A boiler efficiently heats water or produces steam to power heating systems and industrial processes, ensuring consistent temperature control and energy savings. Modern boilers offer advanced safety features and eco-friendly technology to reduce emissions and fuel consumption. Explore the full article to understand how your boiler can optimize comfort and efficiency in your home or business.
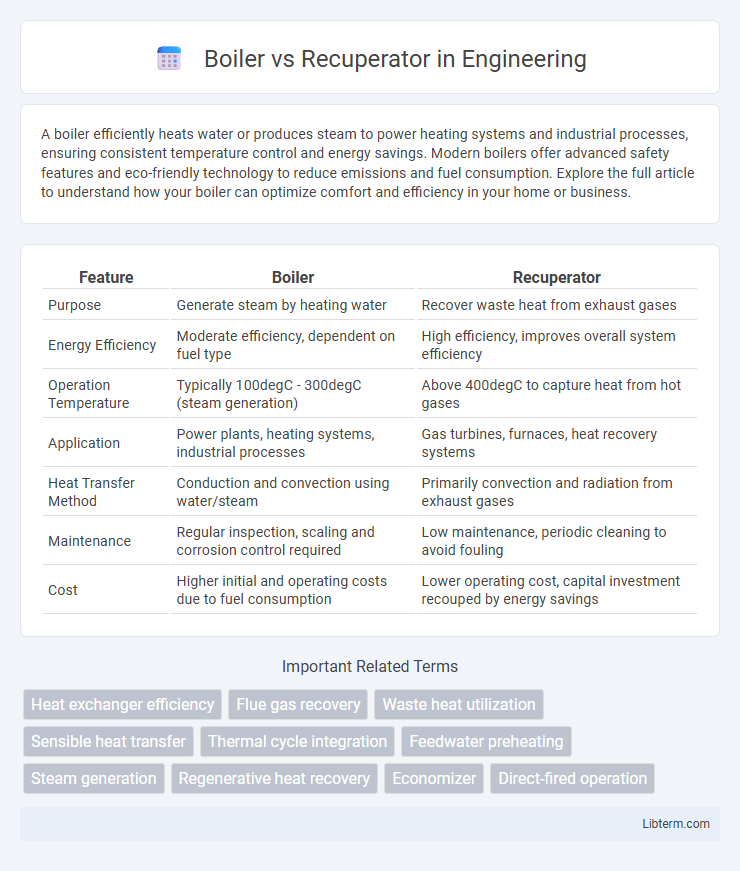
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Boiler | Recuperator |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Generate steam by heating water | Recover waste heat from exhaust gases |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate efficiency, dependent on fuel type | High efficiency, improves overall system efficiency |
| Operation Temperature | Typically 100degC - 300degC (steam generation) | Above 400degC to capture heat from hot gases |
| Application | Power plants, heating systems, industrial processes | Gas turbines, furnaces, heat recovery systems |
| Heat Transfer Method | Conduction and convection using water/steam | Primarily convection and radiation from exhaust gases |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection, scaling and corrosion control required | Low maintenance, periodic cleaning to avoid fouling |
| Cost | Higher initial and operating costs due to fuel consumption | Lower operating cost, capital investment recouped by energy savings |
Introduction to Boiler vs Recuperator
A boiler is a device designed to generate steam or hot water by applying heat to water through combustion of fuel or application of electricity. A recuperator is a heat exchanger that recovers waste heat from exhaust gases to preheat incoming air or fluids, improving system efficiency. Boilers primarily serve steam production for heating or power, while recuperators enhance thermal efficiency by reclaiming residual heat within industrial processes.
Definition and Basic Functions
A boiler is a device that generates steam by heating water using fuel or electricity, primarily utilized in power plants and industrial processes to produce thermal energy. A recuperator is a heat exchanger that recovers waste heat from exhaust gases and transfers it to the incoming air or fluid, improving energy efficiency in heating systems and gas turbines. Boilers focus on steam production, while recuperators enhance energy recovery and reduce fuel consumption.
Key Differences Between Boilers and Recuperators
Boilers generate steam or hot water by burning fuel and transferring heat to water through metal tubes, primarily used for heating and power generation. Recuperators recover waste heat from exhaust gases to preheat combustion air, enhancing efficiency in industrial furnaces and gas turbines. The key differences lie in their function--boilers produce steam or hot water, while recuperators improve thermal efficiency by capturing and reusing waste heat.
Working Principles Explained
A boiler generates steam by transferring heat from fuel combustion to water inside its tubes, creating high-pressure steam for power or heating applications. A recuperator recovers waste heat from exhaust gases and transfers it to incoming air or fluid, improving thermal efficiency in industrial processes or HVAC systems. Boilers rely on direct heat exchange through combustion, while recuperators use indirect heat exchange to recycle energy and reduce fuel consumption.
Efficiency Comparison
Boilers typically convert fuel energy into steam with efficiency ranging from 70% to 90%, depending on design and fuel type, while recuperators enhance overall system efficiency by recovering waste heat from exhaust gases to preheat incoming air or fuel. Incorporating a recuperator can improve thermal efficiency by 10% to 30%, reducing fuel consumption and operational costs in industrial heating processes. The combined use of boilers with recuperators is critical in maximizing energy recovery and minimizing emissions in power generation and manufacturing applications.
Applications and Industries
Boilers are widely used in industries such as power generation, chemical processing, and manufacturing for steam production and heating applications. Recuperators find extensive application in high-temperature industries like steelmaking, glass production, and aerospace for waste heat recovery and improving energy efficiency. Both components enhance thermal systems but cater to distinct industrial needs based on heat generation versus heat recovery functions.
Energy Savings and Environmental Impact
A boiler converts fuel into steam, often resulting in significant energy loss through exhaust gases, whereas a recuperator recycles waste heat from these gases to preheat the incoming air, drastically improving thermal efficiency by up to 25%. Utilizing a recuperator reduces fuel consumption and lowers greenhouse gas emissions, contributing directly to decreased carbon footprints in industrial and power generation applications. Energy recovery systems like recuperators play a critical role in sustainable manufacturing by optimizing fuel use and minimizing environmental pollutants.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Boilers typically involve lower initial capital costs but incur higher operational expenses due to fuel consumption and maintenance, whereas recuperators demand higher upfront investment yet significantly reduce fuel costs by recovering waste heat. The return on investment (ROI) for recuperators is generally faster in industrial settings with continuous high-temperature exhaust streams, providing energy savings that offset initial costs within a few years. Cost analysis should consider factors such as fuel price volatility, maintenance frequency, system efficiency, and operational hours to accurately compare the long-term financial benefits of boilers versus recuperators.
Maintenance and Lifespan Considerations
Boilers require regular inspection and cleaning to prevent scale buildup and corrosion, which directly impact their lifespan, typically ranging from 15 to 30 years depending on operating conditions. Recuperators, often made from high-grade alloys to withstand high temperatures, need periodic maintenance focused on cleaning heat exchange surfaces and checking for thermal fatigue, with lifespans generally extending beyond 20 years when properly maintained. Maintenance strategies for both systems emphasize proactive detection of wear and adherence to manufacturer guidelines to maximize operational efficiency and service life.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between a boiler and a recuperator depends on your specific energy efficiency and heat recovery requirements. Boilers are ideal for generating steam or hot water for heating and industrial processes, while recuperators excel in recovering waste heat from exhaust gases to improve overall system efficiency. Evaluate your operational goals, fuel sources, and temperature ranges to determine which system best aligns with your energy-saving and process demands.
Boiler Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com