Chain drive systems offer efficient power transmission by using interlocking metal links to transfer motion between sprockets. They are commonly used in bicycles, motorcycles, and industrial machinery due to their durability and ability to handle high torque. Discover how a chain drive can optimize Your mechanical setup by exploring the detailed benefits and applications in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
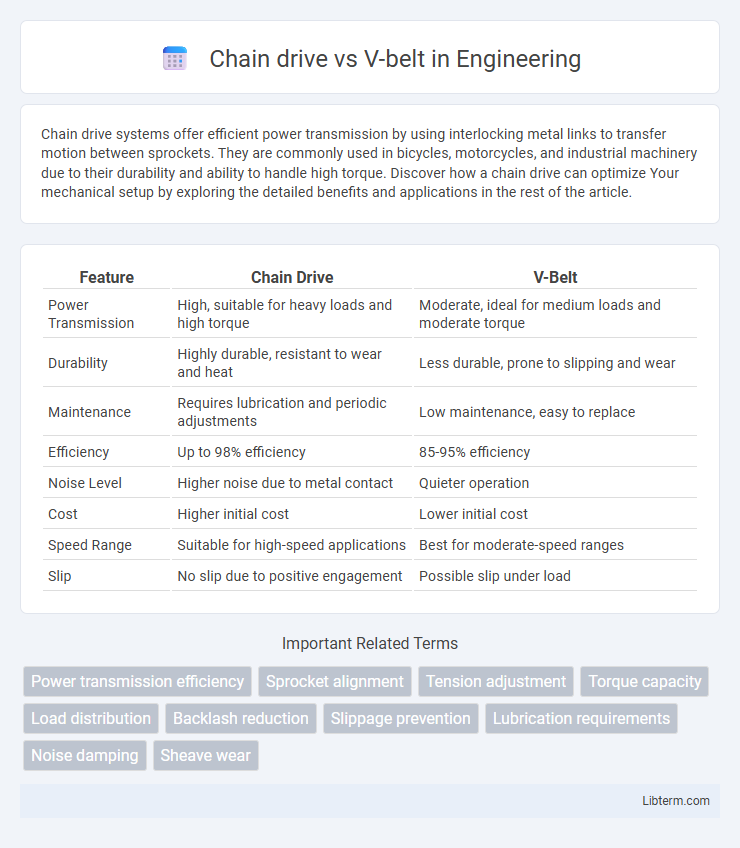
| Feature | Chain Drive | V-Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | High, suitable for heavy loads and high torque | Moderate, ideal for medium loads and moderate torque |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear and heat | Less durable, prone to slipping and wear |
| Maintenance | Requires lubrication and periodic adjustments | Low maintenance, easy to replace |
| Efficiency | Up to 98% efficiency | 85-95% efficiency |
| Noise Level | Higher noise due to metal contact | Quieter operation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Speed Range | Suitable for high-speed applications | Best for moderate-speed ranges |
| Slip | No slip due to positive engagement | Possible slip under load |
Introduction to Chain Drive and V-Belt Systems
Chain drive systems transmit power through interlocking metal links, providing high durability and efficient torque transfer in heavy-duty applications. V-belt systems operate by friction between the belt and pulleys, offering quieter operation and flexibility for varying shaft distances. Both systems serve critical roles in mechanical power transmission but differ significantly in maintenance, load capacity, and efficiency.
How Chain Drives Work
Chain drives transmit mechanical power through a series of linked metal chains engaging with toothed sprockets, ensuring positive drive without slipping. The chains mesh directly with the sprocket teeth, providing high torque transmission and maintaining precise speed ratios in machinery. This mechanism is ideal for heavy-duty applications where durability and efficiency are critical.
How V-Belt Drives Operate
V-belt drives operate through a flexible rubber belt that wraps around pulleys, transmitting power via friction between the belt's sides and the pulley grooves. Their design allows for smooth, quiet operation with the ability to absorb shock loads and accommodate slight misalignments. Commonly used in automotive and industrial machinery, V-belt drives offer efficient power transmission and easy maintenance compared to chain drives.
Key Differences Between Chain and V-Belt Drives
Chain drives offer higher torque capacity and durability for power transmission in heavy-duty applications, whereas V-belt drives provide smoother operation with less maintenance, ideal for lighter loads. Chain drives maintain a constant speed ratio due to their positive engagement, while V-belt drives can slip slightly, affecting speed consistency. The materials differ significantly: chains are made of metal links offering strength and longevity, and V-belts are composed of rubber and fabric, allowing flexibility and quieter function.
Advantages of Chain Drives
Chain drives offer superior power transmission efficiency and are highly durable under heavy loads and harsh conditions compared to V-belts. They maintain consistent speed ratios without slipping, enabling precise mechanical performance in applications like motorcycles and industrial machinery. Low elongation and resistance to heat and oil exposure make chain drives ideal for long-term, maintenance-intensive operations.
Benefits of V-Belt Drives
V-belt drives offer superior flexibility and quieter operation compared to chain drives, reducing noise pollution and maintenance requirements. Their ability to absorb shock loads protects machinery components, extending the lifespan of belts and pulleys. V-belt drives provide efficient power transmission with minimal slippage, enhancing overall system reliability and energy efficiency.
Common Applications for Chain Drives
Chain drives are widely used in motorcycles, bicycles, and industrial machinery for power transmission where durability and load capacity are critical. They excel in applications requiring precise speed ratios and resistance to slipping, such as conveyor systems and agricultural equipment. Unlike V-belts, chain drives perform reliably in harsh environments with high torque demands and minimal maintenance intervals.
Typical Uses for V-Belt Drives
V-belt drives are commonly used in automotive applications, agricultural machinery, and HVAC systems due to their efficiency in transmitting moderate power over varying distances. They excel in environments requiring quiet operation and minimal maintenance, such as conveyor systems and industrial compressors. V-belts provide reliable traction and flexibility, making them ideal for machines with fluctuating loads and misalignment.
Maintenance Requirements: Chain Drive vs. V-Belt
Chain drives require regular lubrication, tension adjustment, and inspection for wear to prevent elongation and failure, whereas V-belts demand periodic alignment checks, tension adjustments, and replacement when cracking or glazing occurs. Chains typically have higher maintenance intensity due to metal-to-metal contact and exposure to contaminants, while V-belts benefit from quieter operation and lower upkeep but degrade faster under high heat or misalignment conditions. Proper maintenance of both systems ensures optimal performance and extends service life in industrial and automotive applications.
Choosing the Right Drive System for Your Needs
Chain drives offer superior power transmission and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring high torque and precision. V-belts provide quieter operation and easier maintenance, suitable for moderate power needs with smoother and more flexible drive systems. Selecting between chain drive and V-belt depends on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, and maintenance preferences to optimize performance and lifespan.
Chain drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com