A tube well is an efficient groundwater extraction system designed to access deep aquifers through a long, perforated pipe, allowing water to be pumped for irrigation and drinking purposes. This sustainable method supports agricultural productivity, especially in regions with limited surface water sources. Explore the detailed benefits and maintenance tips in the rest of the article to enhance your water management strategies.
Table of Comparison
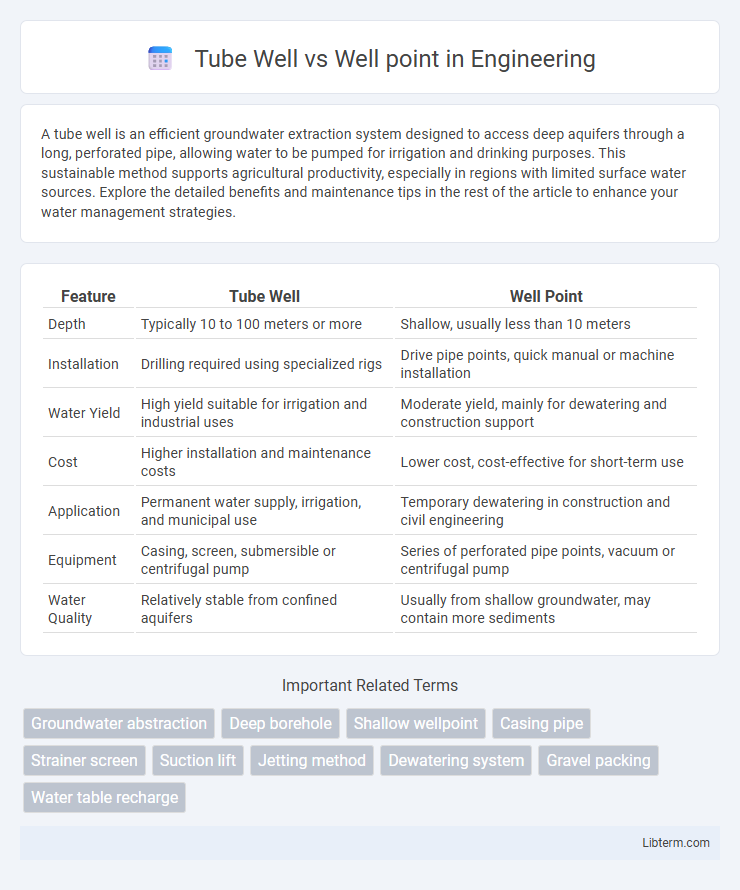
| Feature | Tube Well | Well Point |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | Typically 10 to 100 meters or more | Shallow, usually less than 10 meters |
| Installation | Drilling required using specialized rigs | Drive pipe points, quick manual or machine installation |
| Water Yield | High yield suitable for irrigation and industrial uses | Moderate yield, mainly for dewatering and construction support |
| Cost | Higher installation and maintenance costs | Lower cost, cost-effective for short-term use |
| Application | Permanent water supply, irrigation, and municipal use | Temporary dewatering in construction and civil engineering |
| Equipment | Casing, screen, submersible or centrifugal pump | Series of perforated pipe points, vacuum or centrifugal pump |
| Water Quality | Relatively stable from confined aquifers | Usually from shallow groundwater, may contain more sediments |
Introduction to Tube Well and Well Point
Tube wells are deep, narrow wells drilled into underground aquifers using a steel casing and equipped with pumping mechanisms to extract groundwater efficiently for irrigation and drinking purposes. Well points are shallow, small-diameter wells installed with a screen and connected to a pump system, commonly used for dewatering and supplying water from less deep water tables. Both systems differ in depth, capacity, and application, with tube wells suitable for deeper groundwater extraction and well points preferred for temporary or shallow water sources.
Key Differences Between Tube Well and Well Point
Tube wells are deep, large-diameter wells with casing pipes that penetrate extensive groundwater aquifers, enabling high-volume water extraction, whereas well points are shallow, small-diameter systems designed for dewatering sandy soils with limited water capacity. Tube wells require borehole drilling using heavy machinery, suitable for irrigation and municipal water supply, while well points use a series of small-diameter points connected to a vacuum pump for temporary or localized groundwater control. The structural depth, capacity, installation complexity, and purpose distinctly separate tube wells from well points in groundwater management applications.
Construction Process: Tube Well vs Well Point
The construction process of a tube well involves drilling a deep borehole using rotary or jet drilling methods, followed by casing installation and submersible pump fitting to access groundwater at greater depths. In contrast, a well point requires driving a shallow, perforated pipe with a screened end into the ground using a drive head or hammer, typically suitable for sandy soils and shallow water tables. Tube wells offer higher water yields and are more durable for long-term use, while well points provide a quicker, cost-effective solution for temporary or small-scale water extraction.
Depth and Water Yield Comparison
Tube wells typically reach depths ranging from 30 to over 150 meters, allowing access to deeper aquifers with higher water yield potential compared to well points, which are generally shallow, around 5 to 10 meters. The water yield of tube wells can exceed 5000 liters per hour, making them suitable for irrigation and large-scale water supply, whereas well points produce significantly lower flow rates, usually under 1000 liters per hour, limiting their use to small-scale or temporary water extraction. Depth and aquifer characteristics heavily influence the efficiency and sustainability of both methods, with tube wells preferred for reliable, high-volume water sources.
Suitability for Different Soil Types
Tube wells are ideal for deep aquifers and perform well in cohesive soils such as clay and silt due to their ability to penetrate hard layers and access groundwater at greater depths. Well points suit sandy or loose soils where shallow groundwater is present, enabling effective dewatering by creating a vacuum to draw water out. Soil permeability and groundwater depth significantly influence the choice between tube wells and well points, optimizing water extraction efficiency for agricultural and construction needs.
Installation Costs and Time
Tube wells typically require higher installation costs due to deeper drilling and more robust casing materials compared to well points. Installation time for tube wells ranges from several days to weeks, depending on borehole depth and soil conditions, whereas well points can be installed within hours to a day, making them faster for temporary or shallow groundwater extraction. The choice between tube well and well point installations largely depends on budget, required depth, and project timeline considerations.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Tube wells require regular maintenance including periodic cleaning, pump servicing, and monitoring for corrosion to ensure efficient water flow, with an average lifespan of 15 to 25 years depending on usage and water quality. Well points have simpler maintenance demands such as regular inspection for clogging and pump upkeep, typically lasting 10 to 20 years. Both systems necessitate proper maintenance to maximize durability, but tube wells generally offer a longer operational life due to their robust construction.
Advantages of Tube Well Systems
Tube well systems offer deeper water extraction compared to well points, ensuring a more reliable and sustainable water supply in regions with low water tables. Their robust construction minimizes contamination risks and reduces maintenance frequency, providing long-term operational efficiency. Higher discharge capacity in tube wells supports irrigation and industrial needs, making them ideal for large-scale water sourcing.
Benefits of Well Point Systems
Well point systems offer efficient dewatering solutions by rapidly lowering groundwater levels with minimal equipment footprint, making them ideal for construction sites and groundwater control. They provide flexible installation in tight spaces and can be easily adapted for varying soil conditions compared to tube wells. The low operational cost and quick mobilization of well point systems enhance project timelines and reduce overall expenses.
Choosing the Right Water Extraction Method
Tube wells offer deep water extraction ideal for areas with low water tables, providing a reliable and high-yield source for agricultural and domestic use. Well points are more suitable for shallow water tables, offering a cost-effective and quick installation method, particularly in sandy or unconsolidated soils. Selecting the right water extraction method depends on factors like soil type, groundwater depth, installation cost, and the volume of water required.
Tube Well Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com