Hollow core slabs provide efficient load-bearing solutions with reduced weight due to their voided structure, enhancing construction speed and cost-effectiveness. These precast concrete elements offer excellent thermal insulation and soundproofing, making them ideal for residential and commercial buildings. Discover how hollow core slabs can optimize your construction projects by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
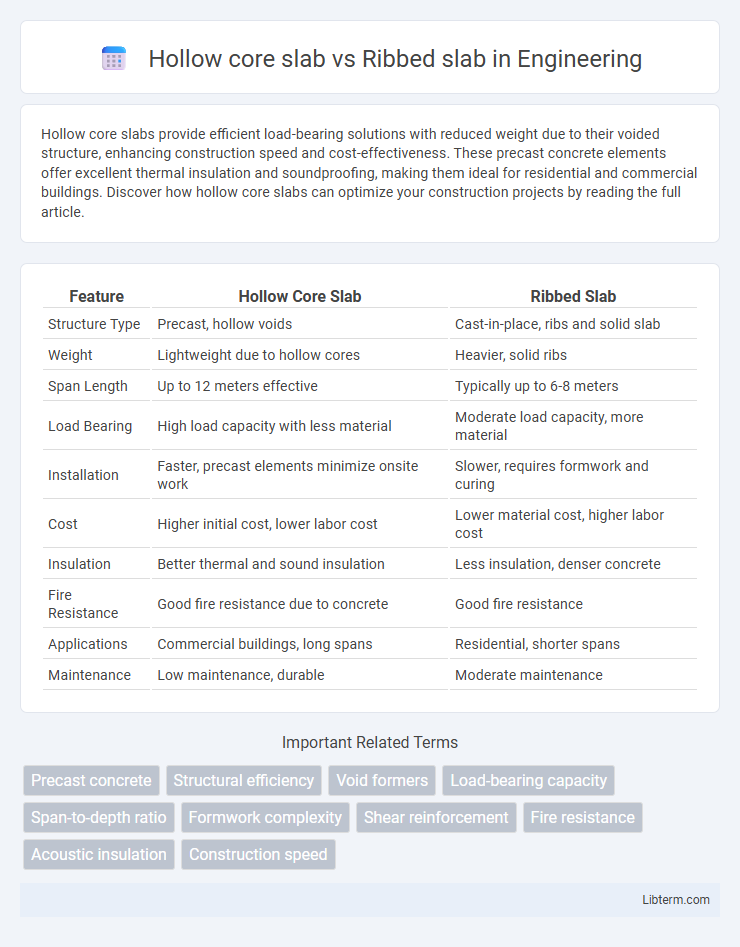
| Feature | Hollow Core Slab | Ribbed Slab |
|---|---|---|
| Structure Type | Precast, hollow voids | Cast-in-place, ribs and solid slab |
| Weight | Lightweight due to hollow cores | Heavier, solid ribs |
| Span Length | Up to 12 meters effective | Typically up to 6-8 meters |
| Load Bearing | High load capacity with less material | Moderate load capacity, more material |
| Installation | Faster, precast elements minimize onsite work | Slower, requires formwork and curing |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower labor cost | Lower material cost, higher labor cost |
| Insulation | Better thermal and sound insulation | Less insulation, denser concrete |
| Fire Resistance | Good fire resistance due to concrete | Good fire resistance |
| Applications | Commercial buildings, long spans | Residential, shorter spans |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, durable | Moderate maintenance |
Introduction to Hollow Core Slab and Ribbed Slab
Hollow core slabs are precast concrete elements characterized by continuous voids that reduce weight and improve structural efficiency, commonly used in floor and roof systems for rapid construction and cost savings. Ribbed slabs, consisting of a series of reinforced concrete ribs separated by voids or blocks, provide enhanced load-bearing capacity and reduced material usage in long-span structures. Both slab types offer distinct advantages in terms of strength, weight distribution, and construction speed, catering to various architectural and engineering requirements.
Structural Design Differences
Hollow core slabs feature pre-stressed concrete with continuous voids, reducing weight and enhancing load-bearing efficiency, while ribbed slabs consist of reinforced concrete beams with a thin slab topping, providing increased rigidity and fire resistance. In structural design, hollow core slabs offer longer spans and faster installation due to their uniform cross-section, whereas ribbed slabs allow for greater customization in beam spacing and depth to accommodate varying load conditions. The choice between these systems hinges on factors such as structural load requirements, span length, and construction speed preferences.
Material Efficiency Comparison
Hollow core slabs offer superior material efficiency due to their pre-stressed concrete design, reducing concrete volume while maintaining structural strength. Ribbed slabs use less concrete than solid slabs by incorporating ribs that optimize load distribution, but typically consume more material than hollow core slabs. The hollow cores significantly decrease dead load and material costs, making hollow core slabs a more efficient choice in large-scale construction projects.
Installation and Construction Methods
Hollow core slabs are precast concrete elements manufactured off-site, allowing rapid installation with minimal on-site labor and reduced curing time due to factory-controlled conditions. Ribbed slabs, constructed using formwork and in-situ casting of concrete with ribs and a solid topping, require more extensive on-site labor, shuttering, and longer curing periods, impacting construction speed. The choice between hollow core and ribbed slabs significantly influences project timelines and labor costs based on their distinct installation and construction methodologies.
Load-Bearing Capacity
Hollow core slabs offer high load-bearing capacity due to their prestressed concrete design, allowing them to support heavy structural loads while minimizing weight. Ribbed slabs provide enhanced load distribution through their reinforced concrete ribs, making them suitable for spans requiring stiffness and reduced slab thickness. Both slab types optimize structural performance, with hollow core slabs excelling in long spans and ribbed slabs ideal for moderate loads and complex architectural layouts.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Hollow core slabs typically offer lower material costs and faster installation times, reducing overall labor expenses compared to ribbed slabs. Ribbed slabs require more formwork and reinforcement, increasing both material and labor costs, which impacts the construction budget significantly. Selecting between these slabs depends on project size, load requirements, and budget constraints, with hollow core slabs often preferred for cost-effective large-span solutions.
Thermal and Acoustic Performance
Hollow core slabs offer superior thermal insulation due to the air voids that reduce heat transfer, making them energy-efficient in building envelopes. Ribbed slabs, with their thinner cross-sections and exposed ribs, typically provide less thermal mass but can incorporate insulating materials to enhance performance. Acoustic performance favors hollow core slabs as the continuous voids dampen sound transmission better than the ribbed slab's open-web design, which may require additional acoustic treatments for noise reduction.
Common Applications
Hollow core slabs are extensively used in residential, commercial, and parking structures due to their lightweight nature and long spans, enabling faster construction and reduced material costs. Ribbed slabs find common applications in industrial buildings and multistory car parks where higher load-bearing capacity and flexibility in beam placement are required. Both slab types support efficient load distribution but are selected based on specific structural and architectural demands.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hollow core slabs reduce material usage by incorporating voids, leading to lower embodied carbon and less concrete production compared to solid ribbed slabs. Ribbed slabs, while offering structural efficiency, often require more raw materials and longer construction times, increasing their carbon footprint. The hollow core design enhances thermal insulation and energy efficiency, contributing to sustainable building practices.
Selection Criteria: Which Slab is Best for Your Project?
Hollow core slabs offer high strength-to-weight ratio and quick installation, making them ideal for long-span floors and projects requiring efficient load distribution with reduced dead weight. Ribbed slabs provide design flexibility with deeper ribs for enhanced load capacity and reduced material usage, suitable for irregular layouts or where vibration control and thermal insulation are priorities. Selection depends on project-specific factors such as span length, load requirements, structural efficiency, cost constraints, and local construction practices.
Hollow core slab Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com