Regulator?
A voltage regulator is an electronic device designed to maintain a constant output voltage regardless of input voltage fluctuations or load variations, ensuring stable and reliable power supply to electronic circuits. Unlike a rectifier that solely converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), the voltage regulator controls and stabilizes the DC voltage level to prevent damage to sensitive components. Common types include linear regulators and switching regulators, widely used in power supplies for electronic devices.
Combined Rectifier and Regulator Circuits
Combined rectifier and regulator circuits integrate AC to DC conversion with voltage stabilization, enhancing power supply efficiency and output quality. These circuits utilize a rectifier to convert alternating current (AC) into pulsating direct current (DC) followed by a regulator to maintain a constant voltage level, reducing ripple and preventing voltage fluctuations. Integrated designs often include components like silicon diodes for rectification and linear or switching regulators for voltage control, critical for sensitive electronic applications requiring stable DC power.
Key Differences: Rectifier vs Rectifier & Regulator
A rectifier converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction, primarily used to convert AC power for electronic devices. A rectifier and regulator combination not only converts AC to DC but also stabilizes the output voltage, ensuring consistent performance despite fluctuations in input voltage or load conditions. The key difference lies in voltage control: rectifiers provide unregulated DC output, whereas rectifier-regulator systems supply a steady, reliable voltage ideal for sensitive electronic components.
Advantages of Using Rectifier with Regulator
Using a rectifier combined with a regulator stabilizes voltage output, ensuring consistent power supply critical for sensitive electronic devices. This combination reduces voltage fluctuations and protects components from damage caused by overvoltage or undervoltage conditions. Enhanced efficiency and extended component lifespan are significant advantages when employing a rectifier with a regulator compared to using a rectifier alone.
Applications in Power Supply Systems
Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) and are essential in power supply systems for providing a stable DC output. Regulators maintain a constant voltage level by compensating for fluctuations in input voltage or load variations, ensuring reliable performance in sensitive electronic devices. Combining rectifiers with regulators enhances the overall efficiency and stability of power supplies, making them suitable for applications such as battery charging, DC motor drives, and digital circuits.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
Rectifiers convert AC to DC but often produce unregulated voltage with ripple, impacting device efficiency and performance. Adding a regulator to a rectifier stabilizes output voltage, reducing fluctuations and enhancing overall system reliability and efficiency. Regulated power supplies deliver consistent voltage, improving electronic device performance and protecting sensitive components compared to standalone rectifiers.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Power Solution
Selecting the right power solution requires understanding that rectifiers convert AC to DC, while regulators ensure stable voltage output by controlling fluctuations. A combined rectifier and regulator system offers efficient power conversion with consistent voltage, ideal for sensitive electronic devices. Opting solely for a rectifier suits applications where voltage stability is less critical, but including a regulator enhances overall performance and device longevity.
Rectifier and Regulator Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com