Round belts offer efficient power transmission in various machinery due to their durability and flexibility. Their circular cross-section provides excellent grip and reduced slip, making them ideal for applications in agriculture, automotive, and industrial equipment. Discover how using round belts can enhance your system's performance and longevity by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
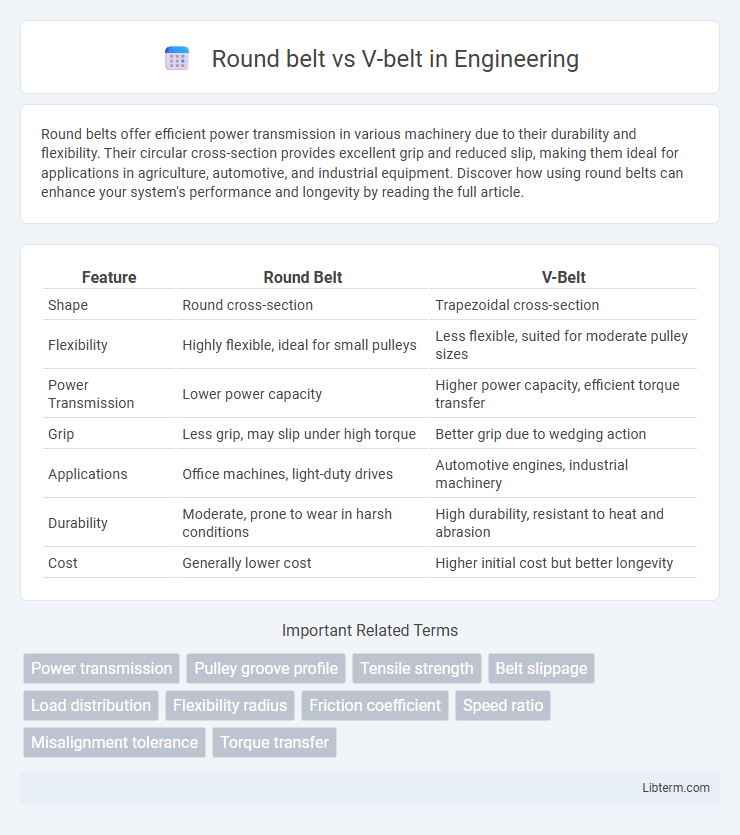
| Feature | Round Belt | V-Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Round cross-section | Trapezoidal cross-section |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, ideal for small pulleys | Less flexible, suited for moderate pulley sizes |
| Power Transmission | Lower power capacity | Higher power capacity, efficient torque transfer |
| Grip | Less grip, may slip under high torque | Better grip due to wedging action |
| Applications | Office machines, light-duty drives | Automotive engines, industrial machinery |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear in harsh conditions | High durability, resistant to heat and abrasion |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial cost but better longevity |
Introduction to Round Belts and V-Belts
Round belts are circular cross-section belts primarily used in light-duty power transmission applications such as small machinery and office equipment, offering flexibility and ease of installation. V-belts feature a trapezoidal cross-section designed to fit into V-shaped pulleys, providing higher friction, efficient power transmission, and stability in medium to heavy-duty industrial machines. Both belts play crucial roles in mechanical systems, with round belts excelling in low-torque environments and V-belts preferred for transmitting higher loads with reduced slippage.
Design and Shape Differences
Round belts feature a circular cross-section, allowing them to fit into small pulley grooves and deliver smooth power transmission ideal for light loads. V-belts have a trapezoidal cross-section designed to wedge into pulley grooves, providing increased friction and grip for higher torque applications. The tapered shape of V-belts enhances their ability to handle greater stress, making them suitable for heavy machinery and automotive engines.
Material Composition Comparison
Round belts typically consist of polyurethane or rubber with embedded polyester or aramid fibers, offering flexibility and resistance to wear. V-belts are commonly made from rubber materials reinforced with fabric cords such as polyester or fiberglass, designed to provide high tensile strength and grip within pulley grooves. The different material compositions of round belts and V-belts cater to specific load capacities and durability requirements in mechanical power transmission systems.
Power Transmission Efficiency
Round belts offer moderate power transmission efficiency suitable for light-duty applications, but their flexibility often leads to slippage and reduced grip under high loads. V-belts provide superior power transmission efficiency due to their wedging action in pulley grooves, which enhances friction and minimizes slippage even at high torque and speed. Industrial applications requiring reliable and efficient power transfer frequently prefer V-belts for their durability and consistent performance in demanding conditions.
Applications and Industry Usage
Round belts excel in light-duty applications such as office equipment and small conveyor systems, offering flexibility and quiet operation in compact spaces. V-belts are preferred in heavy industrial machinery including automotive engines, agricultural equipment, and HVAC systems due to their higher power transmission efficiency and durability under high loads. Industries like manufacturing, mining, and construction rely heavily on V-belts for robust performance and long service life in demanding environments.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Round belts require simpler installation due to their flexibility and ability to fit a variety of pulley sizes without precise alignment, reducing downtime during setup. V-belts need accurate tensioning and alignment to prevent slippage and premature wear, making maintenance more critical and frequent. Proper lubrication is essential for V-belts, whereas round belts generally require less maintenance due to their smoother engagement with pulleys.
Durability and Lifespan
Round belts offer greater durability in applications with misalignment and contamination due to their simple design and flexibility. V-belts provide a longer lifespan under high-torque conditions because their wedging action in pulleys reduces slippage and wear. Choosing between round belt and V-belt depends on specific load demands and environmental factors influencing belt longevity.
Performance in High-Speed Operations
Round belts offer smooth and quiet operation with minimal slip, making them suitable for moderate speeds, but they generally lack the gripping power required for high-speed performance. V-belts provide superior torque transmission and efficient power transfer at high speeds due to their wedged profile, which enhances friction and grip within the pulley groove. In high-speed applications, V-belts maintain tension and performance more reliably, reducing slippage and increasing operational efficiency.
Cost and Availability
Round belts generally offer lower upfront costs compared to V-belts due to simpler manufacturing processes and materials. V-belts, being more widely used in industrial applications, have greater availability and a broader range of sizes from suppliers globally. Despite their higher initial price, V-belts often provide better durability and performance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses.
Choosing the Right Belt for Your Application
Selecting the right belt for your application depends on factors such as load capacity, pulley design, and environmental conditions. Round belts are ideal for light-duty tasks and applications requiring flexibility and smooth operation, often used in small machinery and conveyors. V-belts provide higher power transmission and grip for heavy-duty industrial machines, making them suitable for applications involving significant torque and high-speed operation.
Round belt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com