Bevel gears are essential mechanical components designed to transmit motion between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, ensuring efficient power transfer in machinery. These gears come in various types, including straight, spiral, and hypoid, each offering unique advantages for specific applications such as automotive differentials and industrial equipment. Explore the rest of this article to understand how bevel gears can optimize Your mechanical systems.
Table of Comparison
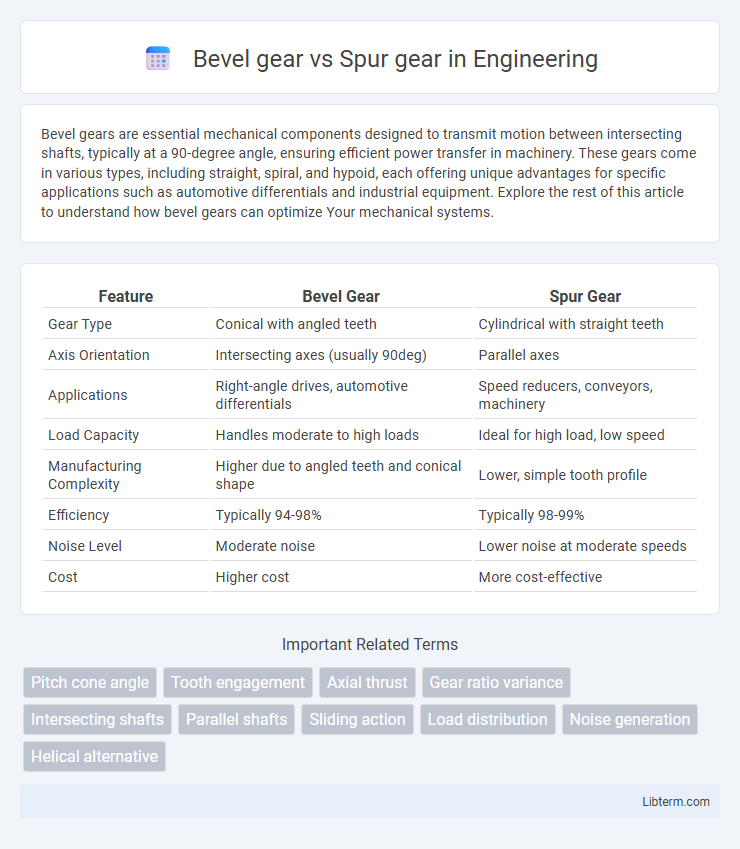
| Feature | Bevel Gear | Spur Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Gear Type | Conical with angled teeth | Cylindrical with straight teeth |
| Axis Orientation | Intersecting axes (usually 90deg) | Parallel axes |
| Applications | Right-angle drives, automotive differentials | Speed reducers, conveyors, machinery |
| Load Capacity | Handles moderate to high loads | Ideal for high load, low speed |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Higher due to angled teeth and conical shape | Lower, simple tooth profile |
| Efficiency | Typically 94-98% | Typically 98-99% |
| Noise Level | Moderate noise | Lower noise at moderate speeds |
| Cost | Higher cost | More cost-effective |
Introduction to Bevel Gears and Spur Gears
Bevel gears feature conically shaped teeth designed to transmit motion between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, enabling smooth angular power transfer in mechanical systems. Spur gears consist of parallel shafts with straight teeth aligned parallel to the axis, providing efficient torque transfer and simplicity in design. Both gears optimize mechanical advantage but differ in applications, with bevel gears suited for changing shaft direction and spur gears ideal for high-speed, low-noise transmission in the same plane.
Key Design Differences
Bevel gears feature conical shapes that allow the transmission of motion between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, while spur gears have cylindrical shapes designed for parallel shaft rotation. The teeth of bevel gears are cut on the cone's surface, resulting in varying tooth size along the face width, whereas spur gear teeth are straight and uniform, running parallel to the gear axis. These design differences impact load distribution, noise levels, and efficiency, with bevel gears suited for angular motion and spur gears optimized for simplicity and high-speed applications.
Working Principles of Spur and Bevel Gears
Spur gears transmit power through parallel shafts by meshing straight-cut teeth, creating efficient rotational motion with minimal axial thrust. Bevel gears operate on shafts intersecting at an angle, typically 90 degrees, utilizing conically shaped teeth to change the direction of torque and speed. The fundamental difference lies in their tooth geometry and shaft orientation, affecting their load distribution and application suitability.
Applications: Where Each Gear Type Excels
Bevel gears excel in applications requiring angular motion transfer, such as automotive differentials and power tools, due to their ability to transmit torque between intersecting shafts. Spur gears are ideal for parallel shaft applications like conveyors and gearboxes, offering high efficiency and simplicity in design. Each gear type is selected based on specific mechanical requirements and shaft orientation.
Efficiency Comparison: Spur vs Bevel Gears
Spur gears typically offer higher efficiency than bevel gears due to their simpler design and less sliding friction between gear teeth. Bevel gears, used for changing shaft angles, can experience greater friction and energy loss because of their angular contact surfaces. Efficiency in spur gears often ranges from 95% to 99%, while bevel gears generally exhibit efficiencies between 90% and 98%, influenced by factors such as bevel angle and lubrication.
Load Capacity and Performance
Bevel gears generally offer higher load capacity and better torque transmission due to their conical shape, which allows for smoother meshing and greater contact area between teeth compared to spur gears. Spur gears excel in high-speed applications but are limited in load capacity because their straight teeth generate more noise and vibration under heavy loads. Performance-wise, bevel gears provide improved efficiency in changing shaft angles, making them ideal for applications requiring precise power transfer and reduced mechanical stress.
Noise and Vibration Characteristics
Bevel gears typically generate higher noise and vibration levels compared to spur gears due to their angled teeth and the meshing forces acting at an angle, which induce axial and radial loads. Spur gears produce more uniform noise and lower vibration as their teeth engage in parallel planes, resulting in simpler load distribution and smoother operation. Proper alignment and high-precision manufacturing reduce noise and vibration in both gear types, but spur gears remain the quieter and less vibration-prone option in most industrial applications.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Bevel gears require regular inspection and precise alignment to prevent premature wear due to their angled teeth and complex contact patterns, which can tolerate less misalignment than spur gears. Spur gears are generally easier to maintain because their straight teeth experience uniform load distribution, resulting in lower wear rates under similar operating conditions. Durability in bevel gears depends heavily on accurate lubrication and mounting, while spur gears typically offer longer service life with simpler maintenance routines.
Cost Factors and Economic Impact
Bevel gears generally have higher manufacturing costs than spur gears due to their complex geometry and precision requirements, increasing production expenses. Spur gears, with simpler design and easier machining, offer cost-effective solutions for applications requiring moderate speeds and loads. Selecting between bevel and spur gears impacts the overall economic efficiency by balancing initial investment with performance needs and maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Gear for Your Application
Bevel gears are ideal for applications requiring a change in shaft direction, typically at 90 degrees, providing smooth and efficient torque transmission in limited space. Spur gears are best suited for parallel shaft operations where simplicity, higher speed, and cost-effectiveness are priorities, offering high efficiency in straightforward power transfer. Selecting the right gear depends on spatial constraints, load requirements, and desired shaft orientation to optimize performance and durability in your mechanical system.
Bevel gear Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com