SCADA systems monitor and control industrial processes by collecting real-time data, while RTUs serve as remote units that transmit this data to central control centers. These technologies enhance operational efficiency and enable prompt decision-making in sectors like energy, water, and manufacturing. Discover how SCADA and RTU can optimize your system performance by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
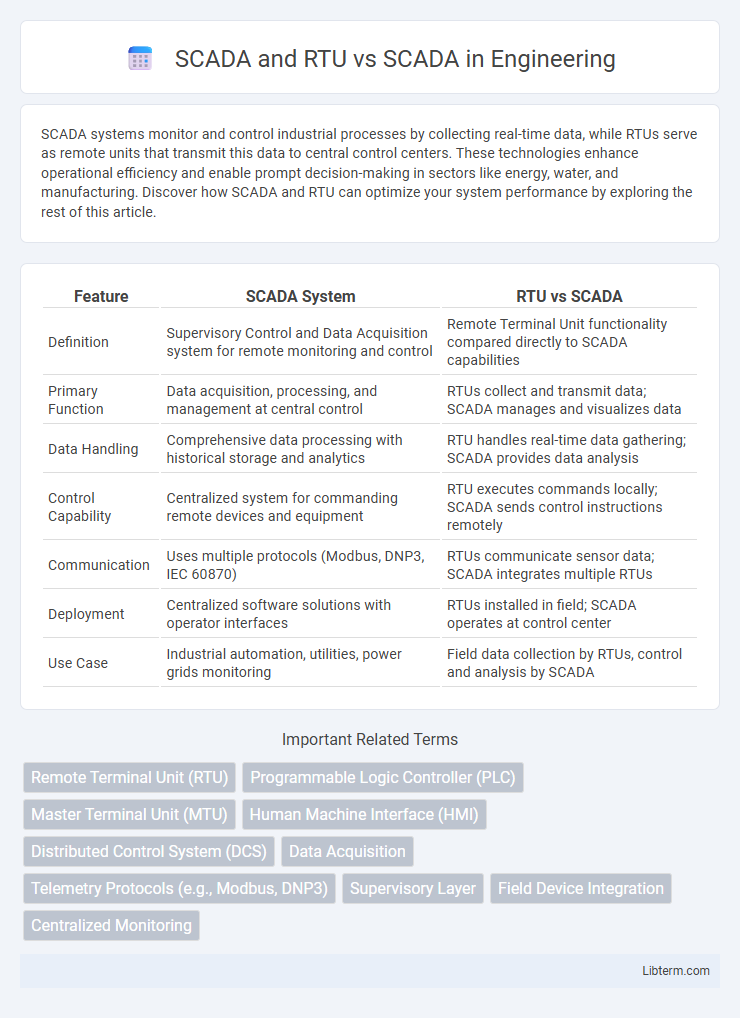
| Feature | SCADA System | RTU vs SCADA |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system for remote monitoring and control | Remote Terminal Unit functionality compared directly to SCADA capabilities |
| Primary Function | Data acquisition, processing, and management at central control | RTUs collect and transmit data; SCADA manages and visualizes data |
| Data Handling | Comprehensive data processing with historical storage and analytics | RTU handles real-time data gathering; SCADA provides data analysis |
| Control Capability | Centralized system for commanding remote devices and equipment | RTU executes commands locally; SCADA sends control instructions remotely |
| Communication | Uses multiple protocols (Modbus, DNP3, IEC 60870) | RTUs communicate sensor data; SCADA integrates multiple RTUs |
| Deployment | Centralized software solutions with operator interfaces | RTUs installed in field; SCADA operates at control center |
| Use Case | Industrial automation, utilities, power grids monitoring | Field data collection by RTUs, control and analysis by SCADA |
Introduction to SCADA Systems
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are critical for real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes across utilities, manufacturing, and infrastructure. RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) serve as field devices within SCADA systems, collecting sensor data and executing control commands remotely to ensure seamless communication between the centralized control system and field equipment. Distinguishing SCADA from RTUs highlights that SCADA provides the overall system architecture and software for data visualization and control, while RTUs function as the hardware that interfaces directly with physical assets.
Overview of Remote Terminal Units (RTU)
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) serve as critical components within SCADA systems, acting as field devices that collect data from sensors and transmit it to the central control system. RTUs facilitate real-time monitoring and control of remote equipment by converting analog signals to digital data, enabling seamless communication over various protocols such as Modbus and DNP3. Their robust design supports harsh environments, making RTUs essential for reliable SCADA operations in industries like utilities, oil and gas, and water management.
SCADA with RTU Integration Explained
SCADA with RTU integration enhances remote monitoring and control by connecting Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems directly with Remote Terminal Units, enabling real-time data collection from widespread assets. RTUs act as field devices that gather sensor data and transmit it to the central SCADA software, improving operational efficiency and response times in industrial environments such as utilities and manufacturing. This integration allows for seamless automation, fault detection, and precise control of distributed equipment, optimizing system reliability and reducing downtime.
SCADA Without RTU: Architecture and Use Cases
SCADA without RTU architecture relies on direct communication between the central monitoring system and field devices using protocols like Modbus TCP/IP or DNP3, eliminating the need for remote terminal units. This setup is ideal for applications with nearby or centralized control infrastructure, such as manufacturing plants or water treatment facilities where sensors and actuators connect directly to the SCADA master station. Use cases include small-scale automation systems with simplified network topologies, reducing hardware costs and minimizing latency for real-time monitoring and control.
RTU vs PLC in SCADA Environments
RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) both serve as critical components in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) environments, with RTUs optimized for remote monitoring and control over vast distances using low power consumption and robust communication protocols. PLCs are designed for real-time control and automation within localized industrial processes, offering high processing speeds and extensive I/O configurations for precise control tasks. Choosing between RTUs and PLCs depends on factors such as site location, communication infrastructure, environmental conditions, and the complexity of control requirements within the SCADA system.
Communication Protocols in SCADA and RTU
SCADA systems utilize various communication protocols such as Modbus, DNP3, and IEC 60870-5-104 to enable reliable data exchange between control centers and remote terminal units (RTUs). RTUs act as field devices that collect telemetry data and use protocols like Modbus RTU or IEC 61850 for real-time communication with SCADA master stations. Efficient protocol selection in SCADA and RTU architectures ensures secure, low-latency transmission vital for monitoring and controlling critical infrastructure.
Key Differences: SCADA and RTU vs Standalone SCADA
SCADA systems integrate Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) to enhance real-time data acquisition and control across dispersed locations, providing centralized monitoring and automation. Standalone SCADA lacks RTU integration, limiting its ability to remotely collect data or directly control field devices, reducing overall system scalability and responsiveness. The key difference lies in RTU's role in extending SCADA's reach for comprehensive asset management and operational efficiency in industrial environments.
Advantages of Using RTU in SCADA Systems
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) enhance SCADA systems by providing reliable data acquisition and real-time control in remote or hard-to-access locations. RTUs offer rugged design and low power consumption, ensuring continuous operation even in harsh environmental conditions. Their ability to perform local processing reduces communication delays, improving system responsiveness and overall efficiency.
Challenges in SCADA and RTU Integration
Challenges in SCADA and RTU integration primarily revolve around communication protocol compatibility, real-time data synchronization, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities. RTUs often use diverse, legacy protocols that complicate seamless data exchange with modern SCADA systems, leading to latency and data inconsistency issues. Ensuring robust encryption and secure authentication is critical to protect integrated SCADA-RTU networks from cyberattacks while maintaining system reliability and operational continuity.
Future Trends in SCADA and RTU Technologies
Future trends in SCADA and RTU technologies emphasize enhanced cybersecurity protocols and the integration of advanced artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance and real-time data analytics. Edge computing is increasingly adopted to reduce latency and improve decision-making speed in critical infrastructure management. Wireless communication advancements and IoT integration enable more scalable, flexible, and cost-effective remote monitoring solutions in industrial automation.
SCADA and RTU Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com