A sheet pile wall is a crucial retaining structure used to support soil and prevent erosion in construction and excavation projects. Made from interlocking steel, vinyl, or wood sections, these walls provide effective lateral resistance and durability in various soil conditions. Explore this article to learn how a sheet pile wall can enhance the stability and safety of your construction site.
Table of Comparison
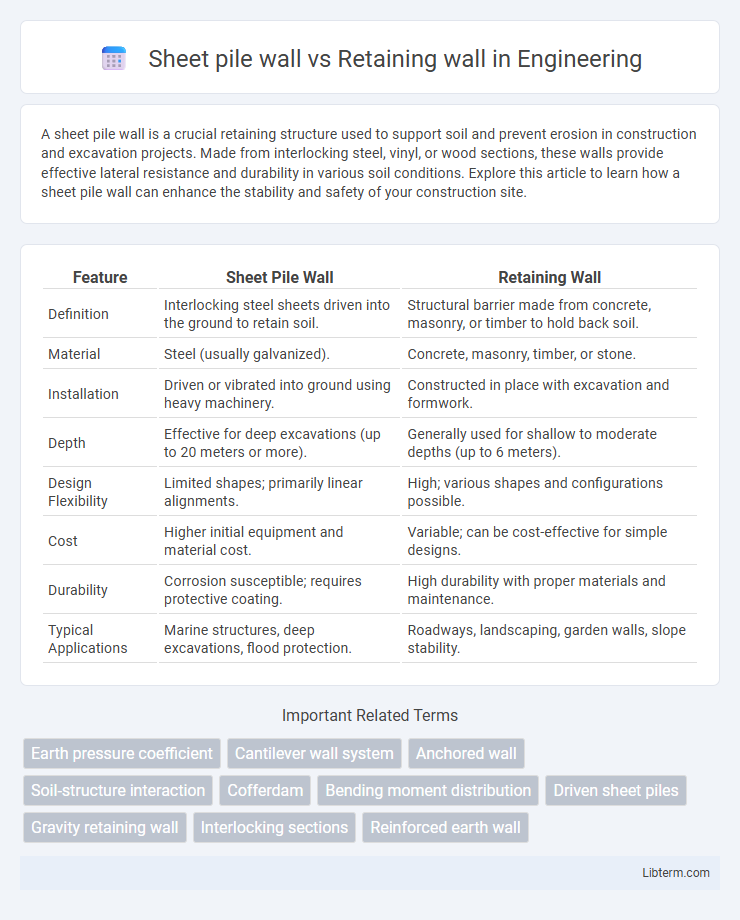
| Feature | Sheet Pile Wall | Retaining Wall |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interlocking steel sheets driven into the ground to retain soil. | Structural barrier made from concrete, masonry, or timber to hold back soil. |
| Material | Steel (usually galvanized). | Concrete, masonry, timber, or stone. |
| Installation | Driven or vibrated into ground using heavy machinery. | Constructed in place with excavation and formwork. |
| Depth | Effective for deep excavations (up to 20 meters or more). | Generally used for shallow to moderate depths (up to 6 meters). |
| Design Flexibility | Limited shapes; primarily linear alignments. | High; various shapes and configurations possible. |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment and material cost. | Variable; can be cost-effective for simple designs. |
| Durability | Corrosion susceptible; requires protective coating. | High durability with proper materials and maintenance. |
| Typical Applications | Marine structures, deep excavations, flood protection. | Roadways, landscaping, garden walls, slope stability. |
Introduction to Sheet Pile Walls and Retaining Walls
Sheet pile walls consist of interlocking steel, vinyl, or timber sheets driven into the ground to provide earth retention and excavation support in waterfronts, trenches, and construction sites. Retaining walls are rigid or flexible structures constructed from materials like concrete, masonry, or stone to hold back soil and prevent erosion or landslides on sloped terrains and embankments. Both systems are essential in geotechnical engineering for stabilizing soil but differ in construction methods, applications, and load-bearing capabilities.
Key Differences Between Sheet Pile and Retaining Walls
Sheet pile walls primarily use interlocking steel sheets driven deep into the ground to form a continuous barrier ideal for water retention and temporary excavation support. Retaining walls, made from concrete, masonry, or timber, provide structural support to hold back soil on sloped terrains and manage lateral earth pressures. Sheet pile walls excel in flexibility and ease of installation, while retaining walls offer greater durability and aesthetic versatility for permanent landscaping solutions.
Structural Design and Load-Bearing Capacity
Sheet pile walls are thin, interlocking steel sections driven into the ground, primarily designed to resist lateral earth pressures in soft soil conditions with limited load-bearing capacity for extreme heavy loads. Retaining walls, constructed from concrete, masonry, or reinforced earth, offer higher structural rigidity and are engineered to support substantial vertical and lateral loads, making them suitable for steep slopes and heavy surcharge applications. The structural design of retaining walls incorporates factors like sliding, overturning, and bearing capacity, whereas sheet pile walls emphasize flexibility and ease of installation with moderate load resistance.
Materials Used in Sheet Pile vs Retaining Walls
Sheet pile walls primarily utilize steel, vinyl, or wood planks driven deep into the ground to create a continuous barrier, offering high strength and corrosion resistance. Retaining walls are commonly constructed from reinforced concrete, stone, masonry, or timber, chosen based on load requirements, aesthetic preferences, and soil conditions. The selection of materials in sheet pile and retaining walls directly influences durability, installation methods, and suitability for different environmental challenges.
Installation Methods and Construction Techniques
Sheet pile walls are installed by driving prefabricated steel, vinyl, or wooden sheets into the ground using vibratory hammers, impact hammers, or hydraulic presses, allowing for rapid installation in soft soil conditions and limited space. Retaining walls involve constructing gravity walls, cantilever walls, or anchored walls using concrete, masonry, or reinforced earth, often requiring excavation, formwork, and curing time, making them more labor-intensive and time-consuming. Installation techniques for sheet piles emphasize minimal soil disturbance and quick setup, while retaining walls demand precise engineering for load distribution and soil retention.
Applications and Use Cases
Sheet pile walls are primarily used in marine and waterfront construction for waterfront retaining structures, cofferdams, and excavation support in soft soils or limited space environments. Retaining walls are versatile in landscaping, roadways, and slope stabilization, managing soil pressure in various terrains, often using concrete, masonry, or reinforced earth. Sheet pile walls excel in temporary or permanent seepage cutoff barriers, whereas retaining walls are ideal for long-term structural support in highways, terraces, and urban developments.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Sheet pile walls generally offer lower upfront costs due to faster installation times and reduced material usage compared to conventional retaining walls, making them economically advantageous for temporary or light-duty applications. Retaining walls, while potentially more expensive initially due to heavier materials like concrete or masonry, provide greater durability and lower long-term maintenance costs, supporting better overall lifecycle value for permanent structures. Economic considerations also include site-specific factors such as soil conditions, height requirements, and project duration, which heavily influence the cost-effectiveness of each wall type.
Durability, Maintenance, and Lifespan
Sheet pile walls, constructed from steel or vinyl, offer high durability with excellent resistance to water and soil pressure, making them suitable for marine and waterfront applications, though they may require periodic corrosion protection and inspection. Retaining walls, typically built from concrete, masonry, or stone, provide long-lasting structural support with lower maintenance demands but are susceptible to cracking and water infiltration without proper drainage systems. The lifespan of sheet pile walls generally ranges from 20 to 50 years depending on material and environment, while well-maintained retaining walls can exceed 50 years, emphasizing the importance of material choice and upkeep for longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sheet pile walls cause minimal soil disturbance and allow for efficient water management, reducing erosion and contamination risks in sensitive environments. Retaining walls often require extensive excavation and concrete use, leading to higher carbon footprints and greater habitat disruption. Sustainable construction favors sheet pile walls when preserving natural sites and minimizing ecological impact is a priority.
Choosing the Right Wall for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate wall type depends on project requirements such as soil conditions, load capacity, and space constraints. Sheet pile walls are ideal for waterfront projects and rapid installation in soft soils, offering flexibility and ease of removal. Retaining walls provide excellent structural support for steep slopes and heavy loads, suitable for landscaping and civil engineering applications requiring durability and aesthetic integration.
Sheet pile wall Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com